In mathematics, students often learn rounding, where a decimal number is converted to the nearest integer. However, “Rounding Down in Python” is different.
In Python, rounding down numbers always moves the value toward the smaller integer, regardless of the decimal part. It is essential in real-world scenarios such as indexing, billing systems, and data calculations.
This article explains correct and exam-safe methods to round down numbers in Python, helping you avoid common mistakes and build strong conceptual clarity.
TL;DR: Round Down In Python
Aspect | Summary |
Concept Overview | Rounding down in Python means converting a floating-point number to the nearest smaller integer. This behavior becomes important when negative values are involved. |
Programming Approach | Python offers multiple methods to round down numbers, such as floor(), int(), and Decimal, each following different internal rules. |
Student Confusion Area | Students often confuse rounding with truncation. This confusion usually occurs because different functions behave differently. |
Best Practice Recommendation | The math.floor() method best matches the mathematical definition of round down. It is the safest and most reliable option for exams and academic use. |
Academic Reliability | Rounding down operations run in constant time and use minimal memory. Since no complex data structures are involved, the approach is efficient and predictable. |
What Is A Round Operation In Python?
Round Operation is the process where the decimal point or decimal instance of the floating point number is ignored. And the number is converted to the nearest integer part. Such a conversation is done as the new number helps to be remembered well.
- Round-Up Method: In this case, the decimal module is converted to the highest nearest integer value. Like, 4.8 is a number rounded & gets the absolute value as 5, which is higher than 4.8.
- Round-Down Method: In this case, the decimal module is converted to the lowest nearest integer value. Like, 5.2 is a number rounded & gets the absolute value of 5, which is lower than 5.2.
In this article, we only intended to focus on the Round-Down Methods in the Python language. However, by the end, we will discuss one method to do a round-up in Python.
Why “Round Down” Confuses Students In Python?
- Many students assume that rounding down means “remove the decimal part,” which is not always true.
- Python provides multiple methods to round down, and each one follows a different rule, which confuses beginners.
- The confusion becomes worse with negative numbers, where the output may look unexpected and incorrect.
- In exams, students lose marks because they use a method that gives the correct output for positive numbers but fails for negative values.
- Python’s rounding behavior does not always match school-level mathematics, which makes students feel that Python is “behaving wrongly.”
How To Round Down Numbers In Python?
In Python Language, there are various ways to convert decimal digits or a decimal class to the nearest integer for any positive numbers or negative numbers. For that purpose, we can use Python’s built-in round method or by doing an import math module.
If you wish to learn about the methods to build a GUI calculator using Python, then you can check out our article article on Building a Python GUI Calculator with Tkinter, where we’ve explained everything in detail.
In this core section, we are going to discuss all the possible ways present to round numbers in Python by eradicating significant digits of decimal places to the nearest integer value which is less than the original decimal number.
Solution 1: Round Down Numbers Using Round() Method
Before diving into the round() method, it’s essential to understand Python’s built-in functions. Our guide on Python String Functions provides insights into various built-in functionalities you can use in your programs.
Also, in the Function Rounds, we can provide some arguments that can help to get decimal points at different decimal places.
Like, if we enter 1 as the argument, one more decimal place will be added to the new integer value that will convert the integer to the floating number. We can use this method for both Positive & Negative Values.
General Syntax: round (Float Number)
#1 Using round() method
num = 20.24 # Assigning The Floating Number
print("The New Rounded Number: ",round(num)) # Rounding Off With Round Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, the floating number with decimal places will be declared in the program.
Now, we will directly call the print statement where the above syntax will be used to round numbers & get the nearest integer value.
Output:
From the above code & output, we can see that the nearest integer 20 value is achieved by removing the 24 decimal points. This is demonstrated by the positive number. However, in the same way, we can do it for the negative numbers as well.
Solution 2: Round Down Numbers Using The Int() Method
Now, after the built-in round function, it is time to check another function that is not dedicated to the rounding of the numbers. It is used on the Floating Numbers to be converted to the integer values. And if we think, we want to achieve the same by doing round numbers.
Here, the Int Method will be used to get the nearest integer value. You will be happy to know that the Int Method can also be used for the Negative numbers as we are doing for the positive numbers in the below example.
General Syntax: int(Float Number)
#2 Using Int method
num = 03.04 # Assigning The Floating Number
print("The New Rounded Number Using Int Mehtod: ", int(num)) # Rounding Off With Int Method
Steps Of The Program:
Here again, at first, we will declare the variable where the decimal value is stored.
