The SQL DELETE statement is used to remove specific rows from a table while keeping the table structure intact. It is different from DROP, which deletes the entire table.
- It removes rows based on conditions.
- Retains table schema, constraints, and indexes.
- Can delete a single row or all rows.
Example: First, we create a demo SQL database and table, on which we will use the SQL DELETE command.
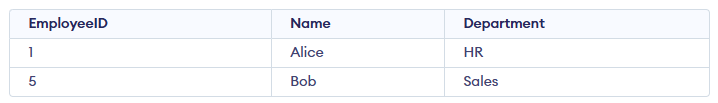
Query:
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeID = 5; Output:
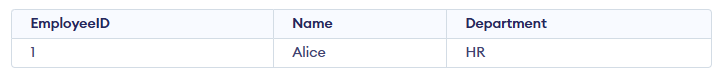
- This query deletes the row from the Employees table where the EmployeeID is 5.
- Only that specific record is removed; all other rows remain unchanged.
Syntax:
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE some_condition;- Some_condition: A condition used to filter the rows you want to delete.
- table_name: The name of the table from which you want to delete the rows.
Note: We can delete single or multiple records using the WHERE clause; if it’s omitted, all records in the table are removed.
Working with the DELETE Statement
Consider the Employee table in SQL, which stores employee details such as id, name, email, and department, as shown below.
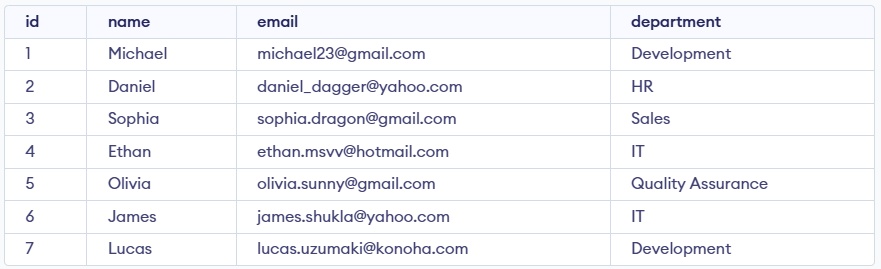
Example 1: Deleting Single Record
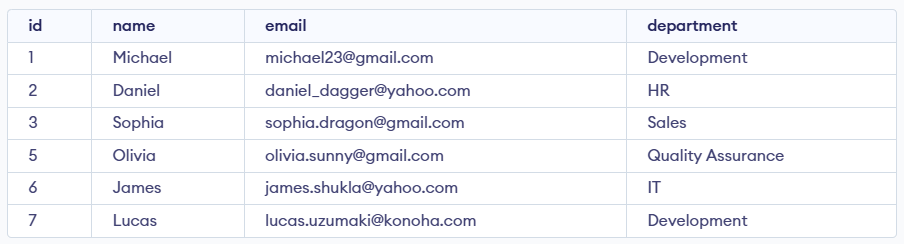
We can use the DELETE statement with a condition to delete a specific row from a table. The WHERE clause ensures only the intended record is removed. We can delete the records named Ethan by using the below query:
Query:
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE NAME = 'Ethan';SELECT * FROM Employees;Output:
Example 2: Deleting Multiple Records
To delete multiple records, you can specify a condition that matches several rows. Let's delete the rows from the table Employees where the department is "Development". This will delete 2 rows (the first row and the seventh row).
Query:
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE department = 'Development'; SELECT * FROM Employees;Output
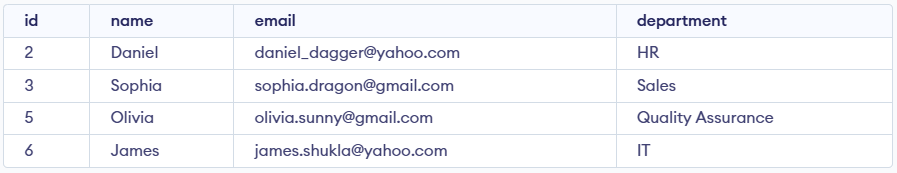
Example 3: Delete All Records from a Table
If we need to delete all records from the table, we can omit the WHERE clause, or alternatively use the DELETE statement with an asterisk (*) to denote all rows.
Query:
DELETE FROM Employees;
Output:
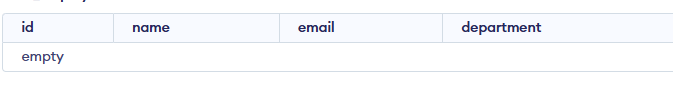
All of the records in the table will be deleted, there are no records left to display. The table Employees will become empty.
Rolling Back DELETE Operations
Since the DELETE statement is a DML operation, it can be rolled back when executed in a statement. If you accidentally delete records or need to repeat the process, you can use the ROLLBACK command.
Query:
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
DELETE FROM Employees;
WHERE department = 'Development';
-- If needed, you can rollback the deletion
ROLLBACK;Explanation: The ROLLBACK command will undo the changes made by the DELETE statement, effectively restoring the records that were deleted during the transaction.
