Have you ever wondered where WordPress stores your blog posts, user comments, settings, and login information?
While your theme and plugin files control how your site looks and behaves, the WordPress database stores everything that gives your site meaning, content, users, and settings.
Think of it as a digital filing cabinet that WordPress reads from and writes to every time someone visits your site. Understanding how this database works is the first step toward maintaining, troubleshooting, and scaling your website confidently.
In this beginner’s guide to WordPress database management, we will walk you through the basics of how it works and the safest ways to access WordPress database settings.
Without further ado, let’s get started!
What is WordPress Database?
At its core, the WordPress database is a structured system that stores all of your website’s content, settings, and user data. While your theme files and plugins are like the “body” of your site, the database is its “memory.”
When you publish a post, its content is stored in the database, not as a static file on your server. Instead, they are sent to the database. Every time a visitor clicks your site, WordPress quickly pulls that information from the database to display it to them.
How Does WordPress Database Work?
WordPress uses MySQL (or compatible systems like MariaDB) to store and retrieve data efficiently. This is a popular system for efficiently storing and retrieving information.
The database works like a structured system of tables, where each table stores a specific type of information that WordPress can quickly query and display, such as;
- Users: Names, passwords, and email addresses.
- Posts: Your articles, pages, and draft content.
- Comments: What your visitors have written on your posts.
- Settings: Your site title, tagline, and layout choices.
It is important to understand that your database and your WordPress files are two different things. Your files (accessed via FTP or a File Manager) determine how the site looks and functions.
Without the database, your website would be an empty shell. It would have a design but no text, no users, and no settings. This is why the database is the most valuable part of your digital property.
Understanding WordPress Database Tables
A standard WordPress installation includes 12 core database tables that work together to store and retrieve your site’s data. Here is a breakdown of all 12 default tables:
- wp_posts: The core table that stores all posts, pages, custom post types, and navigation menu items.
- wp_postmeta: This table stores “metadata” or extra information for your posts. It includes things like featured image IDs or custom field data.
- wp_users: This table holds the list of everyone who has an account. It stores usernames, encrypted passwords, and email addresses.
- wp_usermeta: Similar to postmeta, this stores extra info about your users. It tracks things like user roles (Admin or Subscriber) and nicknames.
- wp_options: Stores global site settings, including the site URL, active plugins, and configuration values.
- wp_comments: Every time someone leaves feedback, that data goes here. It keeps track of the author’s name and the comment text.
- wp_commentmeta: This stores extra details about comments. For example, it might track whether a comment has been marked as spam.
- wp_terms: This is where your categories and tags are named. If you create a category called “Recipes,” that name is stored here.
- wp_termmeta: This stores additional information for your terms. It is often used by plugins to add custom icons or colors to categories.
- wp_term_taxonomy: This table explains the “type” of term. It tells WordPress whether a word in the wp_term table is a Category or a Tag.
- wp_term_relationships: This table acts as a bridge. It links your posts to the specific categories and tags they belong to.
- wp_links: This is a legacy table from older versions of WordPress. It used to manage “Blogrolls,” but it is mostly unused by modern sites today.
How WordPress Connects to the Database
For your website to work, your files must be able to “talk” to the database. This connection happens through a very important file called wp-config.php.
This file acts as the connection layer between your WordPress files and the database. It contains the login credentials that WordPress needs to unlock and read your database tables.
When someone visits your site, WordPress looks at the wp-config.php file first. It finds the database name, the username, and the password.
Once the connection is made, WordPress sends “queries” to the database. A query is just a request for information, such as “Give me the text for the latest blog post.”
If these connection details are wrong, you will see the famous “Error Establishing a Database Connection” message. This usually means WordPress cannot authenticate with the database due to incorrect credentials or a server issue.
Why Access WordPress Database?
In the next section, we will learn exactly how to access your WordPress database. Before accessing your database, it’s important to understand when and why direct database access becomes necessary.
While most people spend their time in the WordPress dashboard, there are moments when the dashboard isn’t enough. Sometimes, the only way to fix a major problem is to go straight to the source.
Accessing your database can be a lifesaver when things go wrong. Here are some of the most common reasons site owners need to look under the hood:
- Resetting Passwords: If you are locked out of your site and the “Lost your password?” link isn’t working, you can manually change your password in the wp_users table.
- Fixing Plugin Conflicts: Disable or reset problematic plugins directly from the database when the WordPress dashboard is inaccessible.
- Bulk Data Updates: If you need to change a specific word across thousands of posts, running a simple database command is much faster than editing each post one by one.
- Optimizing Performance: Over time, your database can get cluttered with old drafts and spam. Cleaning this up can help your website load faster for your visitors.
- Site Migration: When moving your website to a new host, you must move the database to ensure all your content stays intact.
How to Access WordPress Database [2 Easy Ways]
Now that you know what a database is, it is time to learn how to access it. There are two main ways to do this.
The first method is the traditional way using a tool called phpMyAdmin. This is a powerful database management tool commonly used by developers, but it can be risky for beginners due to its unrestricted access.
Method 1: Accessing via phpMyAdmin
If you want to use the traditional method, follow these steps:
- Log in to your web hosting account and find the “cPanel” or “Hosting Dashboard.”
- Locate the “Databases” section and click on the phpMyAdmin icon.
- Once the tool opens, find your website’s database name in the left-hand sidebar, then click it.
- Finally, you will see all your WordPress tables (such as wp_posts) appear on the screen, allowing you to browse or edit their data.
Method 2: Accessing via a File Manager Plugin
A much better and safer way for beginners to manage their site is through a WordPress file manager plugin. Instead of logging into complex hosting panels, you can manage your files and database right from your WordPress dashboard.
For beginners and non-developers, using a WordPress file manager plugin is a safer alternative to phpMyAdmin. Advanced File Manager allows you to manage files, and access the database directly from your WordPress dashboard.
Trusted by over 100,000 active users, Advanced File Manager is widely used for secure WordPress file and database management.
It is designed to be simple enough for beginners while having all the power a developer needs. Here are some of the exciting features that make Advanced File Manager the top choice:
- Complete File Operations: Download, upload, edit, copy, and perform all the actions to manage files directly in the WordPress dashboard. No need for external software.
- Media & Document Previews: Instantly preview PDFs, images, audio, and video files without downloading them, saving time and improving productivity.
- AI-Powered Coding Assistant: Get real-time coding assistance with the built-in AI Code Pilot, which suggests fixes, completes snippets, and highlights potential issues while editing PHP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
- Drag-and-Drop File Uploads: Just drag and drop the file on the file manager to upload it.
- Advanced File Search & Sorting: Quickly browse files with the help of advanced search and sorting features. No need to spend hours trying to find a file.
- Handy Keyboard Shortcuts: Save time with handy keyboard shortcuts that are sure to enhance your productivity and help you get more work done in less time.
- Frontend File Management: Create a front-end document library that lets logged-in and (optionally) non-logged-in users access and manage shared files.
- FTP-Free File Management: Manage all WordPress files directly from the dashboard without relying on FTP clients or hosting control panels, making file handling faster and more beginner-friendly.
- Cloud Storage Integrations: Connect and manage files from popular cloud services like Google Drive, Dropbox, Amazon S3, and GitHub directly within WordPress, allowing you to work with remote files from one centralized location.
- ZIP Archive Management: Create, extract, and compress ZIP archives directly on your server, making it easy to back up files or transfer themes and plugins.
- Hide Private Files: Selectively hide specific files or folders from the file manager view for certain user roles, adding an extra layer of access control.
- Multi-Lingual Support: Use the file manager in multiple languages, making it accessible and easy to use for a global WordPress audience.
- Role-Based & User-Specific Access: Show files only to those who need them! Restrict access using user-specific access restrictions.
- Private & Public Folder Access: Set up private folders for specific users or allow public access for document sharing while maintaining security.
- Built-in Code Editor: Safely edit PHP, HTML, CSS, and configuration files directly within WordPress, with syntax highlighting.
Using Advanced File Manager removes the technical “wall” between you and your database. It gives you the confidence to maintain your site’s health without fear of breaking something.
How to Install Advanced File Manager
Installing Advanced File Manager takes just a few clicks. Follow these simple steps:
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Plugins, then click Add Plugin.
- Search for “Advanced File Manager” in the search bar.
- Click Install Now and then click Activate.
While the basic version of the plugin offers incredible file management features, the ability to manage your database directly is a premium feature. To enjoy the full perks of the Database Manager, you will need to activate Advanced File Manager Pro.
Unlocking the premium perks is the best way to ensure your site stays organized and secure. Here is how you can activate the database features:
- Navigate to the Advanced File Manager pricing page and purchase a plan that fits your needs.
- You will receive a welcome email with the premium plugin’s zip file and a unique license key used to activate premium features.
- Download the zip file on your device and preserve the license key for later use.
- Return to the admin dashboard and navigate to Plugins, then Add Plugin, and finally click the Upload Plugin button in the top left corner.
- Click Choose File and select the downloaded zip file, and click Install.
