Before starting training for a race or project we should determine what are the demands of that event to identify the key factors we need to improve in order to perform and to build a training plan for it.
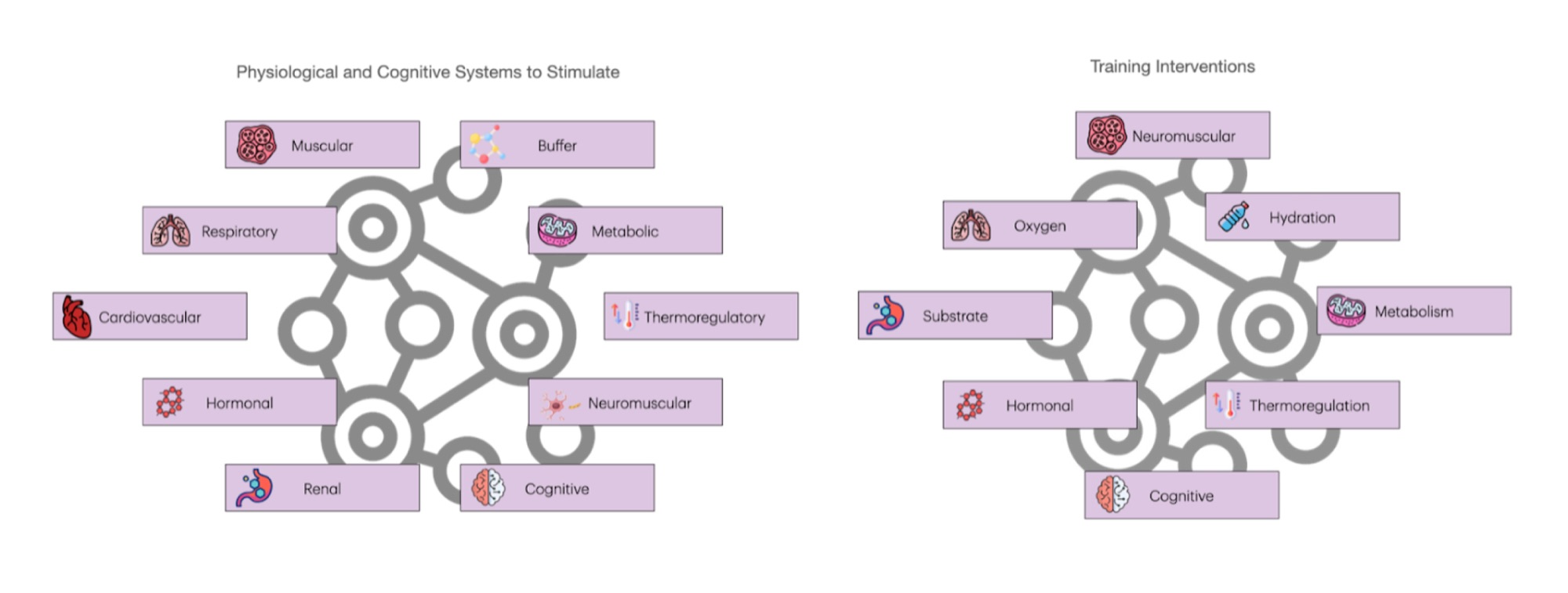
Before entering into analyzing an event is important to understand that to perform a task (doing X race in that time, climbing that summit…) there are several systems that will be activated at different levels, those systems are not working separately (such as a car or a machine) but interacting as a complex system. Those are the systems we will be targeting to modify (change its biology) to improve our output (the external load).
| System | Primary Function | Main Organs / Components | Measurements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | Deliver O₂/nutrients and remove CO₂/metabolites | Heart, blood vessels, hemoglobin | VO₂max, HR, HRV, hematocrit, hemoglobin, echocardiography |
| Respiratory | Gas exchange: O₂ uptake & CO₂ removal | Lungs, diaphragm, airways, alveoli | Spirometry (FEV1/FVC), VE, ventilatory thresholds (VT1/VT2), MIP/MEP |
| Metabolic / Bioenergetic | ATP production (fat/CHO oxidation, glycolysis) | Mitochondria, enzymes, glycogen stores | RER, substrate oxidation, lactate curve, CK/LDH, glycogen ultrasound |
| Neurological / Neuromuscular | Motor control, coordination, fatigue management | Brain, spinal cord, motor units, NMJ | EMG, TMS (central fatigue), RFD, MVIC, Myoton |
| Muscular / Mechanical | Force generation, elasticity, structural resistance | Skeletal muscle, tendons, fascia | Strength tests, jump tests, ultrasound architecture, force plates |
| Endocrine / Hormonal | Regulate energy, stress, adaptation | Hormones: cortisol, T, insulin, thyroid hormones | Cortisol/T ratio, T3/T4, insulin, HOMA-IR, catecholamines |
| Thermoregulatory | Maintain core temperature, heat dissipation | Sweat glands, skin, hypothalamus | Core temp, sweat rate, Na+ concentration, skin temp, HR drift |
| Immune | Protect from infection, repair tissues | WBCs, cytokines, mucosal immunity | Leukocyte count, CRP, IgA saliva, IL-6/TNF-α |
| Psychological / Cognitive | Perceived effort, motivation, pacing, stress | Prefrontal cortex, limbic system, pain modulation circuits | RPE, cognitive tests, mood scales (POMS), HRV, EEG (research) |
| Gastrointestinal | Nutrient/fluid absorption, GI tolerance | Stomach, intestine, microbiota | GI symptoms scoring, CHO absorption tests, H₂ breath test |
| Renal / Fluid-Electrolyte | Fluid balance, sodium regulation | Kidneys, vasopressin system | Creatinine/urea, osmolarity, serum Na+, body weight change |
| Cognitive-Motor / Economy | Efficient movement with low energy cost | CNS–muscle coordination, stiffness, biomechanics | Running economy test (O₂ cost), 3D video analysis, GCT, oscillation |
Event load: We will be assessing the external and estimating the internal load of the event.
