The PHP “while” loop is a simple tool that repeatedly runs a block of code as long as a certain condition remains true. It’s like saying, “Keep doing this task until a specific situation changes.”.
Table of Content
However, this loop is especially handy when we don’t know beforehand how many times we’ll need to repeat the action.
Let’s move into the section below to understand the tasks of the while loop and its syntax in PHP.
PHP While Loop Syntax
The while loop is a control structure that allows you to execute blocks of code until the condition is evaluated as true.
Additionally, it is very useful for tasks such as reading lines from a file until the end is reached or waiting for an event to occur while continually checking for its occurrence.
Here is the syntax of the while loop:
while (expression) {
// Here is the block of code
}It has two parts, which are:
- Condition: This is the Boolean part evaluated before each iteration of the loop.
- Code Block: It is the curly braces {} part that contains the repeated block of code.
Anyway, let’s see how the while loop works in PHP.
How the While Loop Works in PHP?
Check the following figure you will see the full task for the PHP while loop.
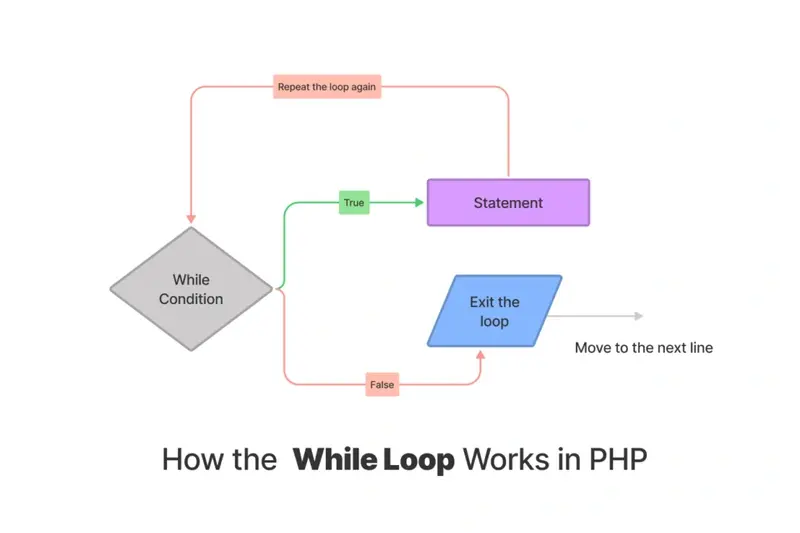
As you understood, the while is doing a loop until it reaches “false” to exit the loop, so if it is true, it will execute the statement part.
For example:
$i = 0;
While( $i < 10 ) {
echo " $i <br />";
$i++;
}The output would be like this 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
So if the condition is returning true when the $i is smaller than 10 so it will do another loop.
Each time it will do the same task, once it reaches the 10 result then it will exit the loop.
In the next section, I will focus on the one statement syntax for PHP while loop. Let’s move forward.
PHP While Infinite Loop
To execute only one line inside the while loop you have to use the following pattern in your PHP code.
while( true )
… statementThis pattern only executes the first line after the condition brace. In this syntax there are no curly braces.
For example.
while( true )
echo "CodedTag.com ";Anyway, in the following section, you will understand the embedded while loop section. Let’s get started.
Embedded PHP While Loop with HTML Markups
The embedded while loop can be worked with any code else such as JavaScript or HTML markup language.
The main pattern for this syntax can be like the following one.
<?php while( true ): ?>
// .. JavaScript, PHP, HTML, OR whatever here ..
<?php endwhile; ?>So, it executes the statement pattern according to the condition. For example.
<?php
$i = 0;
while( $i < 5 ):
?>
<h1>Welcome to CodedTag Tutorials.. </h1>
<?php endwhile; ?>That’s all, in the following section I will move to the nested while loop.
Usage of Nested While Loop
The nested while loop means that you can use while loop inside another while loop. Let’s see an example;
// This example will print the multiplication table.
$basic = 1;
while($basic <= 12 ) {
$factor = 1;
while( $factor <= 12 ) {
echo $basic . " x " . $factor . " = " . ($basic * $factor); // z x y = xyz
echo "<br />";
$factor++;
}
$basic++;
}Let’s summarize it.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, you learned about while loop and you saw many examples for it such as: Nested while loop, one statement while loop, infinite while loop with no curly braces example. Let’s summarize them in a few points.
- Nested While Loop is a while loop inside another while loop.
- One Statement While Loop showing a one single code, so there is no curly braces.
- Infinite While Loop: this indefinitely runs, typically by using a condition that always evaluates to true (
while (true)).
Thank you for reading. Happy Coding!
Similar Reads
The filter_input_array() filters multiple inputs in PHP at once. It helps you to clean and validate data. Understand the filter_input_array…
PHP added the array_map() function to help you apply one function to each item in an array. Understand the array_map…
The first appearance of PHP iterable was in PHP version ( 7.1 ) – Iterables are a powerful feature in…
The array_combine function in PHP creates a new array with one array for keys and another for values. It needs…
The PHP array_diff_ukey function compares keys in two or more arrays. It returns the keys from the first array that…
The abs() function in PHP gives you a number without its sign — it always returns a positive value. That…
PHP array_unshift helps you add new elements to appear before the existing ones. Understand the array_unshift function in PHP The…
let's now dive into PHP comments—these simple but super important integral parts of PHP coding. You can think of comments…
The array_pop function in PHP gives you a direct way to take the last element from an array. Understand the…
When working with big arrays in PHP, things can get messy. That is where php array_chunk() steps in by providing…