Get organic traffic from
Google & ChatGPT
Get recommended by ChatGPT & Rank on Google. Our always-on loop gets your brand visible across Google, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI and other platforms.
How RankLoop builds your AI presence
ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI don't guess — they inherit authority from the web. More content + more backlinks = stronger entity signals = more AI recommendations.
AI Answer Visibility
Each published article creates a new entity signal. More topical coverage = more chances to surface in AI answers.
Entity Trust Signals
Every backlink from a relevant site reinforces your authority. LLMs weight sources by who links to them.
AI Citation Readiness
Expanding entity coverage across related topics builds the context LLMs need to recommend you confidently.
 Site Analyzer
Site Analyzer
Analyzing site structure...
Analyzing competitors...
Fetching backlink data...
AI visibility isn't magic — it's inherited authority. Content + backlinks = entity strength = AI recommendations.
How the magical loop works
We handle content and authority so your rankings compound without manual SEO work.

Deep analysis of your business
We explore your niche, competitors, and target audience. Discover hidden keywords with high traffic potential and low competition.

Get a powerful 30-day plan
We create a strategic content plan where each day focuses on a key phrase with the highest potential for your business.

Content + backlinks on loop
We create and publish SEO-optimized articles daily. Plus, you get real backlinks from our network of niche-relevant blogs.
Feedback Loop
"I used to spend 10+ hours a week writing blog posts or paying $150/article to freelancers. Now RankLoop publishes SEO content daily without me lifting a finger. My blog finally has momentum."
"I was paying $200-400 per guest post before. Now I'm getting 15-20 contextual backlinks monthly for less than a single link used to cost. The math is a no-brainer."
"Skeptical at first — sounded too good. But the links are legit, from real blogs in my niche. My local service business now outranks the big franchises. Best SEO investment I've made."
Content We Publish On Your Blog
These are examples of articles we'd publish on YOUR site. Each post targets keywords you want to rank for and includes contextual links to niche-relevant network members — who link back to you from their posts. Every link is natural and editorially placed.
Understanding Notary Certified: A Complete Guide
 RankLoop
RankLoop
Best Spam Link Detection Tools for Blog SEO
 Will & Trust
Will & Trust
What Is a Living Trust?: Complete Guide
Best Spam Link Detection Tools for Blog SEO
View Live Article →
Spam links can destroy your blog's SEO performance faster than you might think. These low-quality, manipulative links don't just waste your time—they actively harm your search rankings and can trigger Google penalties that take months to recover from.
The good news? You don't have to manually hunt through thousands of backlinks to find the bad ones. Modern spam link detection tools use advanced algorithms to identify toxic links, analyze link quality patterns, and help you clean up your backlink profile before it damages your blog posts and SEO efforts.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the best spam link detection tools available, from enterprise-level platforms to budget-friendly options perfect for indie hackers and SaaS founders. You'll learn exactly what features to look for, how each tool approaches spam detection, and which one fits your specific needs and budget.
1. Ahrefs Site Explorer: The Gold Standard for Link Analysis
When it comes to comprehensive backlink analysis and spam detection, Ahrefs sets the industry standard. Their massive link database and sophisticated spam detection algorithms make it the go-to choice for serious SEO professionals.
Core Spam Detection Features
Ahrefs doesn't just identify spam links—it provides context for why a link might be problematic. The platform's Toxic score ranges from 0-100, with higher scores indicating more dangerous links. This scoring system considers factors like the linking domain's authority, relevance, and historical spam patterns.
The Referring domains report includes several key metrics that help identify spam:
- Domain Rating (DR): Low DR domains (0-20) often indicate spam, especially when combined with other red flags
- Traffic Value: Domains with zero organic traffic despite having backlinks often represent spam networks
- Anchor Text Distribution: Unnatural anchor text patterns that focus heavily on exact-match keywords
Advanced Filtering Capabilities
What sets Ahrefs apart is its granular filtering system. You can filter backlinks by:
- Link Type: Identify suspicious redirects, JavaScript links, or image links
- Platform: Spot links from known spam platforms like forum profiles or blog comments
- Language: Find links from irrelevant foreign language sites
- First Seen Date: Detect sudden spikes in low-quality links
Pro Tip: Use Ahrefs' "Lost Backlinks" report to identify when competitors might be using negative SEO tactics against your site. Sudden losses of high-quality links combined with gains of spam links often indicate an attack.
Real-World Application for Blog SEO
For blog owners focusing on long form content and create SEO content strategies, Ahrefs excels at identifying patterns that hurt content performance. The tool can show you when spam links are diluting the authority of your pillar content pages.
Best Use Cases:
- Large blogs with 10,000+ backlinks
- Sites that have been targeted by negative SEO
- Agencies managing multiple client sites
- Blogs in competitive niches prone to spam attacks
Pricing: Starting at $99/month for the Lite plan, with more comprehensive features in higher tiers.
2. SEMrush Backlink Audit Tool: Automated Spam Detection
SEMrush takes a more automated approach to spam link detection, making it ideal for busy marketers who need quick, actionable insights without deep manual analysis.
Smart Toxicity Scoring System
The SEMrush Backlink Audit tool automatically categorizes backlinks into three groups:
- Toxic: Links that pose immediate risk and should be disavowed
- Potentially Toxic: Links requiring manual review
- Non-Toxic: Safe links that benefit your SEO
This automated categorization saves hours of manual review, especially for sites with thousands of backlinks.
Integrated Disavow File Management
Unlike standalone analysis tools, SEMrush streamlines the entire spam link cleanup process. Once you've identified toxic links, you can:
- Generate Disavow Files: Create properly formatted disavow files directly in the platform
- Submit to Google: Upload files to Google Search Console without leaving SEMrush
- Track Progress: Monitor how disavowing affects your overall link profile health
Competitive Intelligence Features
SEMrush's unique advantage lies in competitive analysis. You can analyze competitors' backlink profiles to:
- Identify spam networks targeting your niche
- Discover if competitors are using questionable link building tactics
- Find legitimate link opportunities in your industry
Key Insight: SEMrush's competitive data helps you understand industry-wide spam patterns, which is crucial for blogs in highly competitive niches like finance, health, or technology.
Best Use Cases:
- Mid-sized blogs (1,000-10,000 backlinks)
- Content marketers managing multiple campaigns
- Businesses needing competitive intelligence
- Teams requiring collaborative workflow features
Pricing: Backlink Audit is included in all paid plans starting at $119.95/month.
3. Moz Link Explorer: User-Friendly Spam Identification
Moz Link Explorer prioritizes simplicity and actionable insights, making it perfect for beginners who need to understand spam links without getting overwhelmed by technical details.
Spam Score Algorithm
Moz's Spam score uses machine learning to analyze 17 different spam signals, providing a percentage score from 0-100%. The algorithm considers factors like:
- Domain age and registration patterns
- Content quality and thin content indicators
- Link velocity and unnatural growth patterns
- Social media presence and engagement levels
Visual Link Profile Analysis
The platform excels at presenting complex data in digestible formats:
- Link Profile Charts: Visual representations of your backlink growth over time
- Anchor Text Cloud: Quick identification of over-optimized anchor text patterns
- Top Linking Domains: Easy spotting of domains contributing the most spam links
Educational Resources and Guidance
Moz stands out for its educational approach. Each spam signal includes detailed explanations of why it matters and what actions to take. This makes it invaluable for indie hackers and SaaS founders learning SEO fundamentals.
