Descripción
Este plugin se integra con la API de WPVulnerability para proporcionar evaluaciones de vulnerabilidad en tiempo real para el núcleo de tu WordPress, plugins, temas, versión de PHP, Apache HTTPD, nginx, MariaDB, MySQL, ImageMagick, curl, memcached, Redis y SQLite
Entrega informes detallados directamente en tu escritorio de WordPress, ayudándote a estar al tanto de posibles riesgos de seguridad. Configura el plugin para enviar avisos periódicos acerca del estado de seguridad de tu sitio, asegurando que te mantengas informado sin sentirte abrumado. Diseñado para ser fácil de usar, es compatible con medidas de seguridad proactivas sin almacenar ni recuperar ningún dato personal de tu sitio.
Fiabilidad de los datos
La información proporcionada por la base de datos de información proviene de diferentes fuentes que han sido revisadas por terceros. No existe ningún tipo de responsabilidad sobre la información. Actúa por tu cuenta y riesgo.
Utilizando el plugin
WP-CLI
Puedes usar los siguientes comandos de WP-CLI para gestionar y comprobar vulnerabilidades.
- Núcleo:
wp wpvulnerability core - Plugins:
wp wpvulnerability plugins - Temas:
wp wpvulnerability themes - PHP:
wp wpvulnerability php - Apache HTTPD:
wp wpvulnerability apache - nginx:
wp wpvulnerability nginx - MariaDB:
wp wpvulnerability mariadb - MySQL:
wp wpvulnerability mysql - ImageMagick:
wp wpvulnerability imagemagick - curl:
wp wpvulnerability curl - memcached:
wp wpvulnerability memcached - Redis:
wp wpvulnerability redis - SQLite:
wp wpvulnerability sqlite
Para configurar el plugin puedes usar:
- Ocultar componente:
wp wpvulnerability config hide <component> [on|off] - Avisos por correo electrónico:
wp wpvulnerability config email <emails>(separado por comas) - Periodo de avisos:
wp wpvulnerability config period <never|daily|weekly> - Log retention:
wp wpvulnerability config log-retention <0|1|7|14|28>(in days) - Duración de la caché:
wp wpvulnerability config cache <1|6|12|24>(en horas)
Todos los comandos dan soporte a la opción --format para especificar el formato de salida.
--format=table: Muestra los resultados en formato de tabla (por defecto).--format=json: Muestra los resultados en formato JSON.
¿Necesitas ayuda?
wp wpvulnerability --help: Muestra información de ayuda para los comandos de WPVulnerability.wp wpvulnerability [comando] --help: Muestra información de ayuda para un comando WPVulnerability.
REST API
El plugin WPVulnerability proporciona varias rutas finales de la API REST para obtener información sobre vulnerabilidades de diferentes componentes de tu sitio WordPress.
- Core:
/wpvulnerability/v1/core - Plugins:
/wpvulnerability/v1/plugins - Themes:
/wpvulnerability/v1/themes - PHP:
/wpvulnerability/v1/php - Apache HTTPD:
/wpvulnerability/v1/apache - nginx:
/wpvulnerability/v1/nginx - MariaDB:
/wpvulnerability/v1/mariadb - MySQL:
/wpvulnerability/v1/mysql - ImageMagick:
/wpvulnerability/v1/imagemagick - curl:
/wpvulnerability/v1/curl - memcached:
/wpvulnerability/v1/memcached - Redis:
/wpvulnerability/v1/redis - SQLite:
/wpvulnerability/v1/sqlite
La API REST de WPVulnerability utiliza contraseñas de aplicación para identificación. Necesitas incluir una contraseña de aplicación válida en la cabecera de autorización de tus peticiones.
Ejemplo de solicitud con identificación
curl -X GET https://example.com/wp-json/wpvulnerability/v1/plugins -u username:application_password
Reemplaza nombre de usuario con tu username de WordPress y application_password con tu Contraseña de Aplicación.