Now, we will directly call the print statement where the Int() Method is used as per the syntax.
Output:
From the above output, we can see that the Float Number Rounded to the Nearest Integer value which is the Number 3. You have to note that the Zero before the Number 3 also gets deleted while printing the number to the output window.
Solution 3: Round Down Numbers Using Trunc() Method Using Math Module
Now, it is time to use the Trunc() Method or the Truncated Number method to get the nearest integer value. To use this property, we need to import math module to the program. After we import math module, we can use the properties & functions of Trunc().
In this case, as well, the decimal digits of the number will be converted to the integer number which is the nearest one. The Whole Number will become the integer number from the float number. Let us check the general syntax of it.
General Syntax: trunc(Float Number)
#3 Using Trunc method
from math import trunc # Importing TRUNC From Math Library
num = 11.22 # Assigning The Floating Number
print("The New Rounded Number Using TRUNC Mehtod: ", trunc(num)) # Round Numbers With TRUNC Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, we have to import Math to the program and from that Import Math, we can get Trunc() Module.
Directly, we are going to draw the print statement on the program. In the print statement, we will use the above syntax to get the nearest integer value.
Output:
The output clearly shows that the import math function works properly & the nearest number is achieved. Here in the code, the 11.22 number is provided which is now converted to the integer value 11 without any error message.
Solution 4: Round Down Numbers Using Floor Method
After the Trunc() Method, it is time to discuss the Floor Method. Sometimes, it is called the Math Floor Method as in this case as well, we need to import math into the program. Without performing import math, the process will not be completed.
We can use the Floor Method or specifically Math Floor Method for the Negative Numbers as well. If we use the Math Floor Method for Negative Numbers, it will not prompt any kind of errors or warning messages.
General Syntax: floor(Float Number)
# Taking user input
message = input("Please enter a message: ")
pincode = input("Please enter the recipient pincode: ")
# Displaying the captured input
print("Message:", message , " " , type(message))
print("Pincode:", pincode, " ", type(pincode))
Steps Of The Program:
At first, we have to import math into the program to use the Floor Function.
Now, we will directly call the Print Statement on the Python Code where the rounding of the number will be done with the above syntax.
Output:
From the above output & the code, we can see that the Python Floor Method successfully converted the whole number to the nearest integer value without any issues. And the Integer Value 22 is achieved with the Module Math on Python.
Solution 5: Round Down Numbers Using Decimal Method
Now, it is time to discuss the Decimal Module to convert the Floating whole number to the nearest integer number. We are sure that, you will find the method a bit more complicated than any other method discussed previously on Python.
In this example, the number of lines occupied in the Python Code is much more than any other example. You should have a good knowledge of Python to understand this function properly. Let us check the following example.
#5 Using Decimal method
import decimal # Importing Decimal Module
decimal.getcontext().rounding = "ROUND_FLOOR" # Declaring The Decimal Number
num = decimal.Decimal(55.85).quantize(decimal.Decimal(1.0)) # Making Decimal Numbers
print("The New Rounded Number Using Decimal Mehtod: ",num) # Rounding Off With Decimal Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, we have to import the Decimal Function to the code to use different modules.
Now, the property of the Decimal Function will be declared where we will inform the function to perform Rounding Down of the whole number.
Now, the decimal value will be provided along with the decimal quantize that will help to remove the decimal part from the whole number in the code.
Now, the new stored number that came from the Decimal Function will be printed in the Python example program.
Output:
The output will be enough to talk about the success of the Decimal Function Example. In the Python Program, we have provided the value of 55.85. And now, the whole number is converted to the nearest integer number as 55.
Solution 6: Round Down Numbers Using String Format Method
Now, it is time to discuss another Rounding Function where no more Math Library Modules will be needed to import. The simple String Format will be used in the Python Example to get the whole number converted to an integer number.
However, the way to use the String Format in this Function Python Rounding Number Example will not be a simple one & we are sure you might be witnessing it for the first time.
General Syntax: int(“{:.0f}”.format(Float Number))
#6 Using String Format method
num = 102.1123 # Assigning The Floating Number
zap = int("{:.0f}".format(num))
print("The New Rounded Number Using String Format Mehtod: ", zap) # Rounding Off With String Format Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, the Float Number will be declared in the Python Example Code.
Now, we will use the above syntax & store the new value in one new variable. This is the Syntax that removes the Decimal Point & converts it to the Integer format.