Why It Matters: Understanding the reasoning behind spam detection helps you make better long-term decisions about your blog posts and SEO strategy, not just fix immediate problems.
Best Use Cases:
- Small to medium blogs (under 5,000 backlinks)
- SEO beginners learning link analysis
- Businesses needing clear, actionable reports
- Teams requiring educational context with data
Pricing: Link Explorer features are available in Moz Pro plans starting at $99/month.
4. Monitor Backlinks: Specialized Spam Detection
Monitor Backlinks focuses exclusively on backlink monitoring and spam detection, offering specialized features that larger platforms might overlook.
Real-Time Spam Alerts
The platform's monitoring system sends immediate notifications when:
- New spam links appear in your profile
- Previously safe domains show signs of becoming toxic
- Competitors gain or lose significant numbers of spam links
- Your disavow file needs updating
Detailed Spam Analysis Reports
Monitor Backlinks provides granular spam analysis including:
- Link Velocity Warnings: Alerts when you're gaining links too quickly
- Anchor Text Diversity: Analysis of natural vs. artificial anchor text patterns
- Geographic Relevance: Identification of links from irrelevant countries or regions
- Content Context: Analysis of the content surrounding your backlinks
White-Label Reporting
For agencies and consultants, Monitor Backlinks offers white-label reports that you can customize and send directly to clients. These reports clearly explain spam risks in non-technical language.
Expert Tip: Use Monitor Backlinks' historical data to track how your spam cleanup efforts affect your search rankings over time. This data proves ROI to stakeholders and helps refine your approach.
Best Use Cases:
- Agencies managing multiple client accounts
- Businesses requiring continuous monitoring
- Sites in high-risk industries (gambling, pharmaceuticals, loans)
- Teams needing white-label reporting capabilities
Pricing: Plans start at $25/month for basic monitoring, with advanced features in higher tiers.
5. Cognitive SEO: AI-Powered Spam Detection
Cognitive SEO leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify spam patterns that traditional tools might miss, making it particularly effective for complex spam networks.
Advanced AI Algorithms
The platform's AI system analyzes multiple data points simultaneously:
- Content Similarity: Identifies networks of sites with duplicate or spun content
- Link Pattern Recognition: Detects artificial link building patterns across domains
- Behavioral Analysis: Spots coordinated linking campaigns and PBN networks
- Historical Pattern Matching: Compares current links against known spam databases
Network Analysis Capabilities
Cognitive SEO excels at uncovering complex spam networks by:
- Mapping Link Relationships: Visualizing connections between suspicious domains
- Identifying PBN Footprints: Finding private blog networks through shared hosting, registrars, or IP addresses
- Cross-Referencing Data: Comparing link patterns across multiple sites to identify coordinated attacks
Comprehensive Competitor Analysis
The platform provides deep insights into competitor link building strategies, helping you:
- Identify if competitors are using spam tactics
- Discover legitimate opportunities in your niche
- Understand industry-wide spam trends
- Protect your site from common attack vectors
Key Takeaway: Cognitive SEO's AI approach is particularly valuable for detecting sophisticated spam operations that use rotating domains, varied anchor texts, and other techniques designed to evade traditional detection methods.
Best Use Cases:
- Large enterprises with complex link profiles
- Sites frequently targeted by sophisticated spam attacks
- Competitive industries with advanced negative SEO tactics
- Businesses needing detailed forensic analysis
Pricing: Custom pricing based on site size and feature requirements, typically starting around $200/month.
6. LinkResearchTools: Comprehensive Risk Assessment
LinkResearchTools (LRT) offers the most comprehensive spam detection suite available, with over 25 different tools focused specifically on link risk assessment and cleanup.
Multi-Tool Spam Detection Suite
LRT's approach involves multiple specialized tools working together:
- Link Detox: Core spam detection with risk scoring
- Link Detox Boost: Identifies your best links for protection during cleanups
- CEMPER Power Trust: Measures link authority and trustworthiness
- Link Alerts: Real-time monitoring for new spam links
DTOX Risk Assessment
The platform's proprietary DTOX system provides the most nuanced spam scoring available:
- Risk Levels: From DTOX 0 (safe) to DTOX 5 (highly toxic)
- Multiple Risk Factors: Analyzes over 100 different spam signals
- Industry-Specific Scoring: Adjusts risk assessment based on your niche
- Historical Context: Considers how long domains have been problematic
Professional Cleanup Services
For businesses lacking internal SEO expertise, LRT offers professional link cleanup services where their experts:
- Analyze your complete backlink profile
- Identify all spam and toxic links
- Create optimized disavow files
- Monitor recovery progress
Pro Tip: LRT's "Link Detox Boost" tool is invaluable during cleanup campaigns—it identifies your highest-value links so you don't accidentally disavow beneficial backlinks during bulk cleanup operations.
Comparison of Key Features
| Tool | Best For | Spam Detection Method | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahrefs | Large sites, agencies | Toxic Score + manual analysis | Largest link database |
| SEMrush | Mid-size sites, automation | Automated toxicity scoring | Integrated workflow |
| Moz | Beginners, education | 17-factor Spam Score | User-friendly interface |
| Monitor Backlinks | Continuous monitoring | Real-time alerts | Specialized monitoring |
| Cognitive SEO | Complex networks | AI pattern recognition | Advanced network analysis |
| LinkResearchTools | Enterprise, professionals | Multi-tool DTOX system | Most comprehensive analysis |
Best Use Cases:
- Enterprise websites with millions of backlinks
- Sites that have suffered major Google penalties
- Agencies offering professional cleanup services
- Businesses in highly competitive, spam-prone industries
Pricing: Plans start at €249/month, with enterprise options available.

7. Google Search Console: The Free Foundation
While not as sophisticated as paid tools, Google Search Console provides essential spam detection capabilities that every blog owner should utilize as a foundation for their link monitoring strategy.
Built-in Link Analysis Features
Google Search Console offers several free tools for basic spam detection:
- Links Report: Shows your most linked pages and linking domains
- Manual Actions: Alerts you to Google-identified spam issues
- Security Issues: Notifications about hacked content or malware
- Core Web Vitals: Performance metrics that can be affected by spam
Disavow File Submission
The platform provides the official method for disavowing spam links:
- Create Disavow File: Format toxic domains and URLs according to Google's specifications
- Submit Through Search Console: Upload files directly to Google's disavow tool
- Monitor Processing: Track when Google processes your disavow requests
- Update as Needed: Add new spam links to existing disavow files
Limitations and Supplementary Needs
While free and authoritative, Google Search Console has significant limitations:
- Limited Historical Data: Only shows recent link data
- No Spam Scoring: Doesn't automatically identify toxic links
- Basic Filtering: Limited ability to segment and analyze link types
- Delayed Updates: Link data can be weeks behind actual link discovery
Why It Matters: Google Search Console should be your starting point for spam detection, but it needs to be supplemented with more sophisticated tools for comprehensive protection. Think of it as your early warning system rather than your complete solution.
Best Use Cases:
- Budget-conscious small blogs
- Starting point for spam detection strategy
- Official disavow file submission
- Monitoring Google's perspective on your links
Pricing: Free with Google account
8. Majestic SEO: Trust Flow and Citation Flow Analysis
Majestic SEO takes a unique approach to spam detection by focusing on Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics, providing insights into link quality that complement traditional spam scoring methods.