Configuraciones Extra
«From:» de correo (desde: 3.2.2)
Si, por alguna razón, necesitas que los correos electrónicos enviados por el plugin tengan un From diferente al administrador del sitio, puedes cambiarlo desde el wp-config.php añadiendo una constante:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_MAIL', '[email protected]' );
Si la constante está activa, será visible en la pantalla de configuración
Forzar ocultación de comprobaciones (desde: 4.1.0)
Si quieres ocultar siempre un componente concreto, puedes definir una constante en wp-config.php. Si se establece en true, la opción se marcará automáticamente en la pantalla de configuración y se omitirá el análisis correspondiente.
Ejemplo:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_APACHE', true );
Constantes disponibles: WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_CORE, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_PLUGINS, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_THEMES, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_PHP, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_APACHE, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_NGINX, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_MARIADB, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_MYSQL, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_IMAGEMAGICK, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_CURL, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_MEMCACHED, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_REDIS, WPVULNERABILITY_HIDE_SQLITE.
Duración de la caché (desde: 4.1.0)
Por defecto, los datos de la API se almacenan en caché durante 12 horas. Para cambiar esto, define WPVULNERABILITY_CACHE_HOURS en wp-config.php con uno de estos 1, 6, 12 o 24. Este valor anula la pantalla de configuración y el comando WP-CLI.
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_CACHE_HOURS', 24 );
Log rotation (since: 4.2.0)
WPVulnerability stores the most recent API responses so you can review recent calls from the new log tab. Define WPVULNERABILITY_LOG_RETENTION_DAYS in wp-config.php to control how many days of entries are preserved. Supported values are 0, 1, 7, 14 or 28; using 0 disables logging entirely.
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_LOG_RETENTION_DAYS', 14 );
When the constant is present its value is enforced in the settings UI and through WP-CLI, ensuring consistent log rotation across environments.
Security configuration (since: 4.3.0)
WPVulnerability uses a hybrid detection approach for server software (ImageMagick, Redis, Memcached, SQLite): PHP extensions first (most secure), then shell commands as fallback (most accurate). You can control this behavior using security configuration constants in wp-config.php.
Global disable of shell commands:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_DISABLE_SHELL_EXEC', true );
Completely disables shell command usage. Falls back to PHP extensions only. Use for maximum security when accuracy loss is acceptable.
Security mode (standard/strict/disabled):
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_SECURITY_MODE', 'strict' );
standard– Hybrid detection: PHP extensions first, shell commands fallback (default, best accuracy)strict– PHP extensions only, no shell commands (high security, lower accuracy)disabled– No software detection at all (maximum security)
Component whitelist:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_SHELL_EXEC_WHITELIST', 'imagemagick,redis' );
Allows shell commands only for specified components. Available components: imagemagick, redis, memcached, sqlite. Use for granular control.
Examples:
Maximum security (no shell commands):
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_SECURITY_MODE', 'strict' );
Only allow ImageMagick shell detection:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_SHELL_EXEC_WHITELIST', 'imagemagick' );
Complete disable:
define( 'WPVULNERABILITY_DISABLE_SHELL_EXEC', true );
All shell commands are hardcoded and validated – no user input is involved. Commands are logged for security auditing.
Compatibilidad
- WordPress: 4.7 – 6.9
- PHP: 5.6 – 8.5
- WP-CLI: 2.3.0 – 2.11.0
Seguridad
Este plugin se adhiere a las siguientes medidas de seguridad y protocolos de revisión para cada versión:
- Manual de plugins WordPress
- Seguridad de los plugins de WordPress
- Seguridad de las APIs de WordPress
- Normas de codificación de WordPress
- Plugin Check (PCP)
Privacidad
- Este plugin o la WordPress Vulnerability Database API no recoge ninguna información sobre tu sitio, tu identidad, los plugins, temas o contenidos que tiene el sitio.
