Given pointer to the head node of a linked list, the task is to reverse the linked list. We need to reverse the list by changing links between nodes.
For Example:
Input:
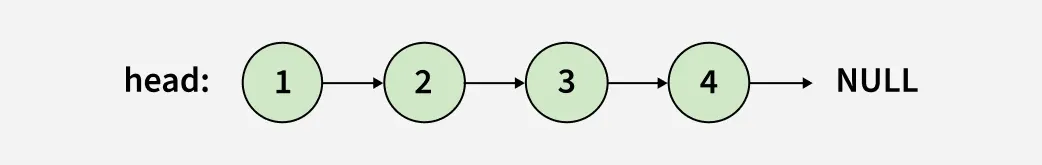
Output:
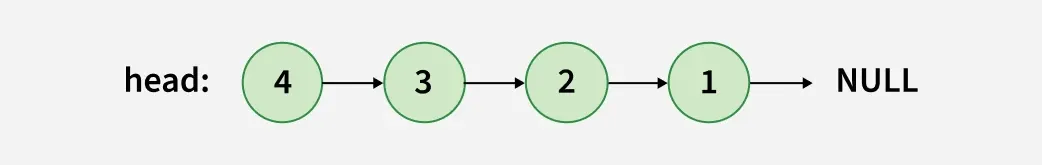
Let's look at the ways to achieve this in Python:
1. Iterative Method
The idea is to reverse the links of all nodes using threepointers:
- prev: pointer to keep track of the previous node
- curr: pointer to keep track of the current node
- next: pointer to keep track of the next node
Starting from the first node, initialize curr with the head of linked list and next with the next node of curr. Update the next pointer of currwith prev. Finally, move the three pointer by updating prevwith currand currwith next.
# Class to represent node of linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Class to define linked list
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data,end=" ")
temp = temp.next
# Creating a linked list and adding elements to it
ll = LinkedList()
ll.push(20)
ll.push(4)
ll.push(15)
ll.push(85)
print ("Given Linked List:")
ll.printList()
prev = None
curr = ll.head
while(curr is not None):
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
ll.head = prev
print ("\nReversed Linked List:")
ll.printList()
Output
Given Linked List 85 15 4 20 Reversed Linked List 20 4 15 85
Explanation:
- prev = None: Initializes the previous node pointer for reversal.
- curr = ll.head: Starts reversing from the first node.
- next = curr.next: Stores the next node before breaking the link.
- curr.next = prev: Reverses the direction of the current node's pointer.
- prev = curr: Moves the previous pointer one step forward.
- curr = next: Moves the current pointer to the next node.
- ll.head = prev: Updates the head to the last processed node, completing the reversal.
2. Recursive Method
The idea is to reach the last node of the linked list using recursion then start reversing the linked list from the last node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverseUtil(self, curr, prev):
if curr.next is None:
self.head = curr
curr.next = prev
return
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
self.reverseUtil(next, curr)
def reverse(self):
if self.head is None:
return
self.reverseUtil(self.head, None)
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data,end=" ")
temp = temp.next
ll = LinkedList()
ll.push(5)
ll.push(4)
ll.push(3)
ll.push(2)
ll.push(1)
print("Given linked list")
ll.printList()
ll.reverse()
print("\nReverse linked list")
ll.printList()
Output
Given linked list 1 2 3 4 5 Reverse linked list 5 4 3 2 1
Explanation:
- reverseUtil(self, curr, prev): Recursive helper function to reverse the linked list.
- if curr.next is None: Checks if the current node is the last node in the list.
- self.head = curr: Updates the head to the last node, which becomes the new first node after reversal.
- curr.next = prev: Reverses the pointer of the current node.
- return: Stops recursion after updating the new head.
- next = curr.next: Stores the next node before changing the link.
- curr.next = prev: Reverses the link between the current and previous nodes.
- self.reverseUtil(next, curr): Recursively processes the next node.
- reverse(self): Public method to start the recursive reversal.
- if self.head is None: Handles the case when the linked list is empty.
- self.reverseUtil(self.head, None): Initiates recursion from the head with no previous node.
- push(self, new_data): Inserts a new node at the beginning of the linked list.
Please refer Reverse a linked list for more details!