Python Project – Web Crawlers
Master Programming with Our Comprehensive Courses Enroll Now!
The Web Scraper project is developed in Python using requests and BeautifulSoup libraries. It provides a simple tool to scrape titles from a specific website and saves the extracted data into a CSV file. This project demonstrates the basic principles of web scraping and data extraction.
About Python Web Crawler Project
The web crawler project automates data extraction from web pages using Python. It employs libraries like Requests for fetching pages and BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML content. Concurrency is managed with ThreadPoolExecutor for efficient parallel processing. Extracted data is stored in structured formats like CSV, facilitating further analysis and applications in data-driven tasks.
Objectives of Python Web Crawler Project
- Develop a robust web crawler to fetch and parse web pages automatically.
- Extract targeted information from HTML documents, such as titles, links, or specific content.
- Implement concurrent crawling techniques to enhance performance and speed.
- Store extracted data in a structured format for subsequent analysis or use.
Python Web Crawler Project Setup
Required Libraries
The project requires the following standard Python libraries:
- Requests: These are for making HTTP requests to fetch web pages.
- Beautiful Soup (bs4): This is used to parse HTML and XML documents to extract structured data.
- Pandas: For data manipulation and storage, they are useful for storing extracted data in tabular format.
Technology Stack
- Python
- Requests
- BeautifulSoup
Prerequisites for Python Web Crawler
- Basic understanding of Python programming.
- Familiarity with HTML and web scraping concepts.
Download Python Web Crawler Project
Please download the source code of the Python Web Crawler Project: Python Web Crawler Project Code.
Step by Step implementation of Python Web Crawler Project
1. Importing Libraries
This helps to import necessary libraries for the GUI of the Web Crawler:-
- tkinter: Used for creating the graphical user interface (GUI).
- messagebox: Provides dialog boxes for displaying messages to the user.
- requests: This is used to make HTTP requests to fetch web pages from the internet.
- BeautifulSoup: It parses HTML and XML documents.
- threading: Enables running tasks concurrently, utilized to play the alarm sound
- pandas: Used for data manipulation and analysis.
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import pandas as pd import threading
2. WebCrawler Class
- __init__ is a constructor method for the WebCrawler class.
- tk.label creates an entry widget for the user to input the URL.
- self.results create a text widget to display the crawling results.
- Finally, it adds a “Save to CSV” button that calls the save_to_csv method.
class WebCrawlerApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("PythonGeeks@Web Scraper")
tk.Label(root, text="Enter URL:").grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=5)
self.url_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=50)
self.url_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=5)
tk.Button(root, text="Start Crawling", command=self.start_crawling).grid(row=0, column=2, padx=10, pady=5)
self.results_text = tk.Text(root, width=80, height=20)
self.results_text.grid(row=1, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=10, pady=5)
3. Start Crawling Method
- This method gets the URL from the entry widget.
- Then, check if the URL is valid and non-empty.
- It starts a new thread to run the crawl method with the provided URL to avoid freezing the GUI.
def start_crawling(self):
url = self.url_entry.get().strip()
if not url:
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Please enter a URL")
return
self.results_text.delete(1.0, tk.END)
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, "Starting crawl...\n")
thread = threading.Thread(target=self.crawl, args=(url,))
4. Crawl Method
- This method clears the text widget before starting the crawl, fetching the web page using requests.get.
- It checks if the request was successful using raise_for_status, then parses the HTML content using BeautifulSoup.
- It finds all elements with the class quote and extracts the text and author for each quote.
- Finally, it stores the extracted quotes in the quotes list and displays them in the text widget.
def crawl(self, url):
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
books = self.extract_books(soup)
if books:
self.save_to_csv(books)
self.display_results(books)
else:
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, "No books were extracted.\n")
except requests.RequestException as e:
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, f"Error fetching {url}: {e}\n")
5. Extract Books Method
- books =[ ]: It initializes an empty list to store the extracted book information.