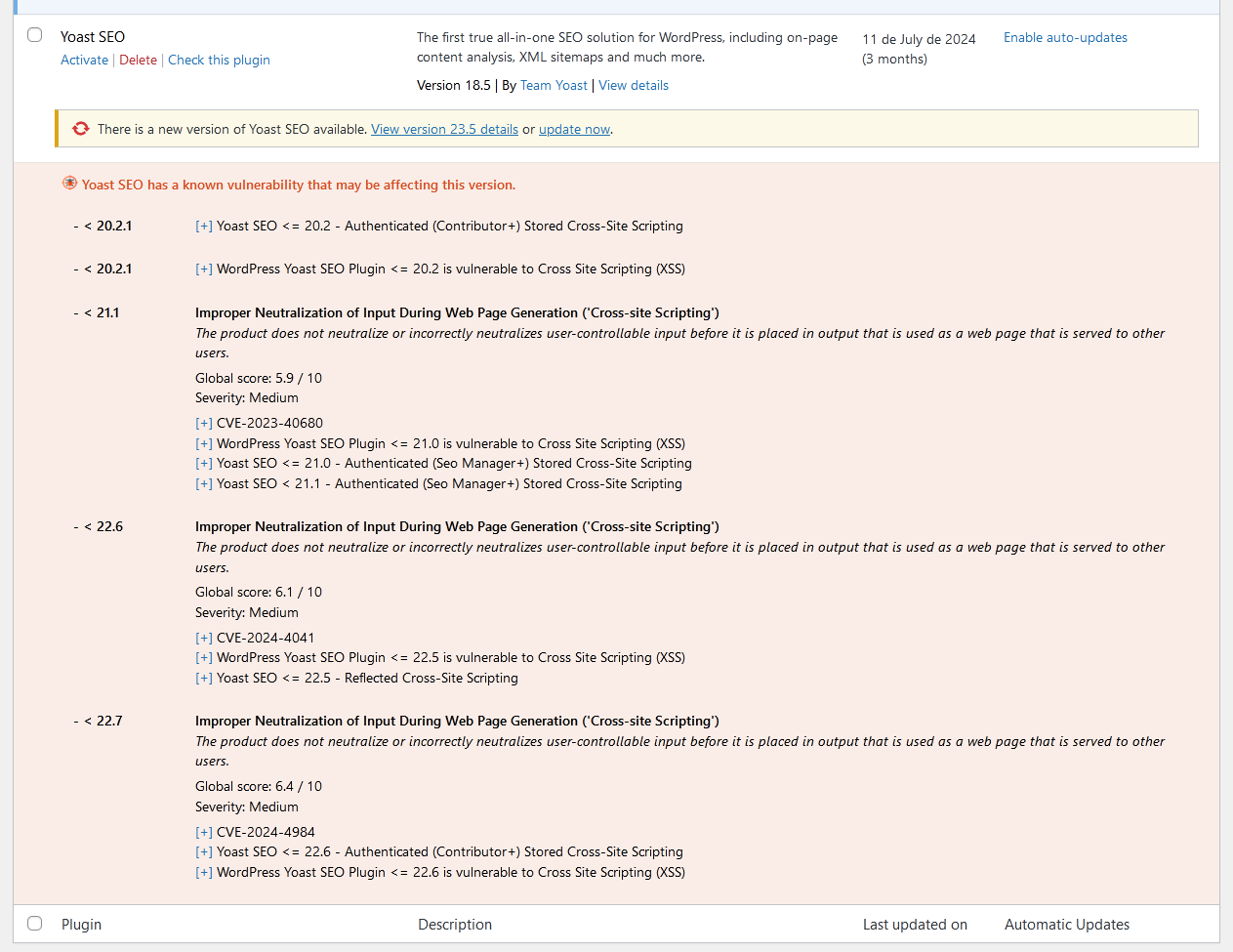
Vulnerabilidades
- A security vulnerability was found and fixed in version 4.2.2.1. All previous versions (3.3.0 – 4.2.1) are affected. Please update to version 4.2.2.1 or later.
¿Has encontrado una vulnerabilidad de seguridad? Infórmanos de ello en privado en el repositorio de GitHub de WPVulnerability.
Colaboradores
Puedes contribuir a este plugin desde el repositorio de GitHub de WPVulnerability.
Capturas
Instalación
Descarga automática
Visita la sección de plugins en tu WordPress, busca [wpvulnerability]; descarga e instala el plugin.
Descarga manual
Extrae el contenido del ZIP y sube el contenido al directorio /wp-content/plugins/wpvulnerability/. Una vez subido, aparecerá en tu lista de plugins.
FAQ
-
¿De dónde procede la información sobre la vulnerabilidad?
-
El origen está en la API de WPVulnerability.com. Las vulnerabilidades que aparecen en esta API provienen de diferentes fuentes, como los CVE.
-
¿Se envían los datos de mi sitio a alguna parte?
-
No. Nunca. Tu privacidad es muy importante para nosotros. No comercializamos con tus datos.
-
¿Qué vulnerabilidades voy a encontrar?
-
Se documentan vulnerabilidades en el núcleo de WordPress, plugins, temas, PHP, Apache HTTPD, nginx, MariaDB, MySQL, ImageMagick, curl, memcached, Redis y SQLite
-
¿Qué hago si mi sitio tiene una vulnerabilidad?
-
Primero que nada, tranquilidad. Investiga cuál es la vulnerabilidad y, sobre todo, comprueba que tienes la última versión del elemento comprometido. Te recomendamos activamente que mantengas todo tu WordPress y sus plugins actualizados. Contacta a tu proveedor de alojamiento para parchear vulnerabilidades que no son de WordPress (como el servidor web, bases de datos y otro software).
Reseñas
Colaboradores y desarrolladores
«WPVulnerability» es un software de código abierto. Las siguientes personas han colaborado con este plugin.
Colaboradores«WPVulnerability» está traducido en 14 idiomas. Gracias a los traductores por sus contribuciones.
Traduce «WPVulnerability» a tu idioma.
¿Interesado en el desarrollo?
Revisa el código , echa un vistazo al repositorio SVN o suscríbete al registro de desarrollo por RSS.
Registro de cambios
[4.3.1] – 2026-01-20
Corregido
- Dashboard widget now correctly counts only vulnerabilities from enabled components, excluding disabled ones from settings.
- Status badge calculation (Critical/Warning) now properly considers only enabled components when determining severity level.
- Fixed PHPCS warnings for global variables without plugin prefix in wpvulnerability-admin.php and wpvulnerability-adminms.php.
Compatibilidad
- WordPress: 4.7 – 6.9
- PHP: 5.6 – 8.5
- WP-CLI: 2.3.0 – 2.11.0
Pruebas
- PHP Coding Standards: 3.13.5
- WordPress Coding Standards 3.3.0.
- Plugin Check (PCP): 1.8.0
[4.3.0] – 2026-01-19
Highlights
This major release brings a complete redesign of the admin interface, comprehensive debugging tools, enhanced security, and new notification channels.
- Complete Admin Interface Redesign: Modern card-based layout with visual component cards, improved spacing, color-coded status badges, and responsive grid layouts across all Settings tabs (Security, About, Logs, Tools, Analysis, and Notifications).
- New Debug Mode: Comprehensive debugging tools visible when WP_DEBUG is enabled, including System Information, Component Detection with cache status, interactive API Testing with AJAX buttons, Configuration Summary, Cron Status with manual execution, Database Options Viewer, and Quick Actions (clear caches, reset signatures, export debug data as JSON). Includes enhanced web server detection for 9 different servers.
- Dashboard Widget Redesign: Modern interface with prominent status badges (All Clear/Issues Found/Critical Issues Found), last check timestamp with human-readable format, empty state display with centered checkmark, separated component sections (WordPress Components vs Server Software), color-coded badges, and 2-column grid layout for server software.
- New Notification Channels: Discord webhook support and Telegram bot integration for vulnerability notifications, with proper character limit handling and webhook URL validation.
