---
createdAt: 2025-04-18
updatedAt: 2025-12-30
title: Angular i18n - How to translate your Angular app – guide 2026
description: Discover how to make your Angular website multilingual. Follow the documentation to internationalize (i18n) and translate it.
keywords:
- Internationalization
- Documentation
- Intlayer
- Angular
- JavaScript
slugs:
- doc
- environment
- angular
applicationTemplate: https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer-angular-template
history:
- version: 8.0.0
date: 2026-01-26
changes: Release stable version
- version: 8.0.0
date: 2025-12-30
changes: Add init command
- version: 5.5.10
date: 2025-06-29
changes: Init history
---
# Translate your Angular website using Intlayer | Internationalization (i18n)
## Table of Contents
<TOC/>
## What is Intlayer?
**Intlayer** is an innovative, open-source internationalization (i18n) library designed to simplify multilingual support in modern web applications.
With Intlayer, you can:
- **Easily manage translations** using declarative dictionaries at the component level.
- **Dynamically localize metadata**, routes, and content.
- **Ensure TypeScript support** with autogenerated types, improving autocompletion and error detection.
- **Benefit from advanced features**, like dynamic locale detection and switching.
---
## Step-by-Step Guide to Set Up Intlayer in an Angular Application
<Tabs defaultTab="code">
<Tab label="Code" value="code">
<iframe
src="https://stackblitz.com/github/aymericzip/intlayer-angular-template?embed=1&ctl=1&file=intlayer.config.ts"
className="m-auto overflow-hidden rounded-lg border-0 max-md:size-full max-md:h-[700px] md:aspect-16/9 md:w-full"
title="Demo CodeSandbox - How to Internationalize your application using Intlayer"
sandbox="allow-forms allow-modals allow-popups allow-presentation allow-same-origin allow-scripts"
loading="lazy"
/>
</Tab>
</Tabs>
See [Application Template](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer-angular-template) on GitHub.
### Step 1: Install Dependencies
Install the necessary packages using npm:
```bash packageManager="npm"
npm install intlayer angular-intlayer
npm install @angular-builders/custom-webpack --save-dev
npx intlayer init
```
```bash packageManager="pnpm"
pnpm add intlayer angular-intlayer
pnpm add @angular-builders/custom-webpack --save-dev
pnpm intlayer init
```
```bash packageManager="yarn"
yarn add intlayer angular-intlayer
yarn add @angular-builders/custom-webpack --save-dev
yarn intlayer init
```
```bash packageManager="bun"
bun add intlayer angular-intlayer
bun add @angular-builders/custom-webpack --dev
bunx intlayer init
```
- **intlayer**
The core package that provides internationalization tools for configuration management, translation, [content declaration](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/dictionary/content_file.md), transpilation, and [CLI commands](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/cli/index.md).
- **angular-intlayer**
The package that integrates Intlayer with Angular application. It provides context providers and hooks for Angular internationalization.
- **@angular-builders/custom-webpack**
Required to customize the Webpack configuration of Angular CLI.
### Step 2: Configuration of your project
Create a config file to configure the languages of your application:
```typescript fileName="intlayer.config.ts" codeFormat="typescript"
import { Locales, type IntlayerConfig } from "intlayer";
const config: IntlayerConfig = {
internationalization: {
locales: [
Locales.ENGLISH,
Locales.FRENCH,
Locales.SPANISH,
// Your other locales
],
defaultLocale: Locales.ENGLISH,
},
};
export default config;
```
```javascript fileName="intlayer.config.mjs" codeFormat="esm"
import { Locales } from "intlayer";
/** @type {import('intlayer').IntlayerConfig} */
const config = {
internationalization: {
locales: [
Locales.ENGLISH,
Locales.FRENCH,
Locales.SPANISH,
// Your other locales
],
defaultLocale: Locales.ENGLISH,
},
};
export default config;
```
```javascript fileName="intlayer.config.cjs" codeFormat="commonjs"
const { Locales } = require("intlayer");
/** @type {import('intlayer').IntlayerConfig} */
const config = {
internationalization: {
locales: [
Locales.ENGLISH,
Locales.FRENCH,
Locales.SPANISH,
// Your other locales
],
defaultLocale: Locales.ENGLISH,
},
};
module.exports = config;
```
> Through this configuration file, you can set up localized URLs, middleware redirection, cookie names, the location and extension of your content declarations, disable Intlayer logs in the console, and more. For a complete list of available parameters, refer to the [configuration documentation](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/configuration.md).
