The SQL CASE statement is used to add conditional logic inside SQL queries. It checks conditions one by one and returns a value as soon as a matching condition is found.
- Works like an IF-THEN-ELSE statement inside SQL.
- Helps categorize data or transform values dynamically.
- Can be used in SELECT, UPDATE, ORDER BY, and other clauses.
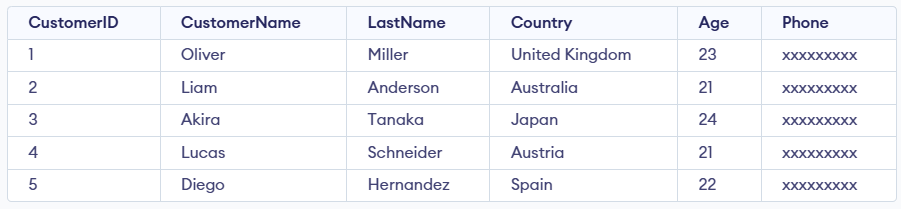
Example: First, we create a demo SQL table, on which we use the CASE statement.
Query:
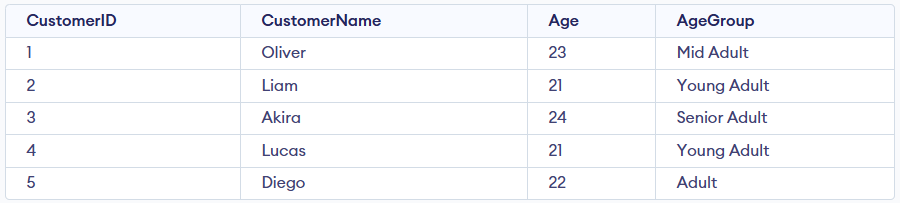
SELECT CustomerID, CustomerName, Age,
CASE Age
WHEN 21 THEN 'Young Adult'
WHEN 22 THEN 'Adult'
WHEN 23 THEN 'Mid Adult'
WHEN 24 THEN 'Senior Adult'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END AS AgeGroup
FROM Customer;
Output:
Syntax:
CASE case_value
WHEN value1 THEN result1
WHEN value2 THEN result2
...
ELSE result
END
- Compares a column or expression with fixed values.
- Returns the result of the first matching value.
CASE
WHEN condition1 THEN result1
WHEN condition2 THEN result2
...
ELSE result
END
- Evaluates multiple logical conditions.
- Returns the result of the first true condition.
Working with the CASE Statement
The SQL CASE statement allows conditional logic in queries by returning different values based on specified conditions.
Example 1: Simple CASE Expression
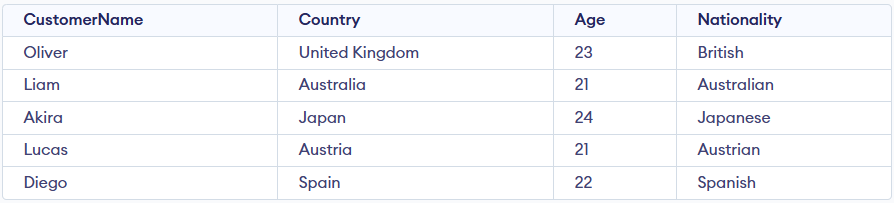
This demonstrates how conditional rules are applied to return a nationality based on each customer’s country.
Query:
SELECT CustomerName, Country, Age,
CASE
WHEN Country = 'United Kingdom' THEN 'British'
WHEN Country = 'Australia' THEN 'Australian'
WHEN Country = 'Japan' THEN 'Japanese'
WHEN Country = 'Austria' THEN 'Austrian'
WHEN Country = 'Spain' THEN 'Spanish'
ELSE 'Other'
END AS Nationality
FROM Customers;
Output:
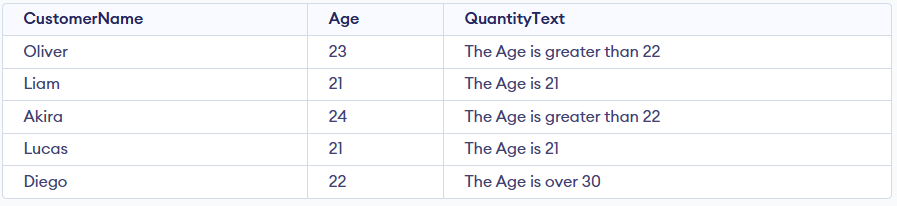
Example 2: SQL CASE When Multiple Conditions
We can add multiple conditions in the CASE statement by using multiple WHEN clauses.
Query:
SELECT CustomerName, Age,
CASE
WHEN Age> 22 THEN 'The Age is greater than 22'
WHEN Age = 21 THEN 'The Age is 21'
ELSE 'The Age is over 30'
END AS QuantityText
FROM Customer;
Output:
Example 3: CASE Statement With ORDER BY Clause
The Customer table contains fields like CustomerID, CustomerName, LastName, Country, Age, and Phone, and its data can be arranged using the ORDER BY clause together with the CASE statement.
Query:
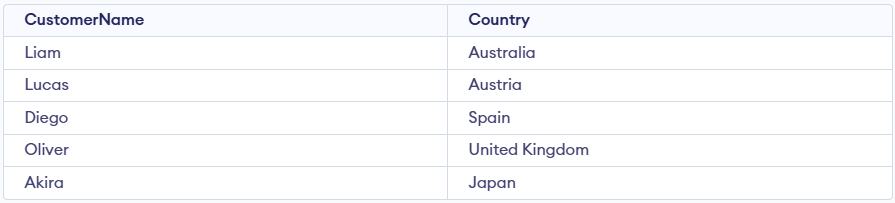
SELECT CustomerName, Country
FROM Customer
ORDER BY
(CASE
WHEN Country IS 'India' THEN Country
ELSE Age
END);
Output: