In Python, you might have worked with a dictionary, and while learning C++, you want to utilize the same. But here is the secret. You will not find any C++ Dictionary concept as it is not valid in C++.
However, the implementation of a dictionary-like data structure can be possible in C++ with the help of the std::map container. In academic assignments and competitive programming problems, C++ dictionaries are commonly used for frequency counting and fast lookups.
In this article, we are going to define the dictionary in C++ in a very simple manner. Let’s begin our discussion.
TL; DR: C++ Dictionary
Aspect | Summary |
Dictionary Concept | C++ does not have a built-in dictionary; map and unordered_map store key–value pairs like a dictionary. |
Types of Maps | Map keeps keys sorted; unordered_map uses hashing and does not maintain order, offering faster access. |
Adding & Accessing Elements | Use map[key] = value; to add elements; loops with .first and .second access keys and values. |
Copying Dictionaries | New dictionaries can be created from existing ones by copying the original map object. |
Common Mistakes & Comparison | Avoid missing headers, wrong data types, or incorrect use of .first and .second; C++ maps are statically typed and slower compared to Python dictionaries. |
What Is A C++ Dictionary? Get To Know
You might be thinking that C++ Dictionary will help to find words like a normal dictionary. But you are wrong here. So, let us start with the introduction!
It is a container where a programmer can store many elements. Now, you might ask in the array, we can store the data, so what is the necessity of the C++ Dictionary? Now, can you find any element with a particular value in the array?
You can use the index number, but for that, there is a need to know the particular index number. In the case of a dictionary in the C++ programming language, you can store an unlimited number of elements that will not occupy much memory space. Also, the key values can be used for printing purposes.
This means that values in a dictionary are associated with unique keys that can be used to access them. We call these key value pairs.
C++ programming language has many uses. If you’re interested in learning more, explore our detailed guide on applications of C++, which covers its role in software development, game engines, and system programming.
In the C++ programming language, there is no Dictionary concept present.
Now, let us understand how we can create a dictionary in the C++ programming language and the concept of object mapping.
Why C++ Does Not Have A Built-in Dictionary Like Python?
C++ does not provide a built-in data structure called a Dictionary like Python because C++ is designed as a low-level and performance-oriented language. C++ gives programmers more control over how data is stored and accessed.
To access dictionary-like behavior in C++, we have to use different containers like std::map and std::unordered_map in the Standard Template Library (STL).
These containers store data in key–value pairs, just like a Python dictionary. It also allows developers to choose between sorted storage and faster access, depending on the problem requirement.
Now, let us understand how we can create a dictionary in the C++ programming language and the concept of object mapping.
How To Create The C++ Dictionary?
Now, after having a piece of good knowledge about the Dictionary in C++ programming language, there is a need to implement it we need to follow some steps. That is the reason, we have made the total process in a step-by-step format.
Let’s get started with the first step of declaring the header files we require in our program.
Declaration Of The Header File:
For using the Map concept in C++ programming, there is a need to declare a special header file.
As the Map is the Dictionary in C++ programming language, we need to import the #include <map> header file to the programming.
#include <iostream> // Declaration Of The Normal Header File
#include <map> // The Necessary Important Header File For Dictionary
Declaration Of The Map:
After we declare the header file in the programming, there is a need to declare the map, too. A Map is a container that stores the key-value pairs in C++ language. To fully understand how Map and other containers function, it’s useful to learn about the C++ Standard Library, which provides essential built-in functionalities. To create a dictionary using a c++ map of the standard template library of STL, we need to first declare it.
We need to first provide the keyword ‘map’ for declaration. Then we are going to provide the data types of the Element & Key Values to form the key-value pairs in it. At last, there is a need to provide the name of the Map object in the C++ programming language. Look at the syntax given below.
General Syntax: map<Element Data Type, Key Value Data Type>Map-Name;
Map stores data in sorted order, which is useful when assignments require output in ascending key order.
Providing Elements & Key Values:
Now, it is time to map elements to create our dictionary. Let us see how we can do it.
After the declaration of the Map in C++ programming language, there is a need to provide the elements & key values to make the key value pairs to it. to provide the values, there is a need to follow a special method. The elements that are needed to be inserted into the Map object in C++ programming language, should be placed in the braces.
storage["Books"] = "Shelf"; // Book Is Element & Shelf Is Key Value
storage["Foods & Drinks"] = "Fridge"; // Foods & Drinks are Element & Fridge Is
Key Value
storage["Cloths"] = "Wardrobe"; // Cloths Is Element & Wardrobe Is Key Value
So, this is how you can map elements and key values. You can access the element by using its key value.
Implementation Of Loop:
After doing all these things, there is a need to develop a loop. Among them, there is a need to implement the for each loop. Because there is a need to access all the elements that are present in the Map in the C++ programming language.
To access these data, there is a need to use the Dot(.) operator. After the name of the Map in the C++ programming language, we need to use two keywords to access it.