### Step 3: Integrate Intlayer in Your Angular Configuration
To integrate Intlayer with the Angular CLI, you need to use a custom builder. This guide assumes you are using Webpack (default for many Angular projects).
First, modify your `angular.json` to use the custom Webpack builder. Update the `build` and `serve` configurations:
```json fileName="angular.json"
{
"projects": {
"your-app-name": {
"architect": {
"build": {
"builder": "@angular-builders/custom-webpack:browser",
"options": {
"customWebpackConfig": {
"path": "./webpack.config.ts"
}
}
},
"serve": {
"builder": "@angular-builders/custom-webpack:dev-server",
"options": {
"customWebpackConfig": {
"path": "./webpack.config.ts"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
> Make sure to replace `your-app-name` with the actual name of your project in `angular.json`.
Next, create a `webpack.config.ts` file at the root of your project:
```typescript fileName="webpack.config.ts"
import { mergeConfig } from "angular-intlayer/webpack";
export default mergeConfig({});
```
> The `mergeConfig` function configures Webpack with Intlayer. It injects the `IntlayerWebpackPlugin` (to handle content declaration files) and sets up aliases for optimal performance.
### Step 4: Declare Your Content
Create and manage your content declarations to store translations:
```tsx fileName="src/app/app.content.ts" contentDeclarationFormat="typescript"
import { t, type Dictionary } from "intlayer";
const appContent = {
key: "app",
content: {
title: t({
en: "Hello",
fr: "Bonjour",
es: "Hola",
}),
congratulations: t({
en: "Congratulations! Your app is running. 🎉",
fr: "Félicitations! Votre application est en cours d'exécution. 🎉",
es: "¡Felicidades! Tu aplicación está en ejecución. 🎉",
}),
exploreDocs: t({
en: "Explore the Docs",
fr: "Explorer les Docs",
es: "Explorar los Docs",
}),
learnWithTutorials: t({
en: "Learn with Tutorials",
fr: "Apprendre avec les Tutoriels",
es: "Aprender con los Tutorios",
}),
cliDocs: "CLI Docs",
angularLanguageService: t({
en: "Angular Language Service",
fr: "Service de Langage Angular",
es: "Servicio de Lenguaje Angular",
}),
angularDevTools: "Angular DevTools",
github: "Github",
twitter: "Twitter",
youtube: "Youtube",
},
} satisfies Dictionary;
export default appContent;
```
> Your content declarations can be defined anywhere in your application as soon they are included into the `contentDir` directory (by default, `./src`). And match the content declaration file extension (by default, `.content.{json,ts,tsx,js,jsx,mjs,cjs}`).
> For more details, refer to the [content declaration documentation](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/dictionary/content_file.md).
### Step 5: Utilize Intlayer in Your Code
To utilize Intlayer's internationalization features throughout your Angular application, you need to provide Intlayer in your application configuration.
```typescript fileName="src/app/app.config.ts"
import { ApplicationConfig } from "@angular/core";
import { provideRouter } from "@angular/router";
import { provideIntlayer } from "angular-intlayer";
import { routes } from "./app.routes";
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
provideRouter(routes),
provideIntlayer(), // Add the Intlayer provider here
],
};
```
Then, you can use the `useIntlayer` function within any component.
```typescript fileName="src/app/app.component.ts"
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import { RouterOutlet } from "@angular/router";
import { useIntlayer } from "angular-intlayer";
@Component({
selector: "app-root",
standalone: true,
imports: [RouterOutlet],
templateUrl: "./app.component.html",
styleUrl: "./app.component.css",
})
export class AppComponent {
content = useIntlayer("app");
}
```
And in your template:
```html fileName="src/app/app.component.html"
<div class="content">
<h1>{{ content().title }}</h1>
<p>{{ content().congratulations }}</p>
</div>
```
Intlayer content is returned as a `Signal`, so you access the values by calling the signal: `content().title`.