- book_elements: This uses BeautifulSoup to find all HTML elements with the class product_pod,
- For each book in book_elements, it extracts the title from the h2 element tag.
- This method returns the list of dictionaries containing book titles and prices.
def extract_books(self, soup):
books = []
book_elements = soup.select('.product_pod')
print(f"Found {len(book_elements)} book elements.")
for book in book_elements:
title = book.h3.a['title']
price = book.select_one('.price_color').get_text(strip=True)
books.append({'title': title, 'price': price})
return books
6. Save & Display Results Method
- This method checks if there are any quotes to save.
- Then, it saves the DataFrame to a CSV file quotes.csv.
- It shows a success message if the data is saved, otherwise an error message if there are no quotes to save.
def save_to_csv(self, books):
df = pd.DataFrame(books)
df.to_csv('books.csv', index=False)
def display_results(self, books):
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, "Crawl completed. Books extracted:\n")
for book in books:
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, f"Title: {book['title']}, Price: {book['price']}\n")
self.results_text.insert(tk.END, "Books saved to books.csv\n")
7. Main Execution
- root = tk.Tk(): It forms the main application window using tkinter function.
- alarm_clock = WebCrawlerApp(root): This is done to form an instance of the WebCrawlerApp class, passing root as an argument. It initializes the Crawler application
- root.mainloop(): It starts the Tkinter event loop, which listens for events and updates the GUI.