Now, we will use the Print Statement in the Python Example to get the New Whole Number.
Output:
From the above output, we can see that the Normal Integer value is coming from the String Format Function in the above Python Code Example. So, you can see that with the simple String helps, we can convert a float to an integer value in Python.
Important Student Warning: String Format Method
- This method may give the correct answer, but many students cannot explain why it works during exams or viva.
- Examiners value clear logic over shortcuts, and this approach often weakens conceptual explanations.
- It is best used for output formatting. It is not used for learning or demonstrating rounding fundamentals.
Solution 7: Round Down Numbers Using Operator Method
Now, if you are searching for any method that is easiest among all the other methods those are discussed above, then you have landed on the right method. It is the easiest & simplest method that is easy to remember as well.
Here, the Arithmetic Operator // will be used to get the Rounding Numbers. However, it is the only method where from the Float Number we don’t get the Integer Number. Rather, it stores another floating number with zero at the decimal point.
General Syntax: Float Number // 1
#7 Using Operator method
num = 16.23 # Assigning The Floating Number
print("The New Rounded Number Using String Format Mehtod: ", num // 1) # Rounding Off With Operator Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, the Flaot Number will be taken in the example in any variable to work on it.
Now, we will directly call the Print Function in the program & using the above syntax we will convert the whole number.
Output:
Important Student Warning: Operator Method
- The simplicity of // 1 often misleads students into assuming it always rounds correctly.
- It behaves differently for negative numbers, causing frequent exam and assignment mistakes.
- Teachers usually expect math.floor(). Any misuse can cost marks despite a correct-looking output.
Comparison Table On Different Python Rounding Methods:
From our experience, we have seen that, as there are many Python Rounding Methods, students often confuse them with their internal rules and rounding techniques.
Hence, they make mistakes in their assignments and homework. A simple comparison table on different rounding methods can help students in their exams.
Method | Logic | Negatives | Accuracy | Exam-Safe | Complexity |
round() | Nearest | Even | Medium | No | Low |
int() | Truncate | Toward-Zero | Low | Partial | Low |
trunc() | Truncate | Toward-Zero | Low | Partial | Medium |
floor() | Lowest | Correct | High | Yes | Medium |
Decimal | Precise | Correct | Very-High | Yes | High |
String Format | Convert | Unclear | Medium | No | High |
Operator (//) | Divide | Shift | Medium | No | Low |
How To Round Down Numbers Stored In Any Python Data Structure?
We have seen the process of Rounding Down Numbers that are present as Solo. However, if there is a series of numbers stored in the Data Structures like Array or List, how can we round down the numbers there? To do so, you can use any one of the above-mentioned methods.
Here, we will use the Int() Method discussed earlier. To make the demonstration live, we will use an Array or List where all the Positive & Negative Numbers are stored. So, let us have a look at the example.
store = [12.21, 22.54, 44.56, 77.66, -105.55] # Storing Numbers In Data Structure
new = [int(x) for x in store] # Converting All & Storing In New Frame
print("The New Rounded Number: ", new) # Printing Numbers
Steps Of The Program:
At first, we will take a series of numbers in the List Data Structure.
Now, using the List Comprehensive Method, we will pass all the numbers through the Int() Module as we have discussed earlier.
Now, all the new data is stored in the new list variable.
At last, we will print the list data to get the updated new values.
Output:
From the above output, we can see all the numbers are converted to the integer values by leaving the decimal tails. Even, if you notice the Negative Number at the end of the data row is also successfully converted to integers by rounding down.
How to Round Up Numbers In Python Programming Language?
At the end of the discussion, we would like to conclude with a simple program that will define the method of Rounding Up in Python language. Till now, we have learned about the Rouding Down method, now it is time to know the Rounding Up Method.
To Round Up in Python, there is only the Celi Method present under the Math Module. In this section, we will discuss the Celi Method along with the Math to get the Upper Nearest Integer Value.
General Syntax: math.celi(Float Number)
# Using Celi method
import math # Importing Math Library
num = 44.78 # Assigning The Floating Number
print("The New Rounded Number Using Celi Format Mehtod: ", math.ceil(num)) # Rounding Off With Celi Method
Steps Of The Program:
At first, the simple Module Math will be declared in the program.
Now, the Print Statement will be called in the program where using the above syntax we will convert the float value.
Output:
In this output, you might notice that the Number 45 is coming instead of the Number 44. We have provided the Number 44.78. so if it is the Round Down Method, we should get the Number 44. But as we are getting Number 45, so it is successfully using the Rounding Up Method.