Trust Flow vs Citation Flow Analysis
Majestic's dual-metric system helps identify spam through quality imbalances:
- Citation Flow: Measures link quantity and popularity
- Trust Flow: Measures link quality based on proximity to trusted sites
- Trust Ratio: The relationship between these metrics reveals spam patterns
Sites with high Citation Flow but low Trust Flow often indicate spam networks or manipulative link building.
Topical Trust Flow
This advanced feature analyzes whether your backlinks come from topically relevant sources:
- Category Matching: Links from relevant industries carry more weight
- Spam Network Detection: Identifies generic link farms that link to unrelated topics
- Content Quality Assessment: Evaluates the editorial quality of linking pages
Historical Link Analysis
Majestic maintains one of the largest historical link databases, allowing you to:
- Track link quality changes over time
- Identify when domains became spammy
- Analyze competitor link building patterns
- Understand long-term trends in your niche
Expert Insight: Majestic's historical data is invaluable for understanding how spam networks evolve. Many domains start legitimate but become spam over time—historical analysis helps you identify these transitions.
Best Use Cases:
- Sites needing topical relevance analysis
- Businesses in trust-sensitive industries (finance, health, legal)
- Long-term SEO strategy planning
- Academic or research-focused content sites
Pricing: Plans start at $49.99/month for Lite, with more features in higher tiers.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Spam Detection Tools
Selecting the right spam link detection tool depends on several critical factors that align with your blog's specific needs and resources.
Database Size and Coverage
The comprehensiveness of a tool's link database directly impacts its spam detection accuracy:
- Fresh Data: How quickly does the tool discover new links?
- Historical Coverage: Can you analyze link patterns over time?
- Global Reach: Does it cover international domains relevant to your audience?
- Update Frequency: How often is the database refreshed?
Accuracy and False Positives
Different tools have varying accuracy rates for spam detection:
- Algorithm Sophistication: How many factors does the spam scoring consider?
- Industry Training: Is the algorithm trained on your specific niche?
- Manual Override Options: Can you adjust scores based on your knowledge?
- Explanation Transparency: Does the tool explain why links are flagged?
Integration and Workflow
Consider how the tool fits into your existing SEO workflow:
- API Access: Can you integrate data into your own systems?
- Export Capabilities: What formats are available for data export?
- Team Collaboration: Can multiple users access and share data?
- Reporting Automation: Can you schedule regular spam monitoring reports?
Budget and Scalability
Spam detection tools range from free to enterprise-level pricing:
- Feature Scaling: What features are available at different price points?
- Usage Limits: Are there restrictions on domains, links, or queries?
- Contract Flexibility: Can you adjust plans as your needs change?
- ROI Justification: How quickly will spam cleanup pay for the tool cost?
Key Takeaway: The best spam detection tool is the one you'll actually use consistently. A simpler, more affordable tool used regularly is better than an advanced tool used sporadically.

Common Spam Link Patterns to Watch For
Understanding common spam patterns helps you identify threats regardless of which detection tool you use. These patterns remain consistent across different tools and industries.
Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
PBNs represent one of the most sophisticated spam threats:
- Shared Infrastructure: Multiple domains on the same hosting, IP ranges, or registrars
- Template Similarities: Sites using identical themes, plugins, or layouts
- Cross-Linking Patterns: Unnatural linking between network sites
- Content Duplication: Recycled or spun content across domains
Comment and Forum Spam
These high-volume, low-quality links are easy to spot but can overwhelm your profile:
- Generic Anchor Text: "Great post!" or "Thanks for sharing" type comments
- Irrelevant Contexts: Links from discussions unrelated to your content
- User Profile Links: Links from forum signatures or profile pages
- Automated Patterns: Multiple links posted within short timeframes
Directory and Bookmark Spam
Low-quality directories remain a common spam vector:
- No Editorial Standards: Directories accepting any submission without review
- Reciprocal Link Requirements: Directories requiring backlinks for inclusion
- Thin Content: Directory pages with minimal content beyond links
- Geographic Irrelevance: Local directories from unrelated locations
Negative SEO Attacks
Competitors might target your site with intentional spam:
- Sudden Link Spikes: Rapid increases in low-quality backlinks
- Exact-Match Anchor Text: Over-optimized anchor text targeting your keywords
- Adult or Gambling Links: Links from inappropriate industries
- Foreign Language Spam: Links from irrelevant foreign language sites
Pro Tip: Document sudden changes in your link profile with screenshots and dates. This evidence helps Google understand that spam links were not your choice if you need to file a reconsideration request.
Best Practices for Ongoing Spam Monitoring
Effective spam detection requires ongoing vigilance rather than one-time audits. Implementing systematic monitoring practices protects your blog posts and SEO efforts from long-term damage.
Establish Regular Monitoring Schedules
Create a consistent monitoring routine based on your site's risk level:
- High-Risk Sites: Weekly monitoring for competitive niches or previously penalized sites
- Medium-Risk Sites: Bi-weekly or monthly monitoring for established blogs
- Low-Risk Sites: Quarterly monitoring for new or low-profile sites
- Post-Campaign Monitoring: Daily monitoring after major content campaigns or PR efforts
Set Up Automated Alerts
Most tools offer alert systems that notify you of significant changes:
- New Spam Links: Immediate alerts for toxic links appearing in your profile
- Link Velocity Changes: Notifications when link acquisition suddenly increases
- Competitor Activity: Alerts when competitors gain or lose significant links
- Tool Updates: Notifications when spam detection algorithms change
Create Documentation Systems
Maintain detailed records of your spam detection and cleanup efforts:
- Link Audit Logs: Document which links you've reviewed and when
- Disavow File History: Track changes to your disavow files over time
- Tool Comparison Notes: Record differences in how tools score the same links
- Recovery Tracking: Monitor how cleanup efforts affect your search performance
Develop Response Protocols
Create standardized procedures for different types of spam discoveries:
- Immediate Threats: High-toxicity links requiring urgent disavowal
- Suspicious Patterns: Links requiring further investigation before action
- Competitor Analysis: Process for analyzing competitor spam tactics
- Client Reporting: Standardized reports for agencies managing multiple sites
Expert Tip: Create a "spam link database" where you track problematic domains across all your sites or clients. This helps you quickly identify repeat offenders and patterns across different properties.
Conclusion
Protecting your blog from spam links requires the right combination of tools, knowledge, and consistent monitoring practices. Whether you choose the comprehensive analysis of Ahrefs, the automation of SEMrush, or the specialized monitoring of dedicated platforms, the key is selecting tools that match your specific needs and actually using them regularly.
Remember that spam detection is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix. The digital landscape constantly evolves, with new spam networks emerging and existing ones becoming more sophisticated. By implementing the tools and strategies outlined in this guide, you'll build a robust defense system that protects your blog posts and SEO investments from both current and future spam threats.
For SaaS founders and indie hackers focused on building sustainable organic traffic, investing in proper spam detection tools pays dividends by protecting the anchor text SEO and long form content strategies that drive business growth. Ready to take control of your link profile? Get started with RankLoop to implement these spam detection strategies effectively and protect your SEO investments for the long term.
Understanding Notary Certified: A Complete Guide
View Live Article →
Understanding the role of a certified notary is essential for professionals across various sectors, especially those in law firms and title agencies. Whether you're dealing with real estate transactions or legal documents, knowing what it means to be notary certified can significantly impact your operations. In this guide, we'll explore the intricate world of certified notaries, how the certification process works, and its importance in today's digital age.