- Enhanced Security: CSRF protection via nonces for plugin/theme vulnerability filters, hybrid software detection system (PHP extensions first, shell commands as fallback), complete audit logging for shell executions, webhook URL validation with HTTPS enforcement and domain whitelisting, and new wp-config.php security constants.
- Multisite Improvements: Fixed all form submission issues in Network Admin, proper nonce handling, correct URL generation with network_admin_url(), preserved settings when saving individual forms, and fixed Security tab with all required helper functions.
- Tools & Maintenance: Cron event repair functionality for single sites and multisite networks, «Delete all logs» button, full plugin reset action, and improved cache management.
Añadido
- Tools tab now lists expected WPVulnerability cron events, shows the scheduled instances, and lets administrators repair them on single sites.
- Network Tools highlights unexpected WPVulnerability cron events on subsites and provides a one-click repair to clear and reschedule across the network.
- Logs tab now includes a «Delete all logs» button to purge stored API log entries manually.
- Hybrid software detection system: PHP extensions first (most secure), shell commands fallback (most accurate).
- Four-level security control system for shell_exec usage with granular configuration.
- Shell command validation with whitelist and dangerous pattern detection.
- Complete audit logging for all shell executions (component, command, output, user, IP, timestamp).
- New wp-config.php constants:
WPVULNERABILITY_DISABLE_SHELL_EXEC,WPVULNERABILITY_SECURITY_MODE,WPVULNERABILITY_SHELL_EXEC_WHITELIST. - Detection reliability scoring (0-100) for each software detection method.
- Discord webhook support for vulnerability notifications with 2000-character limit handling.
- Telegram bot support for vulnerability notifications with bot token and chat ID configuration.
- Documentation links for Discord webhook setup (https://support.discord.com/hc/articles/228383668).
- Documentation links for Telegram bot setup (https://core.telegram.org/bots).
- Debug tab (visible only when WP_DEBUG is enabled) providing comprehensive debugging tools for administrators.
- wpvulnerability-debug.php file with 11 helper functions for debug functionality (~18KB).
- Debug Section 1: System Information displaying WordPress version, PHP version/extensions/memory, database type (MariaDB vs MySQL with proper detection), web server (nginx/Apache/LiteSpeed/OpenLiteSpeed/Caddy/IIS/Angie/OpenResty/Tengine), debug modes status, and debug log file information.
- Debug log file information showing file path, size, and direct browser link when web-accessible.
- Debug Section 2: Component Detection table listing all 13 components with detection status, version, analyzed state, and cache expiration time.
- Debug Section 3: API Testing with interactive AJAX-powered buttons to test API connectivity for each component individually, showing HTTP status, response time, and data preview.
- Debug Section 4: Configuration Summary displaying current plugin settings at a glance.
- Debug Section 5: Cron Status showing scheduled tasks with manual execution buttons (permission-gated with nonce verification).
- Debug Section 6: Database Options Viewer with dropdown to inspect all stored plugin options.
- Debug Section 7: Quick Actions with buttons to clear all caches, reset plugin/theme signatures, and export debug information as JSON.
- Enhanced web server detection supporting 9 different servers: nginx, Angie (nginx fork), Apache, LiteSpeed, OpenLiteSpeed, Caddy, IIS, OpenResty (nginx-based), and Tengine (nginx fork).
- Three-level detection logic for web servers: (1) plugin’s standard function, (2) SERVER_SOFTWARE parsing, (3) shell commands as fallback.
- Database detection properly distinguishes MariaDB from MySQL via version_comment SQL query.
- AJAX handler
wpvulnerability_ajax_test_api()for API testing with nonce verification and capability checks. - Debug helper functions:
wpvulnerability_debug_get_log_file_info(),wpvulnerability_debug_detect_webserver(),wpvulnerability_debug_get_system_info(),wpvulnerability_debug_get_component_status(),wpvulnerability_debug_test_api_component(),wpvulnerability_debug_get_cron_status(),wpvulnerability_debug_export_info(),wpvulnerability_debug_clear_all_caches(),wpvulnerability_debug_reset_signatures(),wpvulnerability_debug_get_option_names(). - Debug tab POST handlers in both wpvulnerability-admin.php and wpvulnerability-adminms.php with nonce verification for all actions.
