Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) form the foundation of effective problem-solving in programming. Python provides several built-in and external libraries that help implement common data structures such as arrays, linked lists, queues, hash maps, heaps, and trees.
Built-in DSA Libraries
These libraries require no installation and are widely used in real-world applications.
1. Array Module
The array module implements the array data structure, where elements of the same data type are stored in contiguous memory locations. It is mainly used when memory efficiency and faster access are required compared to Python lists, especially for numeric data.
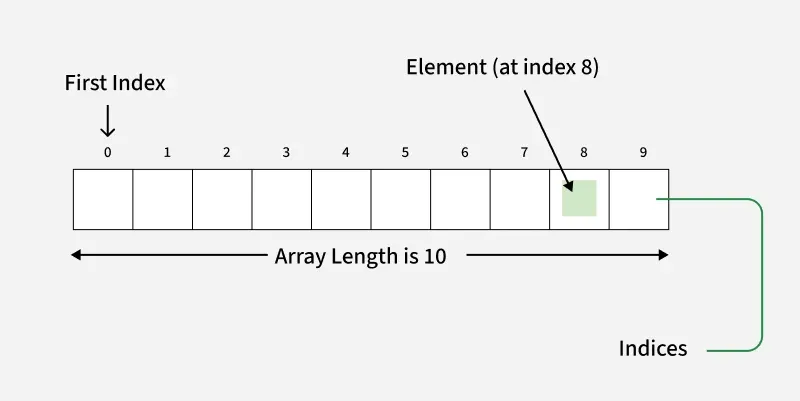
Important Methods
- append(x): Adds a single element at the end of the array
- extend(iterable): Adds multiple elements from another iterable
- count(x): Returns how many times a value appears
- itemsize(): Returns the memory size (in bytes) of one element
- buffer_info(): Returns memory address and number of elements
2. Numpy Library
NumPy provides support for multi-dimensional array data structures and is optimized for high-performance numerical and scientific computations.
Important Operations
- np.array(): Creates 1D, 2D, or N-dimensional arrays
- np.zeros()/np.ones(): Creates arrays filled with zeros or ones
- np.arange()/np.linspace(): Generates numeric sequences
- np.reshape(): Changes the shape of an array
- np.sum()/np.mean()/np.max()/np.min(): Performs mathematical operations
- np.dot(): Matrix and vector multiplication
- Array slicing and indexing: arr[start:stop], arr[row, col]
- Broadcasting: Automatic shape alignment during operations
3. Deque Module
The deque module implements a doubly linked list data structure. It allows constant-time insertion and deletion from both ends, making it ideal for queues and stacks.
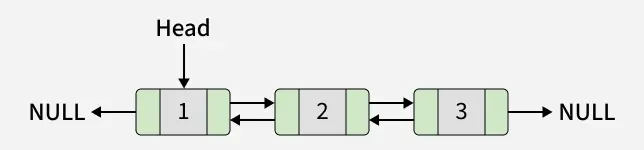
Important Operations
- append(x): Insert element at the right end
- appendleft(x): Insert element at the left end
- pop(): Remove element from the right end
- popleft(): Remove element from the left end
- extend(iterable): Add multiple elements to the right
4. Queue Module
queue.Queue module provides a queue data structure that follows FIFO order. It is designed to be thread-safe and is mainly used in multi-threaded and producer–consumer applications.