What Is a Certified Notary?
A certified notary, or notary public, is a state-appointed official responsible for witnessing the signing of important documents and verifying the identity of the signers. This role ensures that the signers are who they claim to be and that they understand the content of the document they are signing. The certification is crucial for legal documents to be considered valid and enforceable.

Key Insight: A certified notary acts as a neutral third party, ensuring the integrity of transactions by preventing fraud and coercion.
The History and Evolution of Notaries
The concept of notaries dates back to ancient Rome, where they served as scribes, recording public proceedings. Over time, their role evolved into the modern-day notary public, recognized across the United States as a vital part of legal and business transactions.
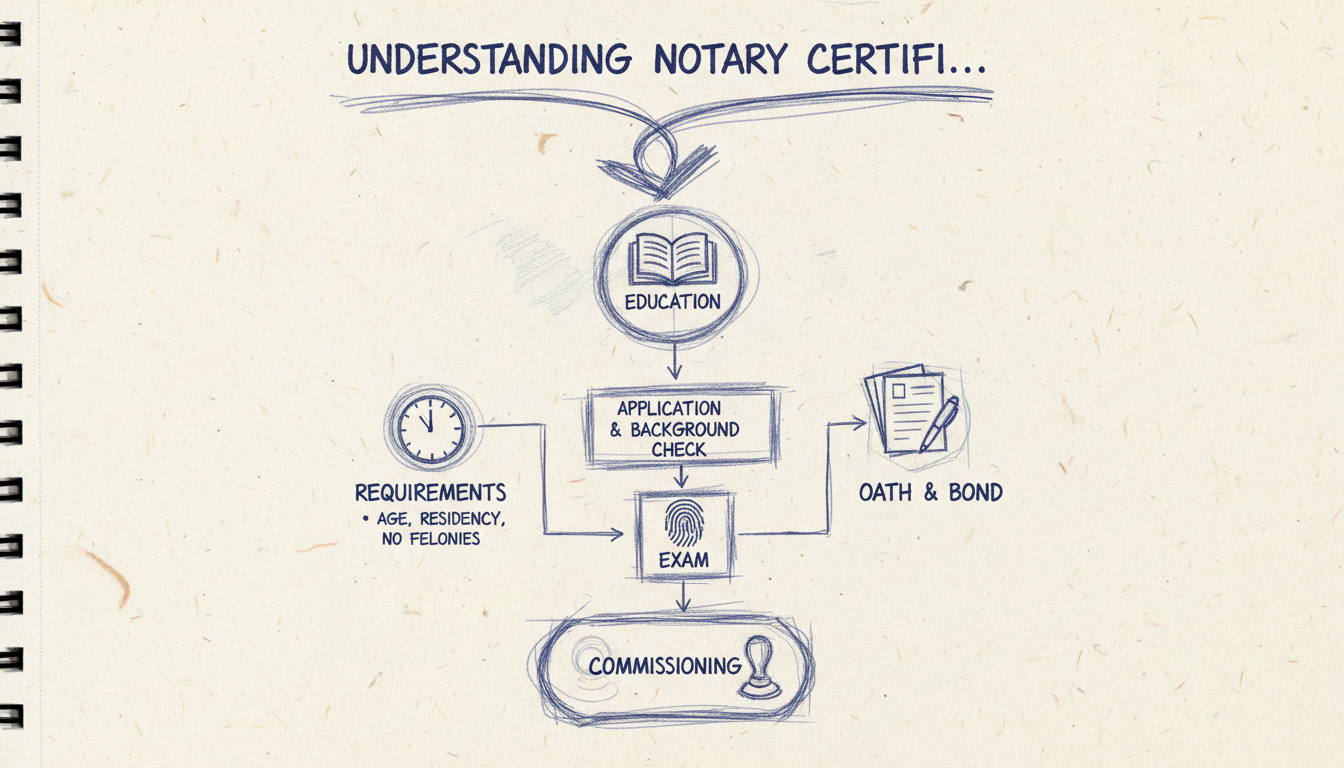
How Certification Works
The process of becoming a notary certified professional varies by state but generally involves several key steps. Understanding this process can help law firms and title agents better utilize notary services.
- Application and Background Check: Aspiring notaries must submit an application to their state's commissioning authority, usually the Secretary of State. A background check ensures the applicant's integrity and suitability for the role.
- Training and Exam: Many states require prospective notaries to undergo training, which covers notary laws, ethics, and procedures. An exam may also be necessary to demonstrate knowledge and competency.
- Oath of Office: Successful candidates must take an oath of office, pledging to perform their duties with honesty and integrity.
- Bonding and Insurance: Notaries often need to purchase a surety bond and may opt for additional insurance to protect against errors or omissions.
Pro Tip: Ensure your notary is properly bonded and insured to minimize risks associated with document errors.
Key Components of Notary Certification
Understanding the components of notary certification can help you choose the right notary services for your needs.
- Notarial Certificate: A statement completed by the notary that includes the details of the notarization, such as the date, location, and type of act performed.
- Notary Seal and Signature: A unique seal and signature authenticate the document, proving it was notarized by an official notary.
- Record Keeping: Notaries must maintain a journal of their notarial acts, providing a detailed record for future reference if disputes arise.
Why It Matters: Proper record-keeping by notaries can provide crucial evidence if a notarized document's validity is ever questioned.
Benefits and Use Cases
Notary certification provides several benefits that enhance the reliability and legality of important documents.
- Fraud Prevention: The presence of a certified notary helps prevent document fraud by verifying identities and ensuring signers are willing participants.
- Legal Compliance: Notarized documents are often required for legal proceedings, making notary certification essential for compliance.
- Convenience: Online notary platforms like BlueNotary allow documents to be notarized remotely, offering convenience without compromising security.
Key Takeaway: Using a certified notary ensures that your documents are legally sound and can withstand scrutiny in legal contexts.
Common Misconceptions About Notary Certification
Misunderstandings about notary certification can lead to ineffective or improper use of these services. Let's clear up some common misconceptions.
- Not All Documents Require Notarization: Not every document needs to be notarized. Generally, notarization is required for documents that carry legal weight, such as affidavits or deeds.
- Notaries Are Not Lawyers: While notaries are knowledgeable about document authentication, they are not authorized to provide legal advice unless they are also licensed attorneys.
- Online Notarization Is Not Less Secure: Contrary to some beliefs, online notarization is as secure as traditional methods, thanks to technologies like identity verification and digital certificates.
Common Questions About Notary Certified
What Documents Commonly Require Notary Certification?
Documents that often require notarization include real estate deeds, affidavits, powers of attorney, and loan documents. Each document type has specific legal implications, making notarization crucial for enforcing these documents in court.
Can a Notary Refuse to Notarize a Document?
Yes, a notary can refuse to notarize a document if the signer does not have proper identification, if the document appears suspicious, or if the signer seems coerced or incapable of understanding the document.
How Does Online Notarization Work?
Online notarization, available through platforms like BlueNotary, allows documents to be notarized via a secure online session. This method uses video conferencing, identity verification, and digital signatures to ensure the process's integrity.
What Are the Legal Implications of Notary Errors?
Errors made by a notary, such as failing to verify a signer's identity, can render a document invalid and lead to legal disputes. Notaries should adhere strictly to their state's guidelines to avoid such consequences.
How Do I Become a Certified Notary?