if __name__ == "__main__": root = tk.Tk() app = WebCrawlerApp(root) root.mainloop()
Python Web Crawler Output
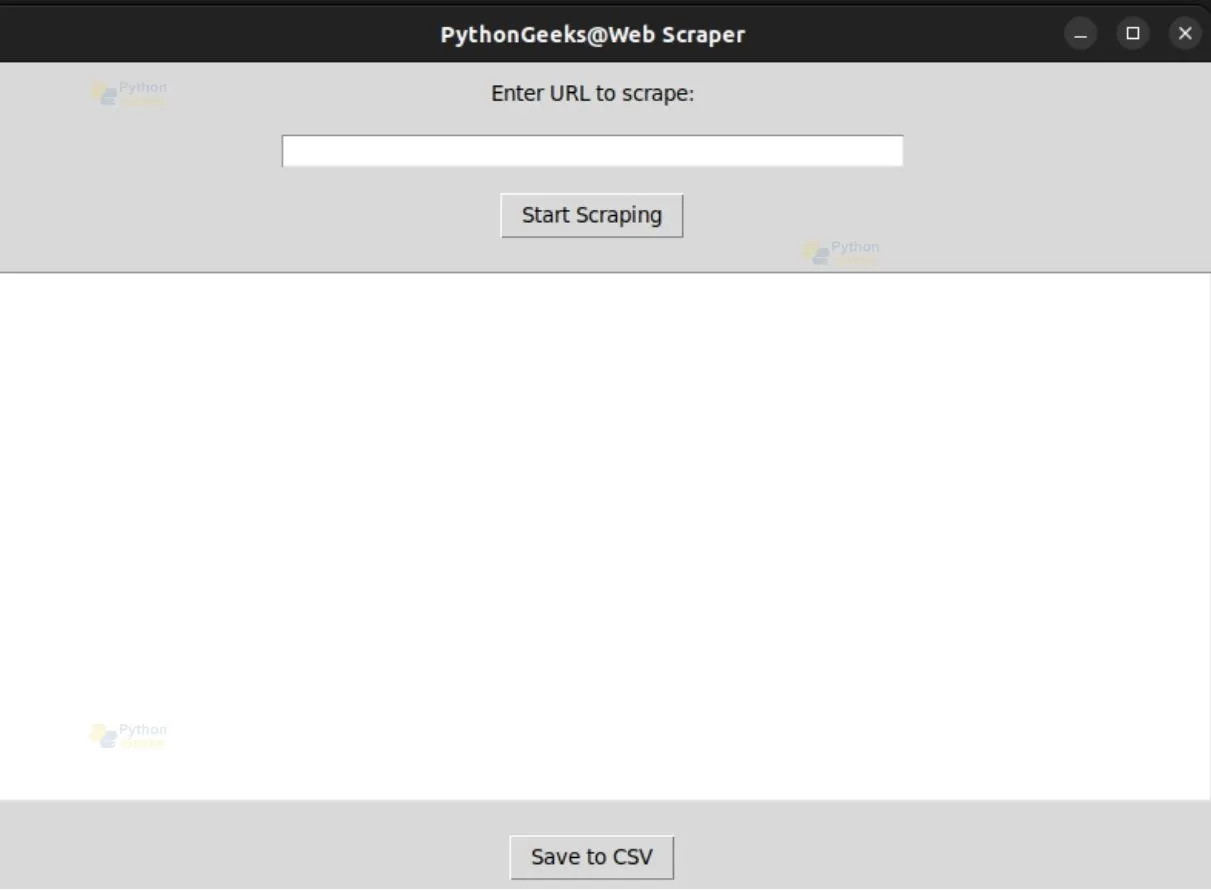
Application Interface
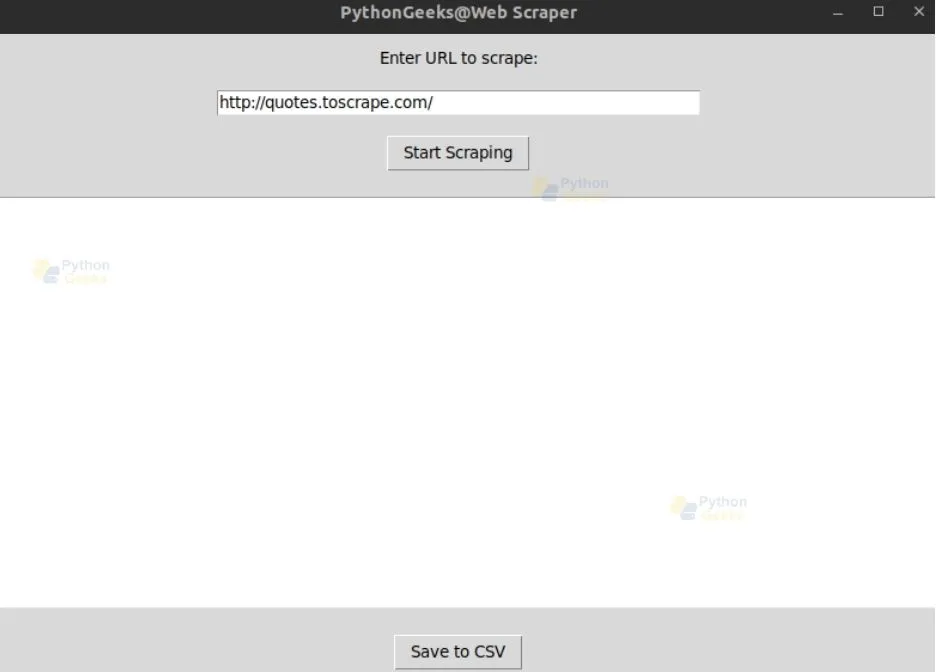
Adding URL
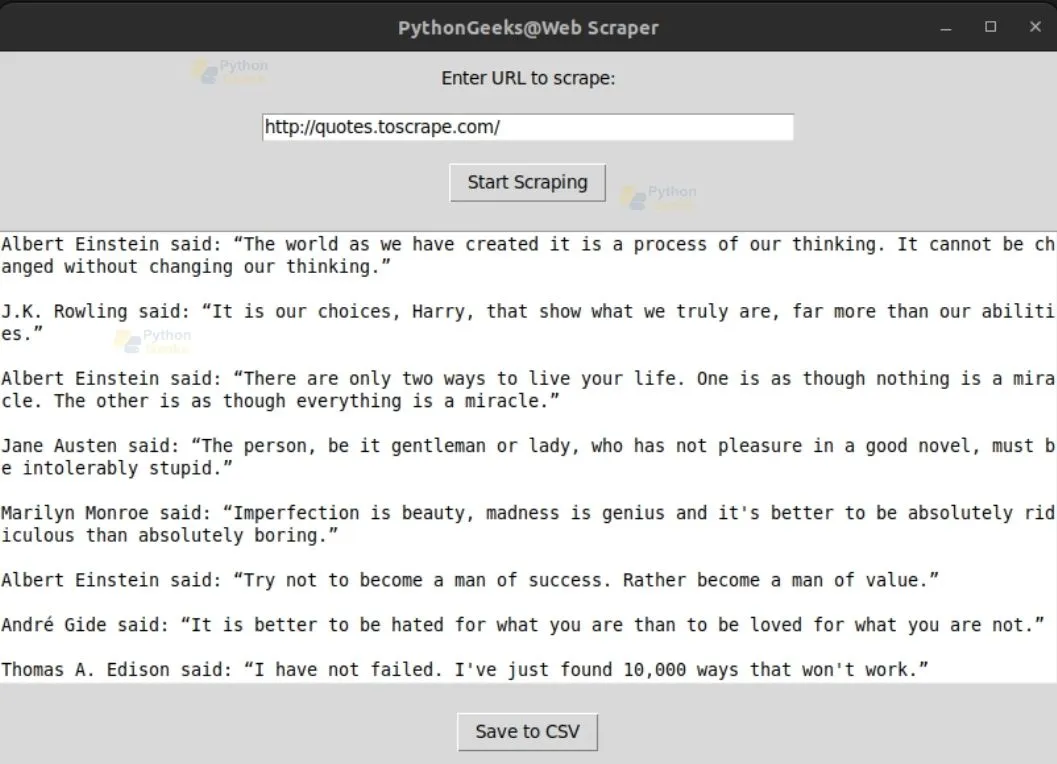
Scraping Done
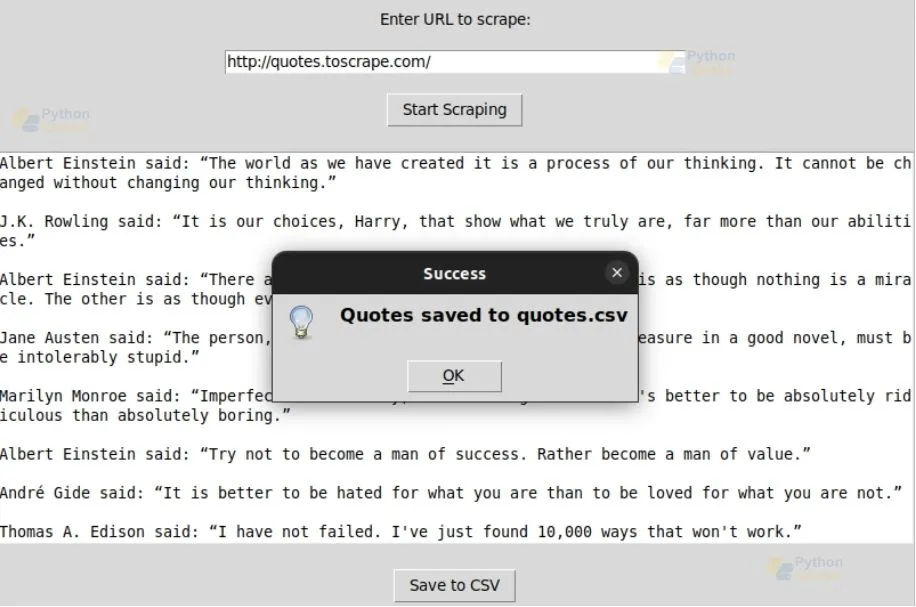
Added to CSV File
Conclusion
The Web Crawler application effectively demonstrates the integration of Tkinter and BeautifulSoup for web scraping. It provides a practical solution for extracting and managing data from web pages. This project can be further enhanced by adding features like pagination handling, more sophisticated data extraction, and improved error handling for a more comprehensive web scraping solution.