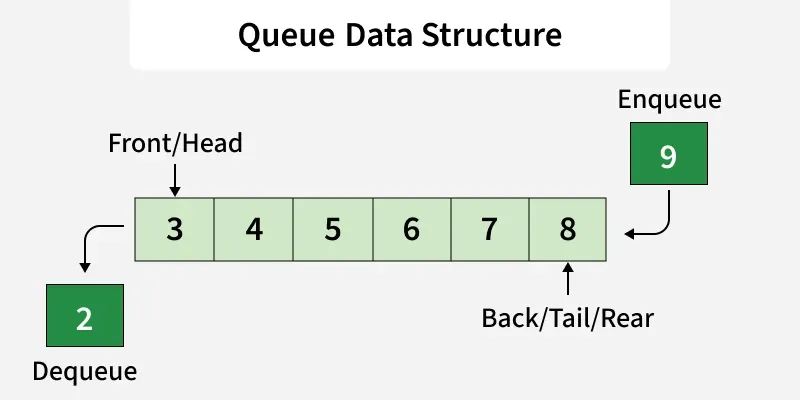
Important Operations
- put(x): Insert an item into the queue
- get(): Remove and return an item
- qsize(): Returns the current number of items
- empty(): Checks whether the queue is empty
- full(): Checks whether the queue is full
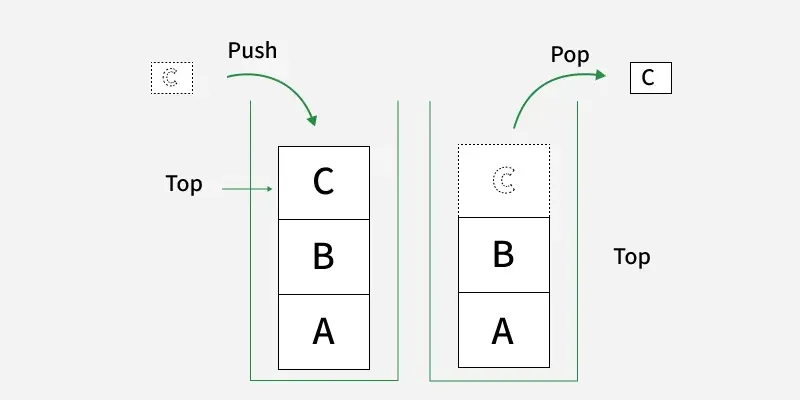
5. Collections Module
The collections module provides specialized data structures that extend Python’s built-in containers. It is commonly used to work with various data structure, mainly with:
- Hash maps: for storing data as key–value pairs with fast access
- Stacks (LIFO): for push and pop operations
- Queues (FIFO): for enqueue and dequeue operations
- Doubly linked lists: for adding and removing elements easily from both ends
- Structured records: for storing related values using names instead of indexes
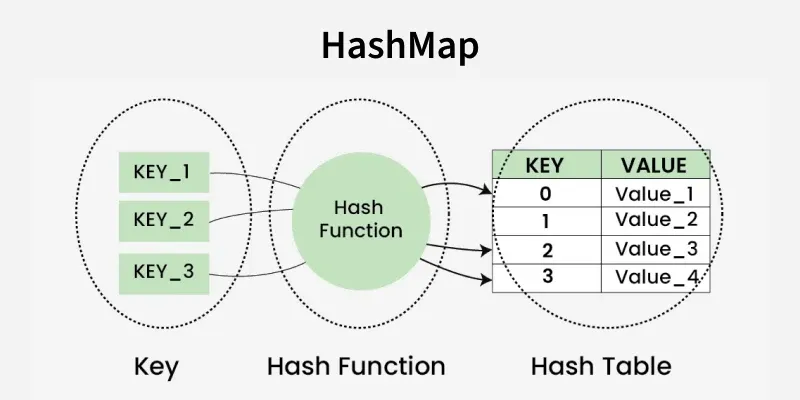
Common Data Structures in collections
- dict stores data as key-value pairs
- collections.Counter counts occurrences of elements.
- collections.defaultdict creates default values automatically.
- collections.OrderedDict keeps keys in insertion order.
- collections.ChainMap combines multiple dictionaries without merging.
- deque used to build queues and stacks
- namedtuple stores data with named fields like an object
Important Operations
- keys(): Returns all keys
- values(): Returns all values
- items(): Returns key–value pairs
- get(key): Retrieves a value safely
- update(dict): Update multiple entries
- append(x): Adds element to right end (deque)
- popleft(): Removes element from left end (deque)
5. Heapq Module
The heapq module implements the heap data structure, specifically a min-heap. It allows quick access to the smallest element and is widely used in priority queues and scheduling algorithms.
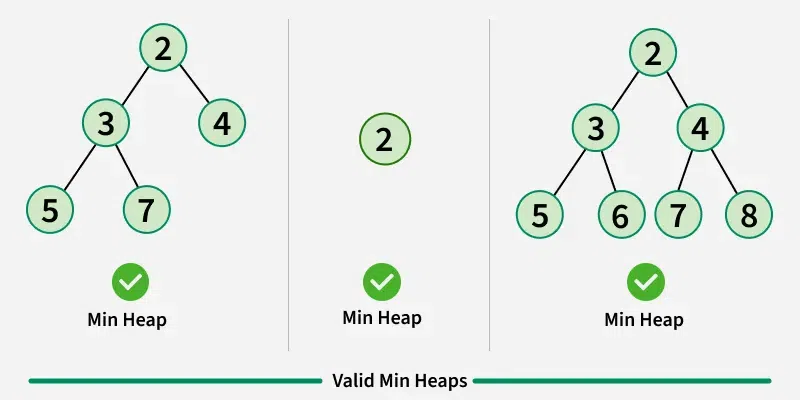
Important Operations
- heapify(list): converts a list into a heap.
- heappush(heap, x): adds an element to the heap.
- heappop(heap): removes and returns the smallest element.
- nlargest(n, iterable): returns n largest elements.
- nsmallest(n, iterable): returns n smallest elements.