The process involves application, background check, training, and passing an exam. Requirements vary by state, so it's essential to check your local regulations.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of a certified notary is crucial for anyone involved in handling legal documents. Whether for real estate, legal, or business transactions, notary certification ensures that your documents meet all legal requirements. Ready to get started? Get Started with BlueNotary to learn more and ensure your documents are in good hands.
What Is a Living Trust?: Complete Guide
View Live Article →
Estate planning can feel overwhelming, but a living trust is one of the most practical tools you can use to protect your assets and simplify things for your loved ones. Unlike a will that only takes effect after death, a living trust starts working immediately while you're alive and continues seamlessly after you're gone.
A living trust is a legal arrangement where you transfer ownership of your assets to a trust that you control during your lifetime. Think of it as creating a protective container for your property—you put your house, bank accounts, and investments into the trust, but you still manage everything exactly as you did before. The key difference is that when you pass away, your chosen successor trustee can immediately step in and distribute your assets according to your wishes, without the delays and costs of probate court.
Why It Matters: A living trust can save your family months of probate proceedings and thousands in court fees while keeping your financial affairs private.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about living trusts. You'll learn exactly how they work, when they make sense, and how to decide if one is right for your situation. Whether you're a law firm advising clients or an estate planner exploring options, you'll find practical insights and clear explanations that cut through the legal jargon.
What Is a Living Trust?
A living trust, also known as a revocable living trust, is a legal document that creates a separate entity to hold and manage your assets during your lifetime and after your death. The person who creates the trust (called the grantor or settlor) typically serves as the initial trustee, maintaining complete control over all trust assets while alive and mentally capable.
The fundamental concept is straightforward: instead of owning assets in your individual name, you transfer ownership to the trust. However, since you're the trustee, you retain all the same rights and powers you had before. You can buy, sell, refinance, or manage trust assets exactly as you could when you owned them directly.
The Three Key Roles in a Living Trust
Understanding a living trust requires knowing the three essential roles involved:
The Grantor (Settlor): This is the person who creates and funds the trust. The grantor establishes the terms, decides which assets to include, and sets the rules for how assets should be managed and distributed. In most cases, the grantor also serves as the initial trustee.
The Trustee: This person or institution manages the trust assets according to the grantor's instructions. During the grantor's lifetime, the grantor typically serves as trustee, maintaining complete control. Upon the grantor's death or incapacity, a successor trustee takes over to carry out the grantor's wishes.
The Beneficiary: These are the people or organizations who will ultimately receive the trust assets. During the grantor's lifetime, the grantor is usually the primary beneficiary, receiving all income and having access to principal as needed. After death, the remainder beneficiaries (often children or other family members) receive their designated shares.
Key Insight: The same person often fills multiple roles initially. You create the trust (grantor), manage it (trustee), and benefit from it (beneficiary) during your lifetime.
How Living Trusts Differ From Wills
While both living trusts and wills are estate planning tools, they work in fundamentally different ways. A will is a set of instructions that only takes effect after death, requiring probate court supervision to ensure proper execution. The probate process typically takes 6-18 months and involves court fees, attorney costs, and public disclosure of your assets and beneficiaries.
A living trust, by contrast, operates like a private contract between you and your chosen successor trustee. When you die, your successor trustee can immediately access trust assets and begin distributions according to your instructions—no court involvement required. This privacy and efficiency make living trusts particularly attractive for people who want to minimize the burden on their families.
The "Revocable" Nature Explained
The term "revocable" means you can change, modify, or completely dissolve the trust at any time during your lifetime, as long as you're mentally competent. This flexibility is crucial because life circumstances change. You might want to add new assets, change beneficiaries, or adjust distribution terms. With a revocable living trust, these modifications are straightforward.
However, this revocable nature has tax implications. Since you retain complete control, the IRS treats trust assets as if you still own them individually. You report all trust income on your personal tax return using your Social Security number—no separate trust tax return is required during your lifetime.
How a Living Trust Works
The mechanics of a living trust center on a legal concept called the "transfer of title." When you create a living trust, you're essentially creating a new legal entity that can own property. The next step involves changing the ownership of your assets from your individual name to the name of the trust.
This process, called "funding the trust," is where many people get confused or make mistakes. Simply creating the trust document isn't enough—you must actually transfer ownership of your assets to make the trust effective. For real estate, this means executing and recording new deeds. For bank accounts, you'll need to change the account ownership or beneficiary designations. For investment accounts, you'll work with your broker to retitle the accounts in the trust's name.
The Day-to-Day Reality of Living With a Trust
Once your assets are properly transferred, daily life continues virtually unchanged. If you're the trustee (which is typical), you manage trust assets with the same authority you had as individual owner. You can buy and sell investments, refinance your mortgage, or open new accounts. The main difference is that legal documents will show the trust as owner rather than your individual name.
For example, instead of owning your home as "John Smith," the deed would show ownership as "John Smith, Trustee of the John Smith Living Trust dated January 15, 2024." This change in title is what enables the trust to function, but it doesn't affect your day-to-day control or use of the property.
What Happens During Incapacity
One of the most valuable features of a living trust becomes apparent if you become unable to manage your affairs due to illness or injury. Your successor trustee can immediately step in to handle trust assets without requiring court-appointed guardianship or conservatorship proceedings.
This seamless transition is particularly important for complex financial situations. If you own rental properties, have ongoing business interests, or maintain multiple investment accounts, your successor trustee can continue managing these assets according to your written instructions. The alternative—having a court appoint someone to manage your affairs—is typically more expensive, time-consuming, and restrictive.
Pro Tip: Choose your successor trustee carefully and ensure they understand your financial situation and wishes. Consider naming both a primary and backup successor trustee in case your first choice is unable to serve.
The Death Benefit Distribution Process
When the grantor dies, the living trust's most significant advantages become apparent. The successor trustee can immediately access trust assets and begin the distribution process according to the trust terms. There's no waiting for probate court approval, no need to publish notices in newspapers, and no requirement to file detailed inventories with the court.
The successor trustee's responsibilities include collecting trust assets, paying final debts and taxes, and distributing remaining assets to beneficiaries. While this process still takes time—typically 6-12 months for tax reasons—it proceeds privately and efficiently compared to probate administration.
Trust Administration After Death
The successor trustee must handle several important tasks after the grantor's death. First, they'll need to obtain multiple certified copies of the death certificate and notify relevant financial institutions about the death. Banks, brokers, and insurance companies will require proof of the successor trustee's authority, typically provided by the trust document and death certificate.
Next, the successor trustee must identify and value all trust assets, pay outstanding debts, and handle final tax obligations. Even though living trusts avoid probate, they don't eliminate tax responsibilities. The successor trustee may need to file final income tax returns for the deceased grantor and possibly estate tax returns if the estate is large enough.
Key Components of a Living Trust
A comprehensive living trust document contains several essential elements that work together to create a complete estate plan. Understanding these components helps you evaluate whether a living trust meets your specific needs and ensures you're prepared for the trust creation process.
Trust Declaration and Terms
The foundation of any living trust is the declaration section, which formally establishes the trust's existence and outlines its basic parameters. This section identifies the grantor, names the initial and successor trustees, and states the trust's primary purposes. The declaration also specifies whether the trust is revocable or irrevocable, though most living trusts are revocable during the grantor's lifetime.
The terms section contains the detailed instructions for how trust assets should be managed and distributed. These provisions can be simple or complex, depending on your family situation and goals. For straightforward estates, the terms might simply direct that all assets go to a surviving spouse, then to children in equal shares. More complex situations might include specific bequests, charitable donations, or ongoing trusts for minor children.