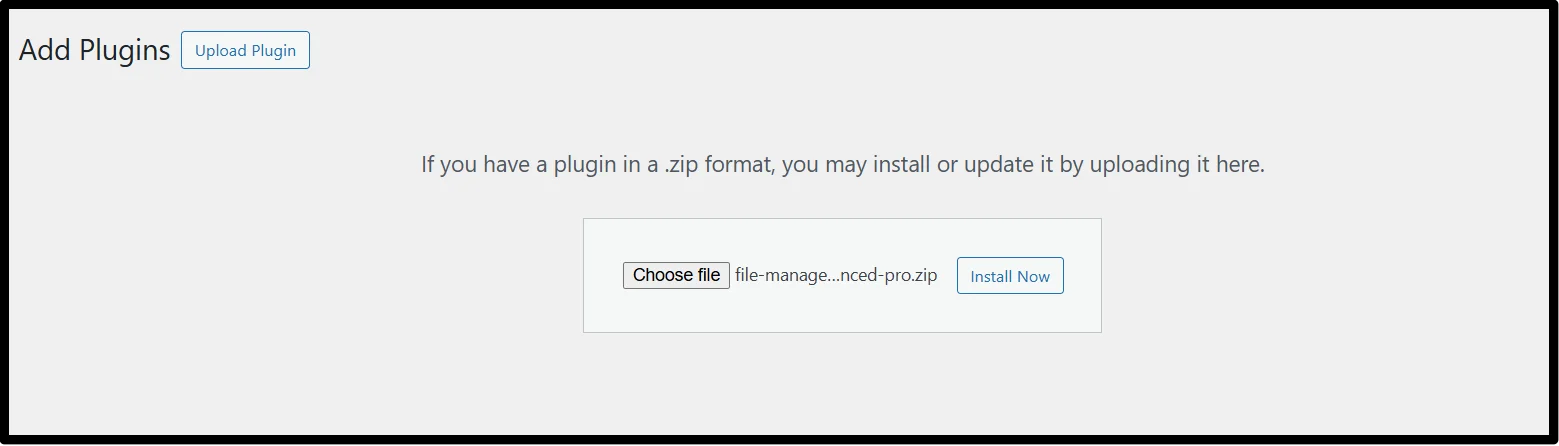
- Once done, click Activate Plugin.
- Finally, start using all the amazing features after validating installation with your license key.
There you have it! The Advanced File Manager Pro is up for use with all the amazing features, including the DB Access, which is short for—you guessed it—database access.
Now that you have Advanced File Manager, navigate to the File Manager tab on your admin dashboard and click DB Access.
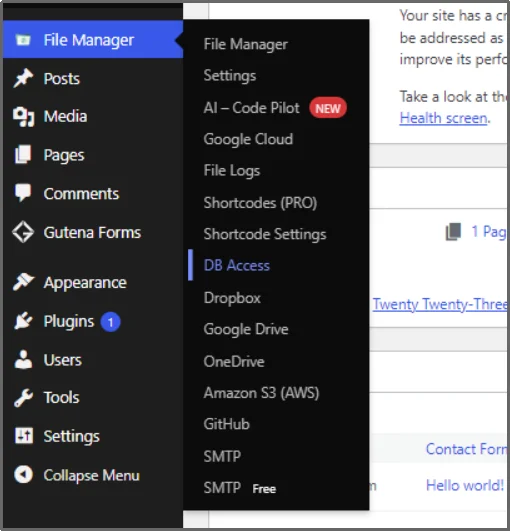
…and, you’re in.
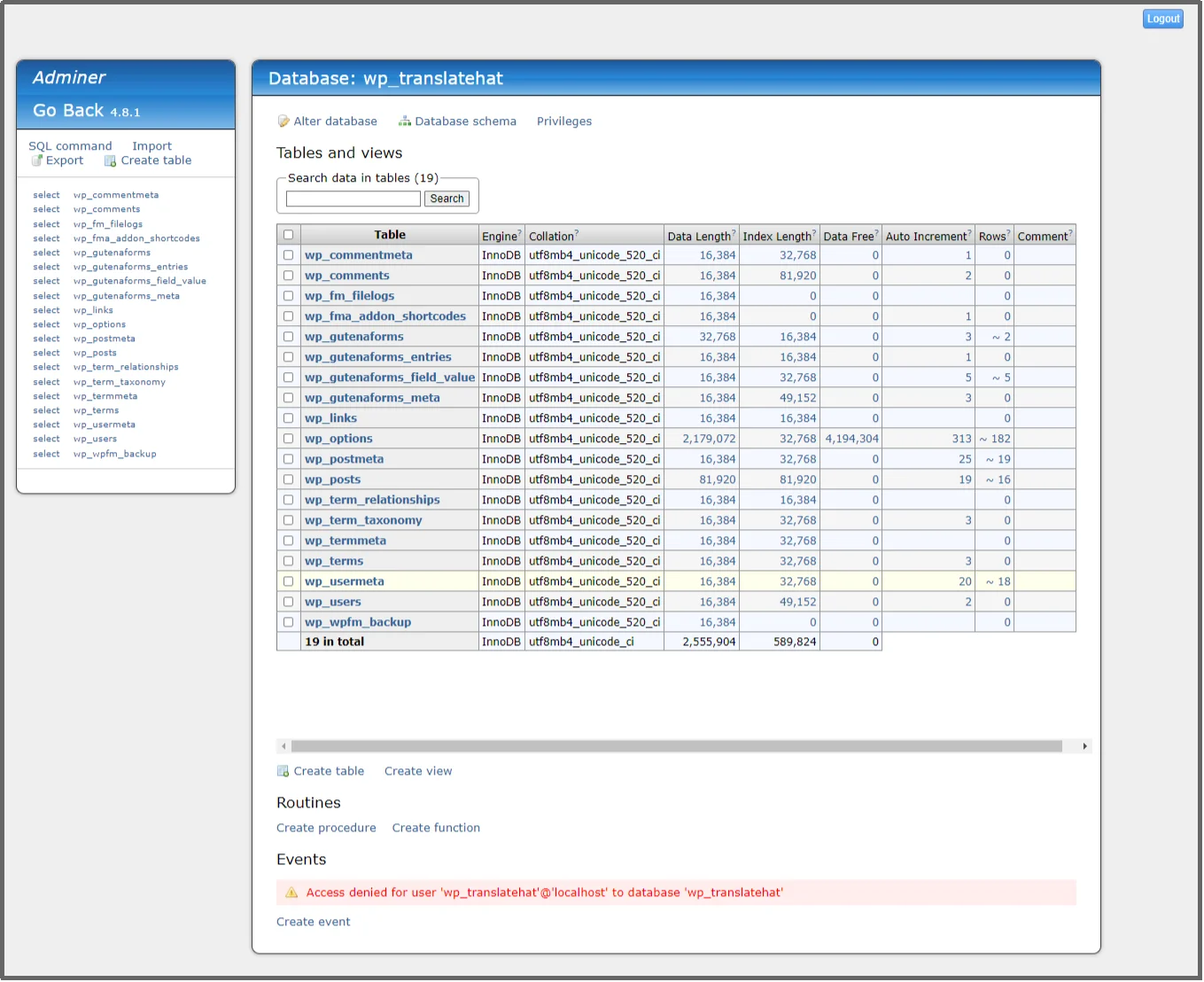
It’s that easy with Advanced File Manager. No need to chase external tools or credentials, it all happens inside your WordPress dashboard.
To learn, check out detailed documentation on DB Access.
Best Practices for WordPress Database Management
Since the database is the “brain” of your website, you must treat it with care. One small mistake can take your entire site offline. For this reason, database security should always be a top priority.
Following a few simple rules will help you maintain a fast and healthy website:
- Always Create a Backup First: Before you touch a single table in your database, make sure you have a full backup. If something goes wrong during your WordPress database management tasks, a backup allows you to restore your site in minutes.
- Use a Unique Database Prefix: By default, WordPress uses the wp_ prefix for all its tables. Changing this to something unique, like mysite_, makes it much harder for automated hacker scripts to find and attack your tables.
- Regularly Delete “Trash” Data: Your database can quickly fill up with old post revisions, deleted comments, and expired plugin data. Cleaning these out periodically keeps your site lean and improves loading speeds.
- Limit Access to Trusted Users: Never give database access to someone you do not fully trust. Only administrators should have the ability to view or edit the database to ensure your sensitive information stays safe.
- Keep Your Plugins Updated: Outdated plugins often have security holes that hackers use to inject “bad code” into your database. Keeping everything up to date is one of the easiest ways to maintain your site’s health.
Take Full Control of Your WordPress Files and Database with Advanced File Manager
Managing your WordPress database doesn’t have to be a scary or overly technical task. By understanding how your data is stored and used, you can make better decisions for your site’s growth and security.
Whether you are fixing a broken plugin or simply cleaning up old post drafts, having the right tools makes all the difference. Advanced File Manager gives you the peace of mind to handle complex tasks with ease.
Don’t let technical hurdles hold your website back from its full potential. Join thousands of other site owners who have simplified their workflow and secured their data. Ready to manage your WordPress files and database with confidence, without leaving your dashboard? Get Advanced File Manager today!