6. Bisect Module
The bisect module supports binary search operations on sorted lists. It helps maintain sorted order while inserting elements efficiently without manually sorting the list.
Important Methods
- bisect_left(list, x): leftmost insertion point.
- bisect_right(list, x): rightmost insertion point.
- insort_left(list, x): inserts at leftmost valid position.
- insort_right(list, x): inserts at rightmost valid position.
- bisect(list, x): alias of bisect_right.
External Libraries for Advanced Data Structures
These are not part of Python by default. They must be installed and are used only when your problem truly needs them.
1. treelib (Tree Data Structure)
The treelib library is used to implement tree data structures, where data is stored in a parent-child hierarchy. It makes creating, managing, and displaying trees readable, which is useful when working with hierarchical data.
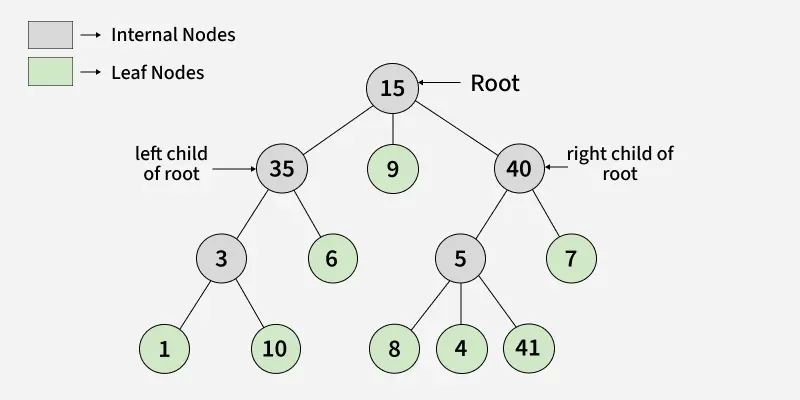
To install treelib use below command:
pip install treelib
Important Methods
- create_node(tag, id, parent): Adds a new node to the tree
- remove_node(id): Removes a node
- get_node(id): Retrieves a specific node
- children(id): Returns child nodes
- show(): Displays the tree structure
2. intervaltree (Interval Tree)
The intervaltree library is used to store and search numeric ranges (intervals) efficiently. It is helpful when you need to quickly find overlapping intervals or ranges.
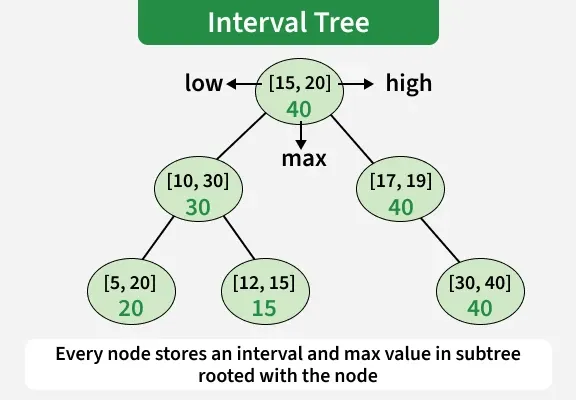
To install intervaltree use below command:
pip install intervaltree
Important Methods
- add(interval): adds an interval.
- remove(interval): removes an interval.
- search(start, end): finds intervals overlapping a range.
- at(point): finds intervals containing a specific point.
- clear(): removes all intervals.
3. pygtrie (Trie/Prefix Tree)
The pygtrie library provides an implementation of the Trie (prefix tree) data structure. It stores strings character by character, making prefix-based searches very fast.
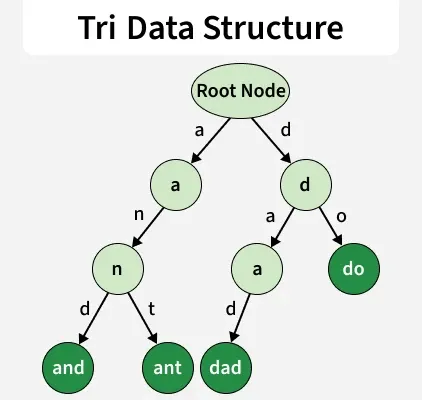
To use trie, install it using below command:
pip install pygtrie
Important Methods
- insert(word): adds a word to the trie.
- search(word): checks if a word exists.
- startswith(prefix): checks if any word has the prefix.
- delete(word): removes a word.
- words(prefix): returns words starting with a prefix.
When Should You Use External Libraries?
Use an external DSA library when:
- Implementing from scratch is time-consuming
- You need specialized structures (tries, interval trees, custom trees)
- The library is maintained and reliable
- You want to improve development speed
Avoid using them when:
- Built-in structures can do the job
- You want maximum performance (built-ins are C-optimized)