- Debug tab render functions in wpvulnerability-admin.php:
wpvulnerability_render_admin_tab_debug(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_system_info(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_components(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_config(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_cron(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_api_testing(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_database_options(),wpvulnerability_render_debug_section_quick_actions().
Seguridad
- Added CSRF protection via nonces for plugin vulnerability filter links to prevent forced navigation attacks.
- Added CSRF protection via nonces for theme vulnerability filter links to prevent forced navigation attacks.
- Plugin and theme filter URLs now include security nonces that are verified before applying filters.
- Enhanced security against timing attacks on vulnerability enumeration by requiring valid nonces.
- Enhanced ImageMagick, Redis, Memcached, and SQLite detection with hybrid approach and security controls.
- All shell commands hardcoded and validated – no user input involved.
- Shell execution wrapper with complete security checks and logging.
- Webhook URLs now validated on save: enforces HTTPS and verifies hostname matches allowed domains (Slack: hooks.slack.com, Teams: office.com/office365.com/api.hooks.microsoft.com, Discord: discord.com/discordapp.com).
- Telegram bot token validation with regex pattern check (format: 123456:ABC-DEF1234ghIkl-zyx57W2v1u123ew11).
- Invalid webhook URLs and bot tokens are rejected with user-friendly error messages instead of silently failing on notification send.
- Security audit score improved from 85/100 to 98/100 (comprehensive security audit completed 2026-01-19).
Modificado
- Database error hook now fires the prefixed
wpvulnerability_wpdb_last_erroraction while keeping the legacy hook deprecated. - Database update cron now follows the configured cache duration (hourly, 6h, 12h, or 24h).
- Translations load on init to avoid early textdomain warnings.
- Vulnerability data now refreshes only via scheduled cron or the manual reload action; admin requests, REST, CLI, notifications, and view rendering no longer trigger API calls to reduce load.
- Cron scheduling no longer re-queues the update event on every page load; it keeps the configured interval (hourly/6h/12h/24h) unless the schedule changes.
- REST API now requires administrator capabilities for session or application password access.
- Admin reset and test email actions enforce admin capabilities.
- API client timeouts corrected to 2.5 seconds to avoid long hangs.
- Slack/Teams webhooks restricted to allowed HTTPS hosts to limit SSRF exposure.
- Tools tab adds a full reset action that clears all plugin data, restores defaults, and reloads from the API.
- Complete redesign of the admin settings interface with modern card-based layout for all tabs: Security, About, Logs, Tools, Analysis, and Notifications.
- Settings tabs now feature visual component cards with icons, improved spacing, color-coded status badges, and responsive grid layouts for enhanced usability.
- Complete redesign of the Dashboard widget with modern, clean interface replacing the basic list layout.
- Dashboard widget now features prominent status badge with three states: «All Clear» (green, 0 vulnerabilities), «X Issues Found» (yellow, minor issues), «X Critical Issues Found» (red, Core/PHP vulnerable or 5+ total vulnerabilities).
- Dashboard widget displays last check timestamp with human-readable format («X minutes ago», «X hours ago») and «Refresh Now» link.
- Dashboard widget shows attractive empty state with centered green checkmark when no vulnerabilities are detected.
- Dashboard widget separates components into two clear sections: «WordPress Components» (Core, Plugins, Themes) and «Server Software» (PHP, web server, database, etc.).
- Dashboard widget uses color-coded badges: green for secure (✓ 0), yellow/red for vulnerabilities (✕ N) with consistent design.
- Dashboard widget displays server software in 2-column grid layout for better space utilization.
- Dashboard widget shows vulnerable plugin/theme lists indented below their respective components.