| Category | External Load (Event Characteristics) | Internal Load (Athlete Response) | Main Systems Involved | Typical Measures for Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration | Time of event (minutes → multi-day) | Accumulated fatigue, metabolic depletion | Metabolic, cardiovascular, endocrine | Lactate drift, HR drift, CHO/fat oxidation, cortisol |
| Intensity | Pace / power requirement | HR zones, VO₂ demand, RPE | Cardiovascular, respiratory, metabolic | HR, VO₂, ventilatory thresholds, RPE |
| Elevation Gain/Loss | Total climb/descent, grade steepness | Eccentric damage, force requirements | Muscular/ mechanical, neuromuscular | Force plates, CK, Myoton, strength asymmetries |
| Altitude | Start/finish altitude, max altitude | Hypoxia stress, ventilation changes | Cardiovascular, respiratory | SpO₂, VE, hematocrit, HR at altitude |
| Technicality | Rocks, snow, exposure, scrambling | Cognitive load, stability, eccentric load | Neuromuscular, cognitive-motor | Economy tests, GCT, stiffness, EMG |
| Temperature | Heat, cold, amplitude changes | Thermoregulation stress, dehydration | Thermoregulatory, renal | Core temp, sweat rate, Na+ loss, osmolarity |
| Weather / Environmental | Wind, storms, humidity | Energy expenditure variability | Thermoregulatory, psychological | WBGT, wind-chill, hydration markers |
| Nutrition Logistics | Aid frequency, carry capacity | GI distress risk, energy availability | GI system, metabolic | CHO tolerance, GI symptom scale |
| Skills | Downhill speed, climbing, ropework | Motor pattern fatigue, coordination | Neuromuscular, cognitive | Movement economy, fatigue index |
| Decision-Making | Navigation, pacing choices | Cognitive fatigue, emotional regulation | Psychological/cognitive | Decision tests, HRV, RPE variability |
| Risk and Exposure | Avalanches, crevasses, night, isolation | Stress response, hormonal load | Endocrine, psychological | Cortisol, mood scales, reaction time |
| Other factors | Sleep deprivation, carry weight… | Cognitive decay, immune load | Cognitive, immune, hormonal | Sleep metrics, IgA, CRP, HRV |
Here you can download a table to assess the Demands of the Event
Since events in trail running are not steady (different uphills, downhills, inclines, weather… during the same event) We should analyze the demands of the event by sections, that way we will be able also to identify the key moments of the event where we need to perform the best and what is the state we will be at that moment, if we need to train more for durability, repeatability, etc.
Step 1: Fill External Load
Example:
- Duration: 4:30h (2h30 uphill, 1h downhill, 1h flat…)
- Intensity: average 167ppm, 175 at uphills (av. 30′)…
- Elevation: 5,300 m, distance and incline of every uphill and downhill
- Terrain: from 1 to 3km runnable, 3-15 rocky granite…
- Temperature: 20º start, 12º in summits, 25º last part…
- etc.
Step 2: Infer Internal Load
- High thermoregulatory strain
- 6300kcal total, in uphills 90%CHO, in downhills 60%…GI load due to heat
- Neuromuscular load from long downhills
- etc.
Step 3: Identify Systems Under Stress
- Thermoregulatory
- GI
- Neuromuscular
- Metabolic (CHO oxidation high)
- etc.
Step 4: Choose how to monitor the change you want to do.
- Vo2 / HR at race pace GAP
- Core temp, sweat rate
- GI tolerance tests
- Downhill eccentric fatigue
- Lactate drift test
- etc.
Then start planning the training for it.



Leave a Reply