Our Products
Our Brands
Markets
Capabilities
About Pexco
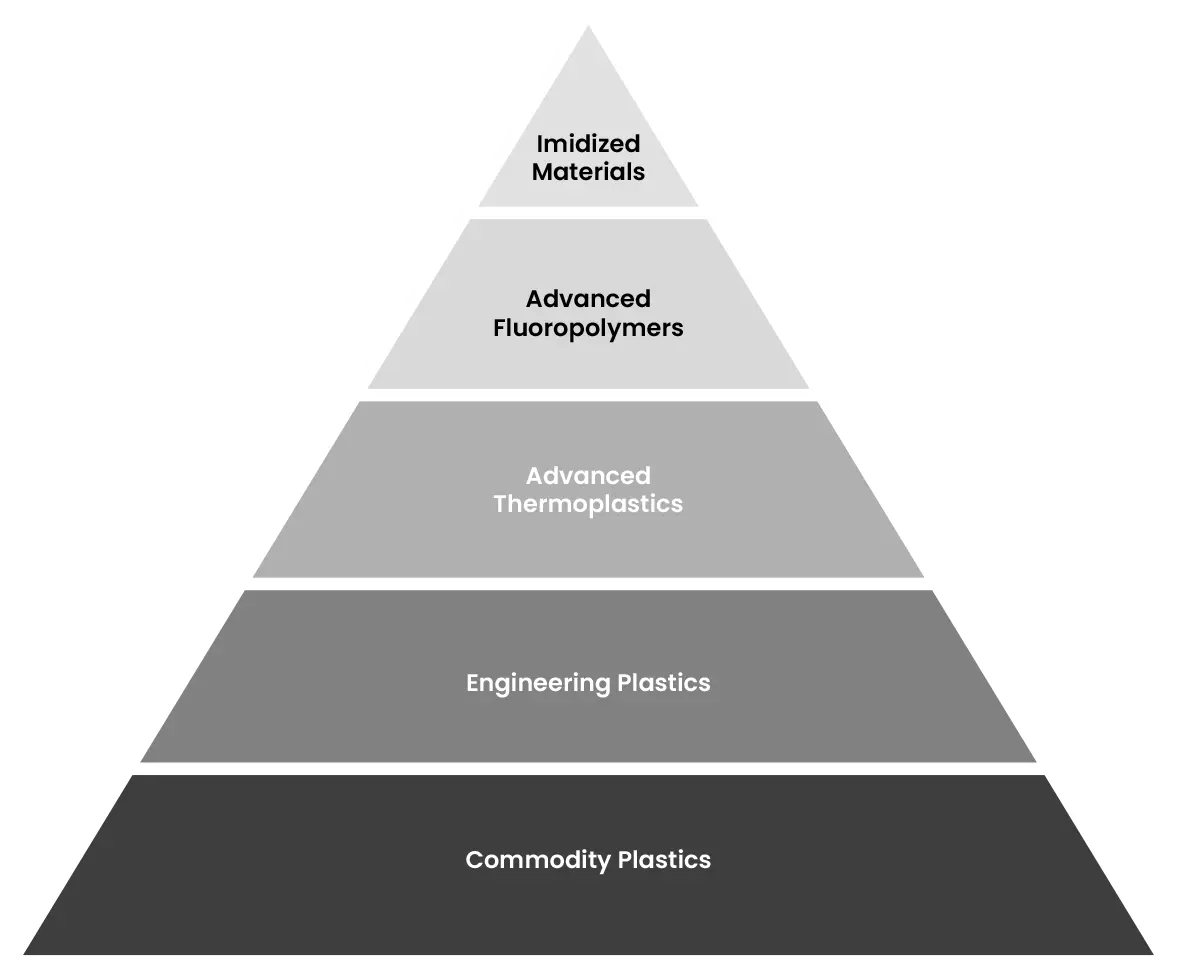
The Pexco Materials Pyramid
From Thermoplastics to Thermosets and Elastomers
Pexco delivers the industry’s broadest range of polymer solutions spanning flexible elastomers, thermoplastics, high-strength amorphous materials, and thermosets engineered for extreme performance.