### (Optional) Step 6: Change the language of your content
To change the language of your content, you can use the `setLocale` function provided by the `useLocale` function. This allows you to set the locale of the application and update the content accordingly.
Create a component to switch between languages:
```typescript fileName="src/app/locale-switcher.component.ts"
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import { CommonModule } from "@angular/common";
import { useLocale } from "angular-intlayer";
@Component({
selector: "app-locale-switcher",
standalone: true,
imports: [CommonModule],
template: `
<div class="locale-switcher">
<select
[value]="locale()"
(change)="setLocale($any($event.target).value)"
>
@for (loc of availableLocales; track loc) {
<option [value]="loc">{{ loc }}</option>
}
</select>
</div>
`,
styles: [
`
.locale-switcher {
margin: 1rem;
padding: 0.5rem;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
width: fit-content;
}
`,
],
})
export class LocaleSwitcherComponent {
localeCtx = useLocale();
locale = this.localeCtx.locale;
availableLocales = this.localeCtx.availableLocales;
setLocale = this.localeCtx.setLocale;
}
```
Then, use this component in your `app.component.ts`:
```typescript fileName="src/app/app.component.ts"
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
import { RouterOutlet } from "@angular/router";
import { useIntlayer } from "angular-intlayer";
import { LocaleSwitcherComponent } from "./locale-switcher.component";
@Component({
selector: "app-root",
standalone: true,
imports: [RouterOutlet, LocaleSwitcherComponent],
templateUrl: "./app.component.html",
styleUrl: "./app.component.css",
})
export class AppComponent {
content = useIntlayer("app");