Trustee Powers and Responsibilities
A well-drafted living trust includes comprehensive provisions outlining the trustee's powers and responsibilities. These provisions are crucial because they determine what actions the trustee can take without seeking court approval. Broad trustee powers typically include the authority to buy and sell assets, manage investments, operate businesses, make distributions, and handle tax matters.
The trust document should also address trustee compensation, which varies based on the complexity of the trust administration and local customs. Some families prefer that trustees serve without compensation, particularly when family members serve in this role. Others provide for reasonable fees based on time spent or a percentage of trust assets.
Distribution Provisions
The distribution provisions represent the heart of your living trust—they specify who gets what and when. These provisions can be immediate (distributing everything outright upon your death) or extended over time. Many parents with minor children include provisions that hold assets in continuing trusts until children reach certain ages or milestones.

Distribution provisions can also include discretionary language that gives trustees flexibility to make distributions based on beneficiaries' needs. This approach is particularly useful when beneficiaries have different financial circumstances or when you want to provide for unexpected future needs like education, healthcare, or emergencies.
Incapacity Planning Features
Modern living trusts include detailed provisions for managing assets if the grantor becomes incapacitated. These provisions typically specify how incapacity is determined (usually requiring written statements from one or more physicians) and outline the successor trustee's responsibilities during this period.
The incapacity provisions should address ongoing financial obligations like mortgage payments, insurance premiums, and living expenses. They might also include specific instructions about healthcare decisions, though these are often handled through separate healthcare directives and powers of attorney.
Expert Tip: Include clear standards for distributions during incapacity, such as maintaining your accustomed standard of living or providing for healthcare needs. Vague language can create confusion for successor trustees.
Comparison of Trust Components
| Component | Purpose | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Declaration | Establishes trust existence | Must clearly identify all parties and trust type |
| Asset Schedule | Lists trust property | Should be updated as assets change |
| Distribution Terms | Specifies who gets what | Balance simplicity with specific family needs |
| Trustee Powers | Defines management authority | Broader powers provide more flexibility |
| Incapacity Provisions | Handles disability scenarios | Include clear standards for decision-making |
| Administrative Terms | Covers ongoing operations | Address accounting, tax filing, and record-keeping |
The administrative provisions handle the practical aspects of trust operation, including requirements for accounting to beneficiaries, tax return filing, and record-keeping. These provisions might seem mundane, but they're essential for smooth trust administration and can prevent disputes among family members.
Benefits and Use Cases for Living Trusts
Living trusts offer several compelling advantages that make them attractive for many estate planning situations. However, these benefits come with costs and complexity that aren't necessary for everyone. Understanding when living trusts provide the most value helps you make an informed decision about whether this tool fits your circumstances.
Probate Avoidance: The Primary Benefit
The most significant advantage of a living trust is avoiding probate court proceedings for trust assets. Probate is the court-supervised process of validating wills, paying debts, and distributing assets after death. While probate serves important purposes, it's also public, time-consuming, and expensive.
In many states, probate costs can reach 3-7% of the estate's total value when you factor in court fees, attorney costs, executor fees, and other administrative expenses. For a $500,000 estate, this could mean $15,000-$35,000 in probate costs that could otherwise go to beneficiaries. A living trust eliminates these costs for trust assets, though some administrative expenses remain.
The time savings can be equally important. Probate typically takes 6-18 months, during which assets are generally frozen and unavailable to beneficiaries. With a living trust, the successor trustee can begin managing and distributing assets immediately after death, providing much faster access to needed funds.
Privacy Protection
Probate proceedings are public records, meaning anyone can access court files to see what you owned, who inherited your assets, and details about your family relationships. This public disclosure concerns many people, particularly those with significant wealth, family conflicts, or simply a preference for privacy.
Living trusts operate privately, without court supervision or public filing requirements. Your trust terms, asset values, and beneficiary information remain confidential between you, your trustee, and your beneficiaries. This privacy extends to ongoing trust administration—if your trust continues for minor children or other purposes, those details also remain private.
Why It Matters: Privacy isn't just about keeping financial information confidential. Public probate records can expose family disputes, reveal business relationships, and even create security risks for beneficiaries who inherit significant assets.
Incapacity Planning Advantages
A properly funded living trust provides seamless asset management if you become unable to handle your affairs due to illness or injury. Your successor trustee can immediately step in to manage trust assets according to your written instructions, without requiring court-appointed guardianship or conservatorship.
This advantage is particularly valuable for complex financial situations. If you own rental properties, operate a business, or maintain multiple investment accounts, your successor trustee can continue managing these assets without interruption. The alternative—court-appointed management—typically involves ongoing court supervision, regular reporting requirements, and restrictions on asset management decisions.
Multi-State Property Management
If you own real estate in multiple states, a living trust can significantly simplify estate administration. Without a trust, your estate might require separate probate proceedings in each state where you own property—a process called "ancillary probate." Each probate proceeding involves separate attorney fees, court costs, and administrative delays.
A living trust eliminates the need for multiple probate proceedings because the trust, not you individually, owns the out-of-state property. Your successor trustee can manage and distribute real estate in any state according to the trust terms, without additional court proceedings.
Specific Use Cases Where Living Trusts Excel
Blended Families: Living trusts provide excellent tools for managing complex family situations, such as second marriages where each spouse has children from previous relationships. Trust provisions can ensure that a surviving spouse is provided for during their lifetime while ultimately preserving assets for the deceased spouse's children.
Business Owners: If you own a business, a living trust can provide continuity of management and ownership succession. Trust provisions can specify how business interests should be managed during incapacity and how ownership should transfer after death, potentially avoiding disruption to business operations.
Parents with Minor Children: Living trusts allow parents to establish ongoing management for inherited assets until children reach appropriate ages. Rather than children inheriting assets outright at age 18 (as typically happens with wills), trust provisions can extend management until children are 25, 30, or older.
High-Net-Worth Individuals: Wealthy individuals often use living trusts as the foundation for more sophisticated estate planning strategies. The trust can be structured to work with other tools like life insurance trusts, charitable trusts, or family limited partnerships to achieve tax and wealth transfer goals.

Geographic Considerations
Living trusts provide particular value in states with expensive or inefficient probate systems. States like California, New York, and Florida have probate procedures that can be costly and time-consuming, making trust benefits more pronounced. Conversely, states with simplified probate procedures and lower costs may make the trust vs. probate decision less clear-cut.
The decision also depends on your state's specific trust and probate laws. Some states have adopted streamlined probate procedures for smaller estates, while others have enacted laws that make trust administration more efficient. Working with local estate planning professionals helps ensure you understand the specific advantages in your jurisdiction.
Common Misconceptions About Living Trusts
Despite their popularity, living trusts are surrounded by misconceptions that can lead to poor decision-making or unrealistic expectations. Understanding these myths helps you evaluate whether a living trust truly fits your situation and ensures you have realistic expectations about what trusts can and cannot accomplish.
Myth: Living Trusts Eliminate All Taxes
One of the most persistent misconceptions is that living trusts provide significant tax advantages. During your lifetime, a revocable living trust provides no tax benefits whatsoever. Since you retain complete control over trust assets, the IRS treats them as if you still own them individually. You report all trust income on your personal tax return using your Social Security number—there's no separate trust tax return required.