You might have learned loops in Python and C programming as well, and most of the students get stuck in the implementation of loops due to a lack of concept clarity. For students struggling with loops and syntax in C, getting C help from experienced programmers can be beneficial.
The first one will be the keyword ‘first’, which will help to access the elements that are inserted into the Map in the C++ programming language. And the other one will be the ‘second’ keyword that will help to access the key values.
for (auto element :storage) { // Running A For Loop To Get All The Elements
cout<<element.first<<" Can Be Stored In "<<element.second<<endl;
Let us try to find out an entire code where all the above code snippets will collaborate to make a complete example. Let us have a look at the following example.
How To Implement A Complete C++ Dictionary?
Now, let us have a look at the example program below to see how we can create and access the elements or the key-value pairs of a user-defined dictionary using the C++ map keyword.
Generally, we need to use std::map, wherever we are using the map keyword. However, to eliminate the need to write this, we can simply use a namespace for the same i.e ‘using namespace std’. You can see how it is used in the below code.
#include <iostream> // Declaration Of The Header File
#include <map> // The Necessary Important Header File For Dictionary
#include <string> using namespace std;
int main(){
map<string, string>storage; // Declaration Of Dictionary or The Map
// Assigning Elements To Dictionary, First One Is The Element In The Braced & The Second One Is The Key Value
storage["Books"] = "Shelf"; storage["Foods & Drinks"] = "Fridge";storage["Cloths"] = "Wardrobe";
for (auto element :storage) { // Running A For Loop To Get All The Elements
cout<<element.first<<" Can Be Stored In "<<element.second<<endl; // Printing Each & Every Element }return 0;}
Let us try to find out the output of the above code. It will help to make us understand the process of implementing Dictionary in C++ programming language.
Output:
From the above output, we can see that the values & the key pairs are shown properly. So, the Dictionary of the C++ programming language works properly in the example.
Now, in the above step-by-step implementation process, we have discussed the creation method of one empty Dictionary in the C++ programming language. But we intend to know all the methods that led to the creation of the Dictionary.
So, a Dictionary can also created by using another Dictionary. We are going to know about that.
How To Create A Dictionary From Another Dictionary In C++?
It is the simplest process to implement. From one already existing Map or Dictionary, one can create another Dictionary & store the object. For that purpose, there is a special syntax present.
According to the new syntax, the existing Dictionary name should be provided first. Following that, the new Dictionary where the details should be copied needs to be posted. And hence, without any issue, the details will be copied.
Let’s see how it will look based on the new syntax in c++.
General Syntax: map <first data type , second data type> existed-map-name(new-map-name);
Code To Implement A C++ Dictionary From Another Dictionary:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
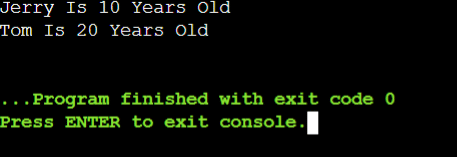
map <string, int> first = {{"Jerry", 10}, {"Tom", 20}}; // Implementation Of First Map
map <string, int> two(first); // Copying All The Items To Another Dictionary
for (auto a = two.begin(); a != two.end(); ++a) { // Implementation Of For Loop
cout << a->first << " Is " << a->second << " Years Old" << endl; // Printing The Data
}
return 0;
}
Steps Of The Program To Implement a C++ Dictionary From Another Dictionary:
- First, implement one Dictionary & provide some value to it. It will be used to copy data.
- Now, using the above syntax copy the content of the first Dictionary to the second Dictionary.
- Implement one for loop & using that extract all the elements & key values of the Dictionary. It will be printed on the screen.
Let us try to find out the output of the above code. It will help us understand the process of implementing a Dictionary in the C++ programming language.
Output:
How Can Students Create A Dictionary Using Unordered_Map In C++?
Not only can students use the Map, but they can also create a dictionary in C++ with the help of the Unordered_Map. Like the Map, here, the keys are not stored in a sorted order. But it uses a hash table to store.
Oftentimes, we have seen in assignments that it has been particularly instructed that the students create a C++ dictionary using Unordered_Map. That is why going through the following code becomes essential.
Since unordered_map does not maintain order, it should not be used when sorted output is required.
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
unordered_map<string, int> marks; // The Dictionary With Unordered
// Key Value Pairs
marks["Newton"] = 85;
marks["Tom"] = 90;
marks["Spike"] = 78;
for (auto item : marks) // Printing The Data
cout << item.first << " Scored: " << item.second << endl;
return 0;
}
The Unordered_Map will create a dictionary where the Key is a student’s name and the value is marks. Here, the data is stored using hashing, so you can see that the output order may vary.
The First represents the key, and the Second represents the value. The loop is used to print all key and value pairs.
Time Complexity of C++ Dictionary Operations:
When working with a C++ dictionary, understanding time complexity is important because it directly affects the performance of your program. This topic is also frequently asked in DSA exams, viva questions, and interviews.
Time Complexity Using Map:
- The map container in C++ stores data in sorted order using a balanced binary tree.
- Searching for an element takes O(log n) time
- Inserting a new key–value pair takes O(log n) time
- Deleting an element also takes O(log n) time
Since the keys are always sorted, a map is useful when ordered output is required, but it is slightly slower compared to hashing-based containers.
Time Complexity Using Unordered_Map:
- The unordered_map container uses a hash table to store data, which allows much faster access.
- Searching for an element takes O(1) time on average
- Inserting a key–value pair takes O(1) time on average
- Deleting an element takes O(1) time on average
In rare cases, when many keys map to the same hash location, the time complexity can become O(n). However, for most practical and academic problems, unordered_map performs much faster than map.
Comparison Table Between C++ Dictionary And Python Dictionary:
Most of the time, we have seen that students get confused between the C++ Dictionary and the Python Dictionary. And the examiner knows this pattern and asks questions from this field of conflict.
So, to overcome such traps in your assignment, you have to know their differences. That is the reason we have brought a comparison table between the C++ dictionary and the Python dictionary.
Feature | C++ | Python |
Name | map | dict |
Order | Sorted | Insertion |
Speed | Slower | Faster |
Typing | Static | Dynamic |
Implementation | Tree | Hash |
Flexibility | Low | High |
Use Case | Academic | Practical |
Real Assignment Question: C++ Program To Remove An Element From A Dictionary For Assignments
I have seen many times that the questioner sometimes asks to remove an element from the dictionary instead of creating it. This is where most students get stuck and fail to submit the code.
To deal with such issues, we erase the () function, which doesn’t belong to this topic, but yes, it is a common assignment question. Let us check its implementation process.
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Declaring A Map As A Dictionary
map<string, int> age;
// Adding Elements To The Dictionary
age["Tom"] = 20;
age["Jerry"] = 18;
// Removing An Element From The Dictionary
age.erase("Tom");
// Printing The Values
for (auto item : age) {
cout << item.first << " : " << item.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- A dictionary is created using a map<string, int> where names are keys and ages are values.
- The erase(“Tom”) function removes the entry with the key “Tom”.
- After deletion, the loop prints the remaining elements in the dictionary.
Common Mistakes Student Make With C++ Dictionary Assignment:
Since we have checked many assignments and homework on the C++ dictionary, we can confidently assert that there are some common mistakes that most students commit during exams in the classroom.
So, to warn you again, we have brought this section, which will help you to avoid committing them.
- Students often forget to include the correct header file, such as <map> or <unordered_map>, causing compilation errors.
- Beginners assume that unordered_map maintains insertion order, which it does not.
- Students confuse first and second while accessing key–value pairs inside loops.
- Using the wrong data type for keys or values often leads to logical errors.
- Some students modify a map while iterating over it, which can cause unexpected behavior.
Conclusion:
Understanding how C++ implements dictionary-like behavior helps students write efficient code and choose the right data structure in exams and real applications.
We need to remember those highlights related to the Dictionary in the C++ programming language. It will make it easier for us to memorize the process more easily.
There is a need to clear the basics of the C++ programming language to get this topic more easily. There is a need to start this topic from scratch to better understand it. We need to remember that there is no concept of a Dictionary present in the C++ Programming Language. It is a concept that will be of use to us in the future.
So, hope you have liked this blog. Share your thoughts in the comments section and let us know if we can improve further.
This concept is widely used in data structures coursework, competitive programming, and real-world systems that require fast data lookup.
Key Takeaways:
- C++ does not have a built-in dictionary, but map and unordered_map provide key–value storage.
- Both map and unordered_map are part of the C++ Standard Template Library (STL).
- Elements in a map are stored in sorted order, while unordered_map uses hashing and does not maintain order.
- Key–value pairs are added using map, and accessed with loops using .first for keys and .second for values.
- A new dictionary can be created from an existing one by copying the original map.
- Common mistakes include forgetting header files, misusing .first and .second, using the wrong data types, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can we use a Python dictionary directly in C++?
No, C++ does not support Python-style dictionaries directly. Instead, we use containers like map or unordered_map from the Standard Template Library (STL), which allow us to store and access data.
What is the difference between map and unordered_map in C++?
A map stores its elements in sorted order based on the keys, while an unordered_map stores elements using hashing, which does not maintain any order. Map is slightly slower due to sorting than unordered_map.
Can a C++ dictionary store duplicate keys?
No, in C++ dictionaries, each key must be unique. If you try to insert a value with an existing key, it will overwrite the previous value associated with that key.
Is unordered_map better than map for assignments?
Unordered_map is not always better than map for assignments—it depends on what the question requires. If the assignment asks for faster searching or counting frequency, then unordered_map is a better choice.