JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight format used for storing and exchanging data. In JavaScript, there are multiple ways to read and parse JSON files. These methods can be used both in browser environments and in Node.js.
1. Using the fetch() API
The fetch() API retrieves JSON files asynchronously and parses them into JavaScript objects.
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<script>
function fetchJSONData() {
fetch('./sample.json')
.then(response => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`HTTP error! Status: ${response.status}`);
}
return response.json();
})
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error('Failed to fetch data:', error));
}
fetchJSONData();
</script>
</body>
</html>
//sample.json
{
"users": [
{
"site": "GeeksForGeeks",
"user": "Lucas"
}
]
}
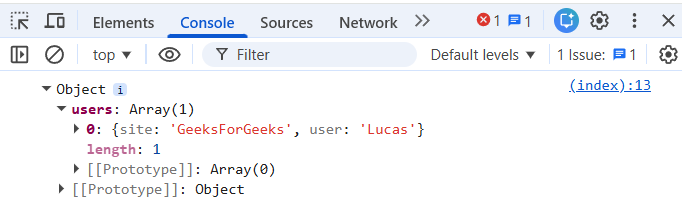
Output
Syntax
fetch('sample.json')
.then(response => response.json()) // Parse JSON
.then(data => console.log(data)) // Work with JSON data
.catch(error => console.error('Error fetching JSON:', error));
- Create a sample.json file with the desired data.
- Use fetch("sample.json"), then parse the response with .json().
- Handle the data or display it, using .catch() for errors.
2. Using require() Method in Node.js
In a Node.js environment, require() is a simple way to read JSON files synchronously.
// Node.js example
const data = require('./sample.json');
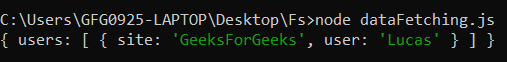
console.log(data);
//sample.json
{
"users": [
{
"site": "GeeksForGeeks",
"user": "Lucas"
}
]
}
Syntax
const data = require('./sample.json');
console.log(data);
- Create the JSON file (sample.json).
- Use require() to import the JSON data.
- Log or manipulate the data.
3. Using the import Statement for ES Modules
In modern JavaScript (ES Modules), use import ... assert { type: 'json' } to load JSON asynchronously in Node.js (v17+) and supported browsers.
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<h1>JSON Import Example</h1>
<p>Check your console for imported data.</p>
<script type="module">
import jsonData from './sample.json' assert { type: 'json' };
console.log(jsonData);
</script>
</body>
</html>
//sample.json
{
"name": "Johina",
"age": 30,
"profession": "Developer"
}
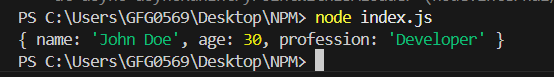
Output
{
"name": "Johina",
"age": 30,
"profession": "Developer"
}
- Browser compatibility :ES Modules with the import syntax are supported in modern browsers.
- Node.js compatibility :Requires Node.js v17 or higher with appropriate module settings.
Syntax
import jsonData from './path/to/jsonFile.json' assert { type: 'json' };
console.log(jsonData);
- Enable ES Modules using .mjs extension or "type": "module" in package.json.
- Use import ... assert { type: 'json' } to load and process JSON data.