After death, living trusts don't eliminate estate taxes for large estates. The federal estate tax exemption (over $12 million per person as of recent years) applies equally whether assets pass through probate or through a trust. State estate taxes, where applicable, also apply to trust assets just as they would to probate assets.
The confusion often stems from mixing up revocable living trusts with other types of trusts that do provide tax benefits. Irrevocable trusts, charitable trusts, and certain specialized trusts can offer tax advantages, but these come with significant restrictions and loss of control that most people aren't willing to accept.
Myth: You Don't Need a Will If You Have a Living Trust
While a comprehensive living trust can handle most of your estate planning needs, you still need a will—called a "pour-over will"—to work alongside your trust. This will serves several important functions that the trust cannot handle directly.
First, the pour-over will covers any assets you forgot to transfer to the trust or acquired shortly before death. Even the most diligent trust funding can miss items, and the will ensures these assets eventually make it to your trust for distribution according to your wishes.
Second, the will handles important appointments that trusts cannot address. If you have minor children, your will is where you nominate guardians to care for them if both parents die. The will also typically contains your funeral and burial instructions, though these can be included in separate documents.
Key Takeaway: Think of your will and living trust as working together, not as competing alternatives. The will handles what the trust cannot, while the trust manages the bulk of your assets more efficiently.
Myth: Living Trusts Are Only for Wealthy People
Many people believe living trusts are only worthwhile for millionaires, but this isn't necessarily true. While wealthy individuals certainly benefit from trusts, middle-class families can also find significant value, particularly in states with expensive probate procedures.
The key factors aren't just the size of your estate, but also its complexity and your family situation. A family with $300,000 in assets spread across multiple accounts, retirement plans, and real estate might benefit more from a living trust than a wealthy person whose assets are primarily in joint accounts or beneficiary-designated retirement plans.
The cost-benefit analysis depends on your specific circumstances. In states with expensive probate procedures, even modest estates can justify the cost of creating and maintaining a living trust. In states with streamlined probate procedures, the benefits might not outweigh the costs unless you have other compelling reasons for wanting a trust.
Myth: Living Trusts Protect Assets From Creditors
During your lifetime, a revocable living trust provides no creditor protection whatsoever. Since you retain complete control over trust assets, creditors can reach them just as easily as if you owned them in your individual name. This includes protection from lawsuits, bankruptcy proceedings, or other financial difficulties.
Some people confuse revocable living trusts with asset protection trusts, which are specialized irrevocable trusts designed specifically to shield assets from creditors. These trusts require giving up significant control over assets and are typically only appropriate for people facing specific liability risks or those with substantial wealth to protect.
After your death, living trust assets may have some protection from your beneficiaries' creditors, depending on how the trust is structured and your state's laws. However, this protection is limited and shouldn't be the primary reason for creating a living trust.
Myth: Living Trusts Are Too Complicated for Average Families
While living trusts are more complex than simple wills, they're not beyond the understanding of typical families. The key is working with experienced professionals who can explain the concepts clearly and help you understand your ongoing responsibilities as trustee.
The complexity primarily lies in the initial setup and ongoing maintenance, not in the day-to-day operation. Once properly established and funded, most people find that managing trust assets is virtually identical to managing individually-owned assets. The main difference is ensuring that new assets are titled in the trust's name and keeping beneficiary information current.
The perceived complexity often stems from marketing materials that either oversimplify trusts ("avoid all taxes and probate!") or overcomplicate them with unnecessary legal jargon. Working with qualified professionals who can explain trusts in plain English helps demystify the process and ensure you understand what you're creating.
Best Practices for Living Trust Success
Creating a living trust is just the beginning—successful trust planning requires ongoing attention and proper maintenance. These best practices help ensure your trust accomplishes your goals and avoids common pitfalls that can undermine its effectiveness.
Proper Trust Funding: The Critical First Step
The most common mistake in living trust planning is failing to properly fund the trust by transferring assets into it. A beautifully drafted trust document is worthless if your assets remain in your individual name. This process, called trust funding, requires changing the legal ownership of your assets from your name to the trust's name.
For real estate, funding requires preparing and recording new deeds that transfer ownership from you individually to you as trustee of your trust. The deed might change from "John Smith" to "John Smith, Trustee of the John Smith Living Trust dated January 15, 2024." This process typically requires working with an attorney or title company to ensure the transfer is properly documented and recorded.
Bank and investment accounts require working with each financial institution to either retitle accounts in the trust's name or change beneficiary designations to the trust. Some institutions prefer to retitle accounts, while others recommend keeping accounts in your individual name but naming the trust as the beneficiary. Either approach can work, but consistency and documentation are important.
Pro Tip: Create a comprehensive list of all your assets and work systematically through the funding process. Don't try to fund everything at once—focus on major assets first, then handle smaller items over time.
Ongoing Maintenance Requirements
Living trusts require regular maintenance to remain effective. As your life changes, your trust should be updated to reflect new circumstances. Major life events that typically trigger trust reviews include marriage, divorce, births, deaths, significant changes in wealth, and moves to different states.
Asset retitling is an ongoing responsibility that many people overlook. When you open new bank accounts, purchase real estate, or acquire other significant assets, these should be titled in the trust's name from the beginning. Failing to maintain proper titling can result in assets being subject to probate despite having a living trust.
Beneficiary designations on retirement accounts, life insurance policies, and other assets should be coordinated with your trust planning. While these assets might not be owned by the trust directly, their beneficiary designations should align with your overall estate plan to avoid conflicts or unintended results.
Choosing and Preparing Successor Trustees
Selecting the right successor trustee is one of the most important decisions in trust planning. This person will have significant responsibilities and authority, so choose someone who is trustworthy, organized, and capable of handling financial matters. Consider both primary and backup successor trustees in case your first choice is unable or unwilling to serve.
Geographic considerations matter when choosing successor trustees. While modern technology makes remote trust administration possible, having a trustee who lives near beneficiaries or major assets can be advantageous. However, don't compromise on trustworthiness and competence for geographic convenience.
Prepare your chosen successor trustees by explaining your trust provisions, sharing information about your assets and advisors, and ensuring they understand their responsibilities. Consider providing them with copies of important documents and contact information for your attorney, accountant, and financial advisors.
Professional Team Coordination
Successful living trust planning typically involves coordinating with multiple professionals, including attorneys, accountants, financial advisors, and insurance agents. Each professional should understand how their services fit into your overall trust strategy to ensure consistent advice and implementation.
Your attorney should draft trust documents that reflect your specific goals and family situation, not just use generic forms. They should also help with the initial funding process and provide guidance on ongoing maintenance requirements.
Your accountant should understand the tax implications of your trust structure and help ensure proper tax reporting during your lifetime and after death. While living trusts don't require separate tax returns during the grantor's lifetime, proper record-keeping is still important.
Financial advisors should understand how trust ownership affects investment management and beneficiary planning. Some investment strategies or products may work differently when owned by a trust rather than individually.
Documentation and Record-Keeping
Maintain comprehensive records of your trust planning, including the original trust document, amendments, funding documentation, and correspondence with professionals. These records will be essential for your successor trustees and beneficiaries.
Consider creating a trust administration manual that explains your trust structure, lists all assets and their locations, provides contact information for advisors, and includes any special instructions for your successor trustees. This document can be invaluable during incapacity or after death.
Keep beneficiaries informed about the trust's existence and general provisions, even if you don't share all details. This advance communication can prevent surprises and conflicts later, particularly if your trust includes provisions that beneficiaries might not expect.

