You use integers (int) in PHP to count items, set page numbers, handle IDs, and manage loop counters. In this article, you will learn how PHP handles integers and what types it supports.
Table of Content
Understand What PHP Integer Is
An integer in PHP is a whole number. It does not have any decimal or fractional part.
PHP uses the int type to handle these numbers. You can use both positive and negative integers. As long as the number fits within PHP’s limits, it works fine.
There are some constants in PHP that set the limits for integers. These limits include the maximum and minimum values an integer can have.
PHP_INT_SIZEkeeps track of how many bytes something uses. It is usually 8 bytes.
PHP_INT_MAXgives you the largest possible integer value in PHP. It’s a big number: 9223372036854775807.
PHP_INT_MINshows the smallest whole number in PHP, and it’s – 9223372036854775808.
Remember that the size of a number in PHP depends on the platform you’re using. But, it allows for a maximum value of 2 billion to be stored in an integer variable.
You write integers without quotes. Do not add any symbols except the minus sign for negative numbers.
Here’s how you write them:
$positive = 100;
$negative = -50;
$zero = 0;Use the assignment operator = to assign integers to variables. PHP considers it as a data type and uses it for numeric operations.
Here are the types of integers PHP can interpret:
- Decimal (base 10): The default number system.
- Octal (base 8): Starts with a leading 0.
- Hexadecimal (base 16): Starts with
0x. - Binary (base 2): Starts with
0b.
Each type has its own use.

Let’s focus on each one in-depth.
Types of PHP Integers
PHP allows different number systems for integers. You can use alternative bases like binary or hexadecimal. These types represent numbers in unique ways while storing the same values.
You usually use decimal values. But sometimes, when you deal with memory or bitwise operations, you may need binary or hex. PHP supports the following types.
Decimal Numbers in PHP
Decimal integers are what you use most often. They include digits 0 through 9. These values do not start with any prefix.
Decimal number has point, which is usually on the right side of the number, may have one or more digits. Ten is the maximum number of digits in base 10 that come after the decimal point.
This is the standard number system in daily use. If you write 20 or -7, PHP reads it as a decimal integer.
For example:
$x = 100;
$y = -45;
$z = $x + $y; // 55To make numbers in PHP simpler to understand, group them together with underscores.
For example:
<?php
echo 4_487_456 // 4487456 decimal;
echo 145 // 145 decimal;
?>Let’s go on to the next section, where we’ll look at hexadecimal numerals in more depth.
Hexadecimal Numbers in PHP
Hexadecimal refers to base-16 digits between 0 and 15. It deals with single-digit integers ranging from 0 to 9. The extra six digits are replaced with characters in the sequence of ‘a’ to ‘f’ based on their individual records.
The following list shows the double digits that would be used in place of the alphabetical characters:
- 10 -> a
- 11 -> b
- 12 -> c
- 13 -> d
- 14 -> e
- 15 -> f
Hexadecimal numbers use the digits 0 to 9 and the letters A to F to represent values. You need to know how these letters differ from regular digits to understand how the system works.
To combine letters and numbers in hexadecimal, start with 0x. This prefix tells PHP to treat the value as a hexadecimal number.
Here is an example:
echo 0x2FD; // decimal 765 The result in this case is 765. If you check the steps again, you will see that we use base-16 in the hexadecimal system. This means the conversion works like the example shown below.
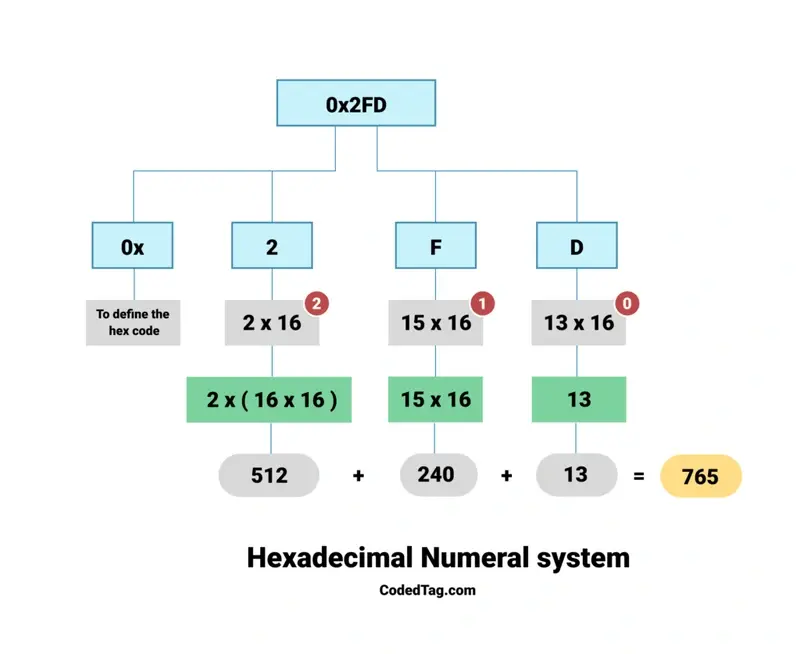
Check the three numbers with the red circle, from right to left: 0, 1, and 2. These numbers begin with zero and address the kind. For instance, a 162 type denotes 16 x 16, while a 164 type denotes 16 x 16 x 16 x 16, and so on.