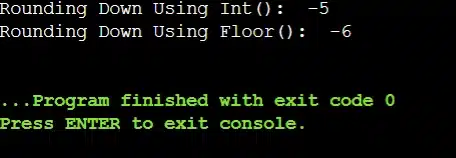
Real Assignment Question: Why does int(-5.3) give -5, but floor(-5.3) gives -6?
As a real assignment question, we have brought an infamous exam trap that is often asked in lab exams to confuse students. This confusion usually appears when students start working with negative floating-point numbers.
Students expect that all rounding down methods will behave the same with negative numbers and use int() there, which makes the code fail in Autograder. But if the floor has been used, it will be accepted.
- The int() function does not round down; it simply removes the decimal part.
- When Python sees -5.3, int() cuts off the decimal and returns -5, moving the value towards zero.
- On the other hand, math.floor() always moves the number to the nearest smaller integer, regardless of whether the number is positive or negative.
import math
num = -5.3 # A Negative Number
print("Rounding Down Using Int(): ", int(num)) # Conversion Using int()
print("Rounding Down Using Floor(): ", math.floor(num)) # Conversion Using floor()
When int(-5.3) is executed, Python cuts off .3 and moves the value towards zero, resulting in -5. The math.floor() function, however, always returns the nearest smaller integer.
Since -6 is smaller than -5.3, math.floor(-5.3) correctly returns -6.
This is why many students lose marks in exams. The int() looks like a round-down method, but it actually performs truncation, not true rounding. If negative numbers are involved and the question clearly says round down, math.floor() is the correct and safest choice.
Which Python Round Down Method Should Students Use?
The major student pain point arises after learning the entire Python Rounding Down methods. We have seen multiple times in assignments that students pick the wrong round-down methods and utilize them.
Students often ask which rounding method will be the best to use. But there is no solid answer. There is no single method that fits every situation.
The correct choice depends on what you are learning, where you are using it, and how your answer will be evaluated.
- If you want a true mathematical round-down for both positive and negative numbers, then the math.floor() is the safest and most reliable method.
- If you are only working with positive numbers and learning basic type conversion, the int() can be used with caution.
- In financial calculations or decimal precision where accuracy matters, the Decimal module is the best option.
- For exams and academic submissions, using math.floor() is recommended because it matches textbook definitions.
Why Does Python Round 0.5 to 0?
If you try rounding the Number 0.5, you will always get the Number 0 in the Python Language. Because Python follows the Round Half Strategy. In the round-half strategy, the floating number is converted to the Nearest Even Number.
In the case of 0.5, on one side there is the Number 1 and on another side, there is the Number 0. The Number 1 is not even from any angle of argument. So, the Number 0.5 is always being converted to the Number 0 while working on the Python Compiler.
So see, there are many funs & enjoyments involved to play with the Number Rounding & Python Language. So, try something new from your side to unlock some new facts by yourself.
Conclusion:
As we can see, it is very important & good to know the methods to do “Round Down Numbers in Python”.
The Rounding Down Numbers in Python generally fall under the Basic Python Umbrella. So, we would like to recommend to practice on this topic as much as possible. It will help to free your hands on the Python Language as well as increase your coding capability.
If you’re facing any issues while working on your Python coding homework, you can always get Python Homework assistance from our experts online.
Takeaways:
The Rounding in Python is generally a conversion of a Float Number to a Nearest Integer Number.
There are two different Rounding Operations are present. They are Round Up & Round Down.
If the Float Number is getting converted to the Upper Nearest Integer Number, it will be the Round-Up Operation.
If the Float Number is converted to the Lower Nearest Integer Number, it will be the Round-Down operation.
Python has a special Round() Method to work on the Round Down Process.
Other than the Round() Method, we can use other custom approaches as well.
You can convert any numbers stored in any Data Structure using any of the methods.
The Celi() is the method only used for the Python Round Up Process.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Question by Students)
For academic purposes, the safest choice is the floor() method that matches the mathematical definition and works consistently. Teachers and evaluators prefer approaches that show conceptual clarity, not shortcuts or formatting tricks.
This happens because the round() function does not mean round down in Python. Python’s round() chooses the nearest value, and in some cases, it rounds to the nearest even number instead of always moving down.
In mathematics classes, rounding rules are often simplified for learning. However, Python follows precise and standardized rules designed for programming accuracy. This behavior is mathematically correct but often different from what students are taught.