Common Questions About Living Trusts
How Much Does It Cost to Set Up a Living Trust?
The cost of creating a living trust varies significantly based on your location, the complexity of your situation, and the professional you work with. Simple living trusts for straightforward situations might cost $1,500-$3,000, while complex trusts for blended families or significant wealth can cost $5,000-$10,000 or more.
These upfront costs should be weighed against the potential savings in probate costs and the other benefits trusts provide. In states with expensive probate procedures, a living trust can easily save more than its creation cost, even for modest estates. However, in states with streamlined, inexpensive probate, the cost-benefit analysis might favor simpler planning approaches.
Don't forget about ongoing costs, including periodic trust updates, tax return preparation after death, and potential trustee fees. While these costs are typically modest, they should be factored into your decision-making process.
Can I Modify or Revoke My Living Trust?
Yes, revocable living trusts can be modified or completely revoked at any time during your lifetime, as long as you're mentally competent. This flexibility is one of the key advantages of revocable trusts over irrevocable alternatives.
Modifications can range from simple changes like updating beneficiary information to major revisions of distribution provisions. Minor changes are typically handled through trust amendments, while major overhauls might require restating the entire trust. Your attorney can advise on the best approach for your specific changes.
If you decide to revoke your trust entirely, you'll need to transfer all assets back to your individual name and notify relevant parties about the change. While revocation is possible, it's relatively uncommon once people understand how trusts work and experience their benefits.
What Happens If I Forget to Fund My Trust?
Unfunded or partially funded trusts are unfortunately common, and they can significantly undermine your estate planning goals. Assets that remain in your individual name will be subject to probate despite having a living trust, defeating one of the primary purposes of trust planning.
However, all is not lost if you forget to fund certain assets. Your pour-over will can direct unfunded assets to your trust, though they'll still go through probate first. This process takes longer and costs more than proper funding, but it ensures assets ultimately reach your intended beneficiaries according to your trust terms.
The best approach is prevention through systematic funding and ongoing maintenance. Work with your attorney to create a comprehensive funding plan and review your asset titling regularly to ensure everything remains properly funded.
Do Living Trusts Work in All States?
Living trusts are recognized and enforceable in all 50 states, though specific laws and procedures vary by jurisdiction. If you move to a different state after creating your trust, the trust remains valid, but you should have it reviewed by an attorney in your new state to ensure it complies with local laws and takes advantage of local benefits.
Some states have more favorable trust laws than others, particularly regarding trustee powers, creditor protection, and administration procedures. If you're considering a move or spend significant time in multiple states, these differences might influence your trust planning strategy.
Multi-state property ownership is one area where living trusts provide particular benefits. A properly drafted trust can own real estate in multiple states without requiring separate probate proceedings in each jurisdiction, significantly simplifying estate administration.
How Do Living Trusts Affect Retirement Accounts?
Retirement accounts like 401(k)s and IRAs have special rules that affect how they work with living trusts. While you can name your trust as the beneficiary of retirement accounts, this approach isn't always optimal and requires careful consideration of the tax implications.
When individuals inherit retirement accounts, they can often stretch distributions over their lifetime, minimizing current taxes and maximizing long-term growth. When trusts inherit retirement accounts, the distribution options may be more limited, potentially accelerating tax obligations.
However, naming a trust as retirement account beneficiary can make sense in certain situations, such as when beneficiaries are minors, have special needs, or have creditor protection concerns. The key is working with knowledgeable professionals who understand both trust law and retirement account regulations.
Can Living Trusts Help With Medicaid Planning?
Revocable living trusts provide no protection from Medicaid spend-down requirements because you retain complete control over trust assets. For Medicaid eligibility purposes, trust assets are treated exactly the same as individually-owned assets.
Some people confuse revocable living trusts with Medicaid asset protection trusts, which are specialized irrevocable trusts designed specifically to help preserve assets while qualifying for Medicaid benefits. These trusts require giving up control over assets and have strict timing requirements, but they can be effective tools for long-term care planning.
If Medicaid planning is a concern, work with an attorney who specializes in elder law and understands both Medicaid regulations and trust planning. The rules are complex and change frequently, making professional guidance essential for effective planning.
Conclusion
A living trust can be a powerful estate planning tool that provides privacy, avoids probate, and ensures smooth asset management during incapacity. However, it's not the right solution for everyone, and success depends on proper setup, funding, and ongoing maintenance.
The decision to create a living trust should be based on your specific circumstances, including your state's probate laws, the complexity of your assets, your family situation, and your personal preferences for privacy and control. While living trusts offer significant benefits for many families, simpler planning approaches might be more appropriate for others.
The key is working with qualified professionals who can help you understand your options and create a comprehensive estate plan that fits your unique needs. Whether that plan includes a living trust, a simple will, or other planning tools, the important thing is taking action to protect your family and ensure your wishes are carried out.
Ready to explore whether a living trust is right for your situation? Will & Trust provides comprehensive resources and professional guidance to help you make informed estate planning decisions that protect your family's future.
Simple pricing
- 30 blog posts/mo
- ~20 backlinks/mo
- AI visibility tracking
- Automated content
- Full transparency
- DR, anchor, target visible
- No PBNs or per-link fees
Why SEO still sucks (and why RankLoop exists)
Google and AI assistants like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI all pull from the same source: the web. To show up in search results AND get recommended by LLMs, you need two things: quality content and authority signals. The old way of getting there? Still completely broken.
😵 Link building is broken
Cold outreach. Begging bloggers. Paying $300+ for a single link. Sketchy marketplaces. PBNs that get you penalized. It's exhausting, expensive, and doesn't scale.
🤖 AI changed the game
ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other LLMs recommend brands they find across trusted sources. More high-quality content + more backlinks = more authority = more AI visibility. The playbook is the same — but the stakes are higher.
🚀 RankLoop runs the loop for you
We publish content on your blog. That content links to other members. Their content links back to you. The loop spins continuously — building authority that Google AND AI assistants recognize.
Frequently Asked Questions
Everything you need to know about RankLoop.
How does the backlink exchange work?
RankLoop is a network of real blogs. We publish content on your blog that includes contextual links to other niche-relevant members' sites. In exchange, their blogs publish content that links back to you. Every link is editorially placed within relevant content — exactly how Google says links should work. No spam, no link farms, no footprints.
What content gets published on my blog?
We analyze your niche and target keywords to create SEO-optimized blog posts that help you rank. Each article is long-form, well-researched, and relevant to your site's topic. The posts include contextual links to other network members — this is how you "give" links in the exchange. In return, similar posts on other members' blogs link back to you.
Where do my backlinks come from?
Your backlinks come from other members' blogs in the RankLoop network — real businesses in related niches. We use entity-based matching to pair you with topically relevant sites, so every link appears naturally within content that makes sense. This is white-hat link building aligned with Google's guidelines: real sites, relevant context, editorial placement.
How many backlinks will I get per month?
On average, members receive ~20 backlinks per month from other blogs in the network. The exact number depends on how many members are in your niche and network activity. As the network grows, everyone gets more links.
Can I see where my backlinks are placed?
Yes. RankLoop provides full transparency on every backlink—you'll see the placement URL, domain rating (DR), anchor text, target page, and link type. Everything is tracked in your dashboard.
What happens if I want to cancel?
You can cancel anytime. There are no long-term contracts or cancellation fees. Your content and backlinks remain on the network sites—you just stop receiving new ones after cancellation.