The Future interface is a part of java.util.concurrent package, introduced in Java 5. It represents the result of an asynchronous computation, a value that will be available in the future after the task completes.
- Future interface used to check the status of a task (completed, running, or cancelled).
- It allows retrieving the result of a Callable once it’s done.
- Supports cancellation of tasks that are still running.
Declaration
public interface Future<V>
Here, V -> The type of result returned by the asynchronous computation.
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class GFG{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// Create an ExecutorService
ExecutorService executor
= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// Define a Callable task
Callable<Integer> task = () ->
{
System.out.println("Processing...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return 10 * 5;
};
// Submit the task and get a Future object
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(task);
// Check if task is done
System.out.println("Task completed? "
+ future.isDone());
// Retrieve the result
System.out.println("Result: " + future.get());
// Check again
System.out.println("Task completed? "
+ future.isDone());
// Shutdown the executor
executor.shutdown();
}
}
Output:
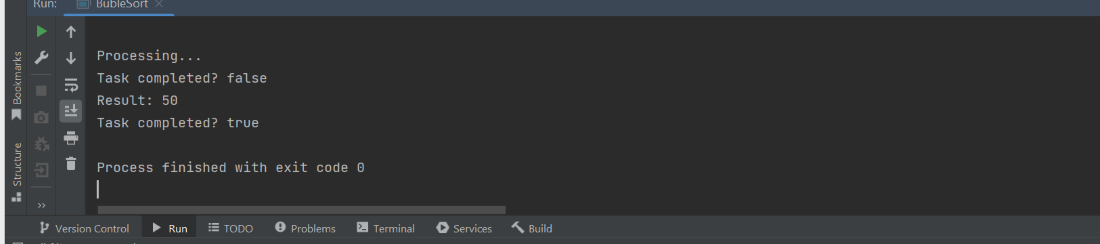
Explanation:
- A single-threaded executor is created to run a task.
- The task sleeps for 1 second and returns 50.
- Before completion, isDone() returns false.
- After the result is retrieved using get(), it returns true.
- Finally, the executor is shut down.
Methods of Future Interface
- cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning): Cancels the execution of the task if possible.
- isCancelled(): Returns true if the task was cancelled before completion.
- isDone(): Returns true if the task is completed or cancelled.
- V get(): Waits (if needed) and returns the computed result.
- V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit): Waits up to the given time and returns the result if available.
Example: Canceling a Task
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ExecutorService executor
= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Callable<String> task = () ->
{
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "Task Completed";
};
Future<String> future = executor.submit(task);
// Cancel the task before it finishes
boolean cancelled = future.cancel(true);
System.out.println("Task cancelled? " + cancelled);
executor.shutdown();
}
}
Output:
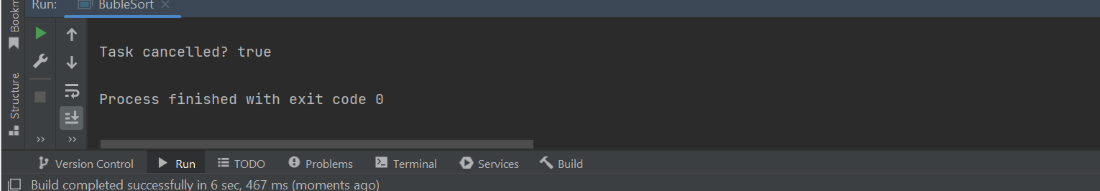
Callable vs Future
| Feature | Callable | Future |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Represents a task that returns a result | Represents the result of an asynchronous task |
| Return Type | Returns a result when executed | Holds the result of the Callable |
| Execution | Submitted to ExecutorService | Returned by ExecutorService.submit() |
| Methods | Has one method — call() | Has methods like get(), isDone(), cancel() |
| Usage | Defines what to execute | Controls and monitors the task execution |