}
```
### Configure TypeScript
Intlayer uses module augmentation to get benefits of TypeScript and make your codebase stronger.
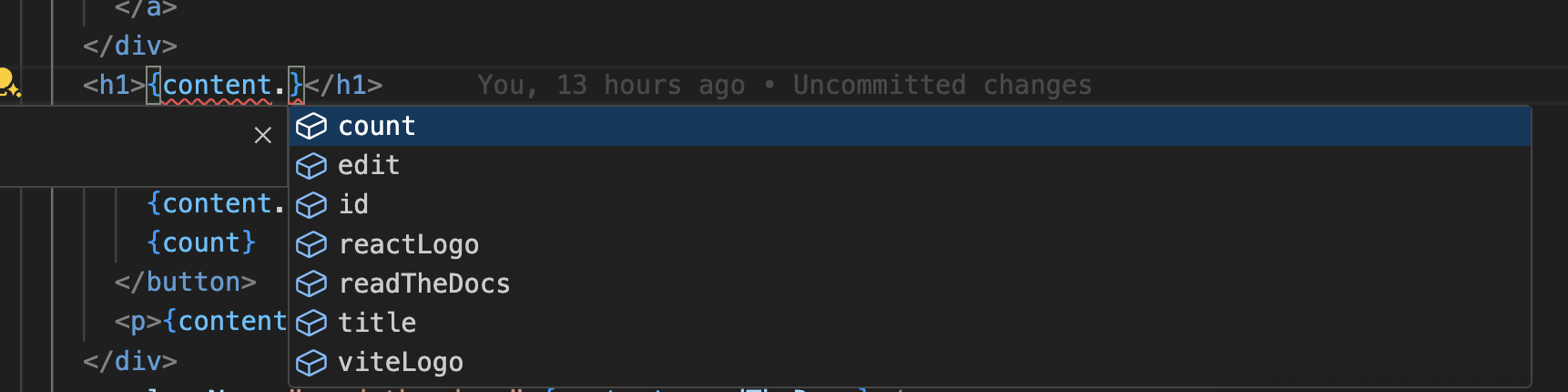
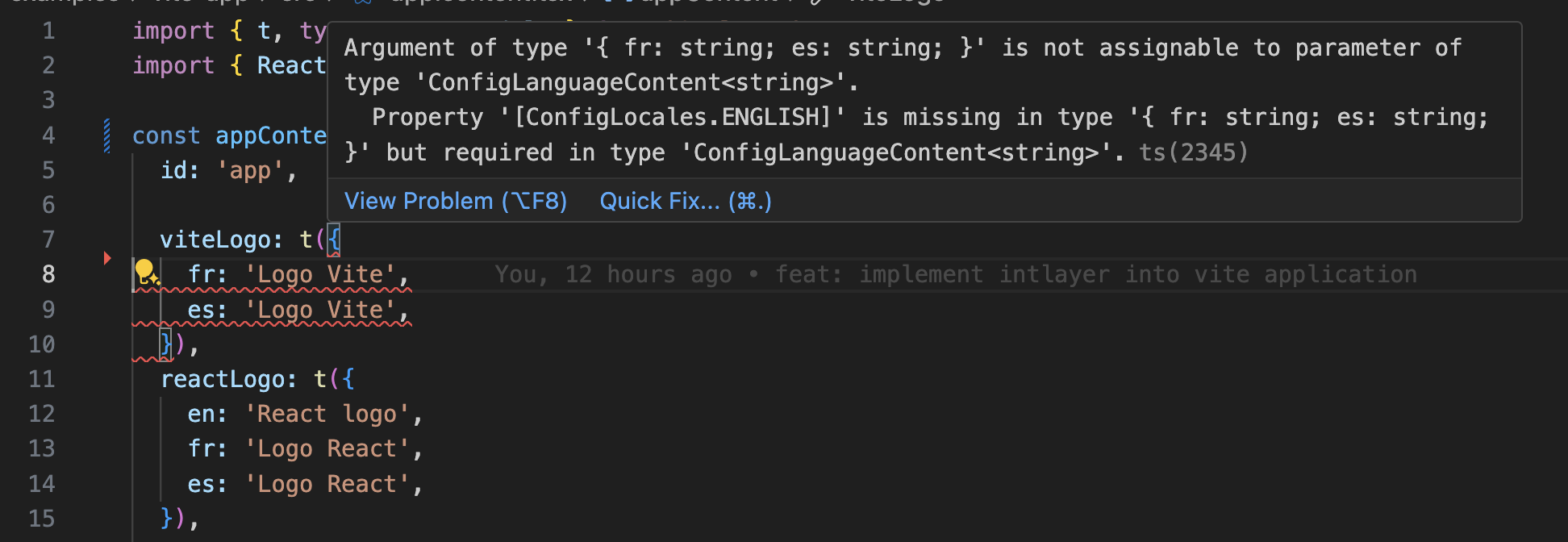
Ensure your TypeScript configuration includes the autogenerated types.
```json5 fileName="tsconfig.json"
{
// ... Your existing TypeScript configurations
"include": [
// ... Your existing TypeScript configurations
".intlayer/**/*.ts", // Include the auto-generated types
],
}
```
### Git Configuration
It is recommended to ignore the files generated by Intlayer. This allows you to avoid committing them to your Git repository.
To do this, you can add the following instructions to your `.gitignore` file:
```plaintext
# Ignore the files generated by Intlayer
.intlayer
```
### VS Code Extension
To improve your development experience with Intlayer, you can install the official **Intlayer VS Code Extension**.
[Install from the VS Code Marketplace](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=intlayer.intlayer-vs-code-extension)
This extension provides:
- **Autocompletion** for translation keys.
- **Real-time error detection** for missing translations.
- **Inline previews** of translated content.
- **Quick actions** to easily create and update translations.
For more details on how to use the extension, refer to the [Intlayer VS Code Extension documentation](https://intlayer.org/doc/vs-code-extension).
---
### Go Further
To go further, you can implement the [visual editor](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/intlayer_visual_editor.md) or externalize your content using the [CMS](https://github.com/aymericzip/intlayer/blob/main/docs/docs/en/intlayer_CMS.md).
---