Let’s break down the figure line by line, starting from the left.
- Hexadecimal is represented by adding “0x” to the beginning of numerals.
- As discussed in the last section, you should enter the numbers in the resultant line, starting with zero and going from right to left.
- Increase the primary number to (2 x 16)₂ from the left, and it will increase to (2 x (16 x 16). The result is 512.
- The next number expands to (15 x (16)): (15 x 16) ₁. The result is 240.
- Then, there is a similar growth in the number (13 x 16) 0. The result is 13.
- Adding up these red font results gives us the number 765.
Anyway, let’s move on to octal numbers in PHP.
Octal Numbers in PHP
Octal numbers use digits from 0 to 7, which gives a total of eight values (base 8). To define an octal number, start with 0, or use 0o if you are using PHP 8.1.0 or later. For example:
echo 0457; // decimal 303 The figure below shows how the calculation works and explains each step.
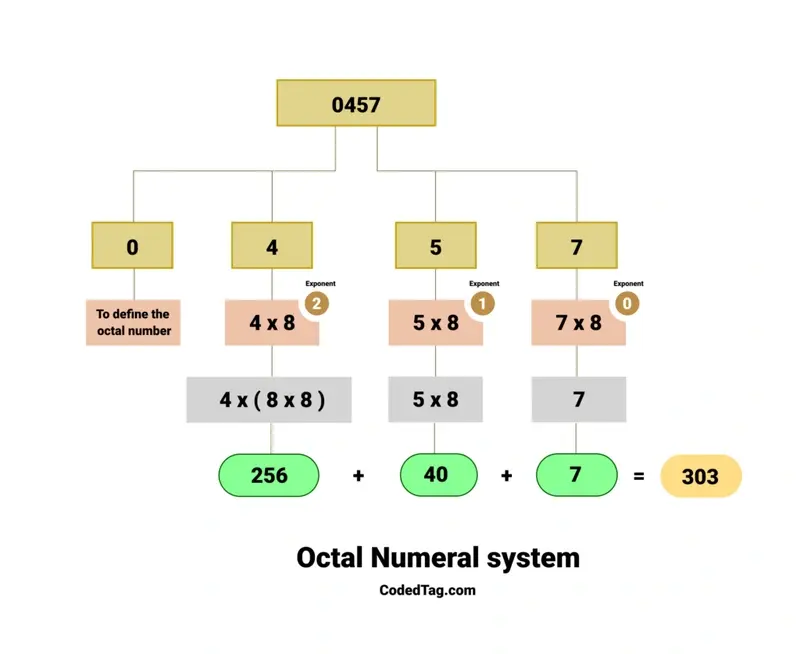
The number 0457 is written in octal. In this system, digits range from 0 to 7. Its decimal equivalent is shown below:
4 * (8^2) + 5 * (8^1) + 7 * (8^0) = 303This gives a decimal value of 303.
The Binary Numbers in PHP
The binary number system just uses the (0s) and (1s), which are called binary bits. This system starts with 0s.
Binary numbers are very important to machine code, which is a basic type of computer language.
Here is an example.
echo 0b101111; // Decimal 47The figure below shows how to calculate the binary numeral system.
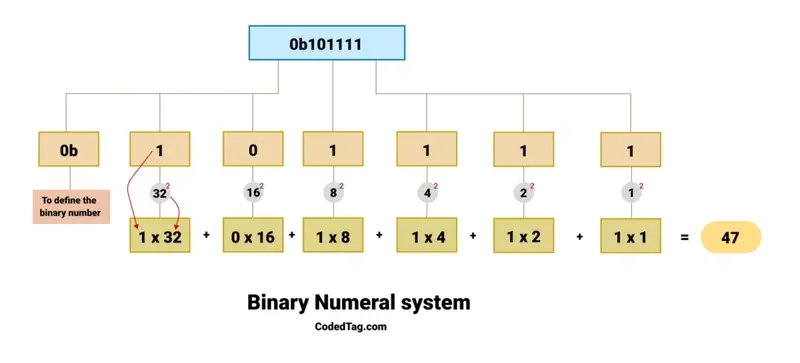
Look at this binary number: 0b101111. The prefix 0b shows that the number is in binary. The digits after 0b—which are 101111—represent powers of 2, as shown below.
(1) x ((2 ^ 0) = ( 1 ) = (1)) = 1
(1) x ((2 ^ 1) = ( 2 ) = (2)) = 2
(1) x ((2 ^ 2) = ( 2 x 2 ) = (4)) = 4
(1) x ((2 ^ 3) = ( 2 x 2 x 2) = (8)) = 8
(0) x ((2 ^ 4) = ( 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 ) = (16)) = 0
(1) x ((2 ^ 5) = ( 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2) = (32)) = 32Here is an analysis of the above calculation.
- The rightmost digit is (1), which represents (2 ^ 0), so usually the first digit in the right position is (1).
- In the next number, the digit is (1), so it exposes the exponentiation like this: (2 ^ 1) = (2).
- We are still moving from right to left in the calculation. The next digit is (1), which is the number (2) that equals (2 ^ 2) = (4).
- And then the following number is (1), which would take (2 ^ 3) = (8).
- The next digit is 0, representing (2^4). Since this digit is (0), it contributes (0) to the total.
- In the final digit, which is the most left number, it is (1). It takes (2^5), and that equals (32).
Here is the sum of the whole calculated number:
32 + 0 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1 = 47So, (0b101111) in binary is equal to (47) in decimal.
Check if a Value is an Integer with is_int()
Sometimes you need to confirm that a value is an integer. PHP provides a function called is_int() to do this. It serves as a way to confirm that the value is an integer.
For example:
$age = 18;
if (is_int($age)) {
echo "Yep, it’s an integer!";
} else {
echo "Nope, that’s not an integer.";
}In the example above, is_int($age) checks if the variable $age holds an integer. Since 18 is a whole number, PHP returns ‘Yep, it is an integer!’.
How to Convert Values to Integers
If you have a float like 5.7 but want to convert it to an integer, type casting helps. It tells PHP to treat the number as a whole number.
$decimal = 5.7;
$integer = (int)$decimal;
echo $integer; // Output: 5(int) tells PHP to drop the decimal part and keep only 5. This works well when you need to make sure numbers become integers, even if they start as floats.
Limits in PHP Integers
PHP integers have their limits, and if you exceed them, PHP converts the number to a float. It’s called integer overflow, and here’s what it looks like:
$bigNumber = 2147483647;
$bigNumber += 1;
echo $bigNumber; // Could become a float if it exceeds max limitIn this case, $bigNumber reaches the maximum integer limit for a 32-bit system. When the value goes beyond that, PHP converts it to a float.”
Wrapping UP
In this article, you learned what integers are in PHP and how PHP handles different integer types. You also understood how to write integers in decimal, hexadecimal, octal, and binary forms.
Then, you saw how to check if a value is an integer with the is_int() function and how to convert other values to integers with type casting.
Here is a quick recap:
- Integers are whole numbers without decimal parts, represented by the
inttype in PHP. - PHP supports four integer types: decimal (base 10), hexadecimal (base 16), octal (base 8), and binary (base 2).
- Hexadecimal numbers start with
0x, octal numbers start with0or0o(PHP 8.1+), and binary numbers start with0b. - You can use
is_int()to check if a value is an integer. - Use
(int)to convert other number types, like floats, into integers by dropping the decimal part. - PHP integers have size limits based on your system. When a number exceeds these limits, PHP converts it to a float automatically.
Similar Reads
Whether you are just trying to keep your app from crashing or making sure your users’ uploads don’t accidentally overwrite…
The abs() function in PHP gives you a number without its sign — it always returns a positive value. That…
Classes and objects are important parts of OOP in PHP. They help you organize your code so you can update…
Essentially, “require” and “require_once” are directives in PHP to include and evaluate a specific file during the execution of a…
PHP 5 added support for classes and interfaces. This made object-oriented code possible with one feature being polymorphism. That means…
PHP namespace solves the problem of name conflicts. Different developers may create functions-classes, or constants with the same name. PHP…
The sizeof function in PHP exists to help developers know how many items an array holds. Understand the sizeof Function…
You deal with user input, file reads, or formatted strings. PHP needed a way to remove extra characters from the…
The PHP named arguments are the names of the arguments through which the values are passed, allowing you to add…
The array_combine function in PHP creates a new array with one array for keys and another for values. It needs…