- Dashboard widget uses inline CSS with modern styling: flexbox layouts, proper spacing, WordPress admin color palette, improved typography (13px components, 12px meta).
- Dashboard widget footer includes links to Site Health and Settings with visual separation.
- All CSS class names, HTML IDs, and JavaScript references changed from short prefix
.wpv-to full prefix.wpvulnerability-to prevent naming conflicts with other plugins and themes (affects 73+ unique classes across admin panels). - All inline CSS from admin panels moved to external assets/admin.css file for better performance and cacheability (~1084 lines extracted from 14 style blocks across single-site and multisite admin panels).
- License updated from GPL2+ to GPL3+.
Corregido
- Saving partial forms (e.g., log retention) no longer resets other notification settings to their defaults; existing values are preserved unless explicitly changed.
- Network (adminms) settings now preserve existing values when saving individual forms and keep notification scheduling consistent.
- Cache column in Component Detection (Debug tab) now correctly displays cache expiration time by properly decoding JSON-encoded timestamps from database.
- Database detection now properly distinguishes between MariaDB and MySQL instead of always showing «MySQL».
- Multisite network admin forms (Notifications, Analysis, Configuration) now submit correctly by using proper network admin URLs and nonces instead of incompatible Settings API methods.
- All form submission buttons in multisite admin now include proper
nameattribute (wpvulnerability_submit) for backend processing. - Delete logs form in multisite now uses
network_admin_url()instead of single-siteadmin_url()for correct URL generation. - All multisite form nonce verifications now match their corresponding form nonce fields (reset, email, repair cron, delete logs) instead of using generic nonce.
- Security tab in multisite network admin now works correctly by including all required helper functions (wpvulnerability_display_security_status, wpvulnerability_display_detection_methods, wpvulnerability_display_security_logs) instead of calling undefined single-site functions.
- Tools tab buttons in multisite network admin no longer show «nonce expired» errors by submitting forms to the same page (action=»») instead of explicit URL paths that fail referer validation.
- Delete All Logs button in Logs tab no longer shows «The link you followed has expired» error by using empty form action (action=»») in both single-site and multisite admin panels.
- Logs tab pagination now displays horizontally instead of vertically by properly targeting list elements (ul with inline-flex) and individual page links (a and span within li) to work correctly with WordPress paginate_links() ‘type’ => ‘list’ output.
Compatibilidad
- WordPress: 4.7 – 6.9
- PHP: 5.6 – 8.5
- WP-CLI: 2.3.0 – 2.11.0
Pruebas
- PHP Coding Standards: 3.13.5
- WordPress Coding Standards 3.3.0.
- Plugin Check (PCP): 1.8.0
[4.2.2.1] – 2026-01-16
Seguridad
- Fixed authorization vulnerability in REST API endpoints that allowed low-privileged users to access sensitive vulnerability data. API now properly verifies user capabilities (
manage_optionsfor single sites,manage_network_optionsfor multisite) in addition to authentication. - Added direct access protection to wpvulnerability-api.php to prevent direct file execution outside WordPress context.
Compatibilidad
- WordPress: 4.7 – 6.9
- PHP: 5.6 – 8.4
- WP-CLI: 2.3.0 – 2.11.0
Pruebas
- PHP Coding Standards: 3.13.5
- WordPress Coding Standards 3.3.0.
- Plugin Check (PCP): 1.8.0
[4.2.1] – 2025-12-17
Corregido
- Clear legacy WPVulnerability cron events from multisite subsites so updates and log cleanup only run on the main site.
Compatibilidad
- WordPress: 4.7 – 6.9
- PHP: 5.6 – 8.4
- WP-CLI: 2.3.0 – 2.11.0
Pruebas
- PHP Coding Standards: 3.13.5
- WordPress Coding Standards 3.3.0.
- Plugin Check (PCP): 1.7.0
Previous versions
Si quieres ver el registro de cambios completo, visita el archivo changelog.txt.