Pexco’s Vast Plastic Expertise
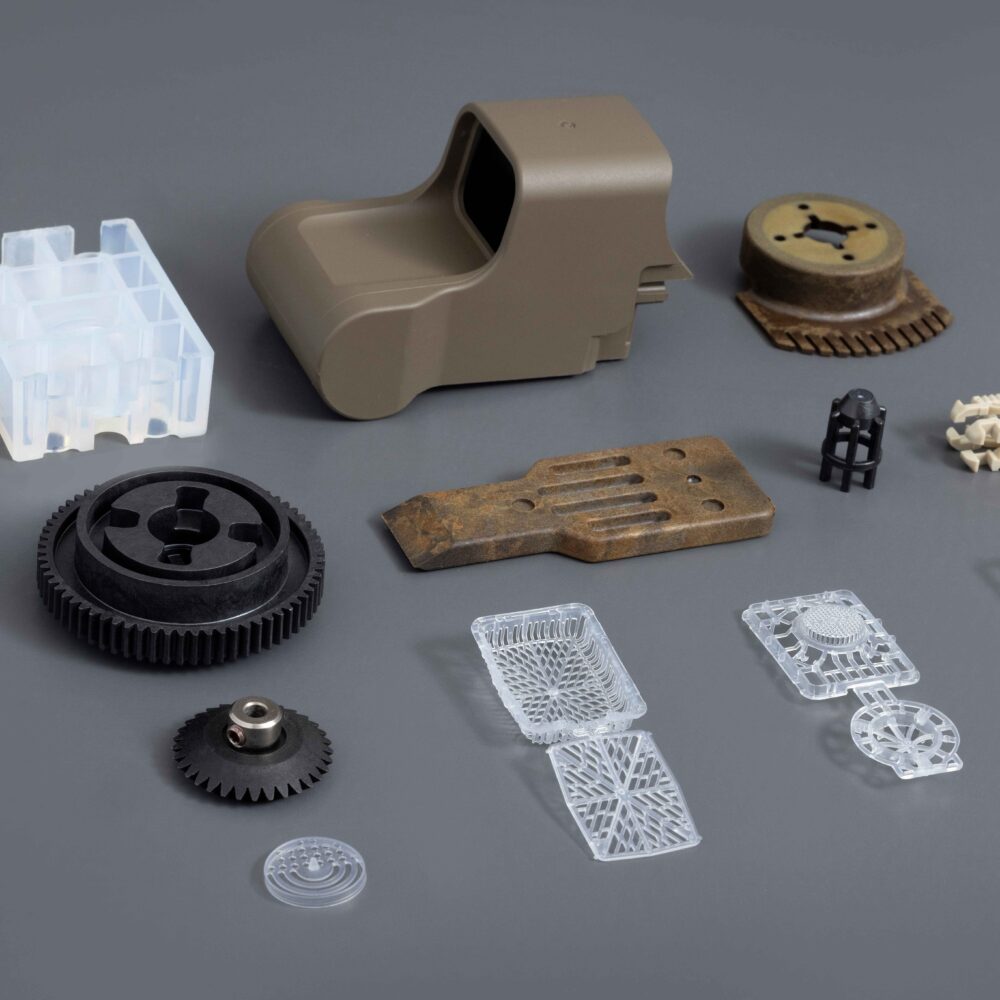
Pexco processes more than 50 prime polymer resin families and blends across our U.S. manufacturing facilities, serving industries that demand purity, precision, performance, and reliability. Our Materials Pyramid illustrates the depth of our materials expertise, spanning from general-purpose plastics to specialized, high-purity polymers for nearly every market and application.
Each tier of the pyramid represents a balance between temperature performance, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-efficiency. Whether you need the versatility of PVC or the extreme performance of PAI and PBI, Pexco is your U.S.-based supply partner with the engineering depth to deliver.

Balancing Performance, Processability, and Cost
Each level of the Pexco Materials Pyramid reflects a balance between performance, processability, and cost, while also accounting for polymer structure and behavior. As materials move up the pyramid, they typically offer increased temperature resistance, chemical durability, and mechanical strength, with added complexity in processing and material selection.
Pexco’s materials expertise spans thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers, enabling engineers to select the right material class based on how a part must perform, be manufactured, and function over its service life.
Polymer Types and Structures Explained
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics soften when heated and solidify when cooled, allowing them to be reprocessed, welded, and recycled. They offer excellent design flexibility and are used across nearly every tier of the Materials Pyramid, from commodity plastics to advanced fluoropolymers and high-performance engineering resins.
Typical Advantages
- Reprocessable and weldable
- Suitable for extrusion, injection and compression molding, and machining
- Broad range of mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties
Thermosets
Thermosets undergo a permanent chemical crosslinking during processing and cannot be remelted once cured. This structure provides exceptional thermal stability, dimensional integrity, and resistance to creep under load, making thermosets ideal for extreme environments.
Typical Advantages
- Excellent high-temperature performance
- Superior dimensional stability under load
- Long-term mechanical strength
Amorphous Thermoplastics
Amorphous polymers have a random molecular structure, resulting in uniform properties and consistent shrinkage during processing. These materials are often transparent and offer excellent impact resistance and bonding with solvents.
Typical Advantages
- Good impact resistance and toughness
- Elongation
- Hold up under multiple cycles of sterilization
- Often transparent
Examples: PEI, PSU, PPSU, PC
Crystalline Thermoplastics
Crystalline polymers have an ordered molecular structure, which contributes to higher chemical resistance, stiffness, and temperature capability. These materials often provide superior performance in aggressive chemical or mechanical environments.
Typical Advantages
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Improved wear and fatigue resistance
- Self-lubricating
Examples: HDPE, PA, PEEK, PPS, PTFE, PFA, PVDF
Elastomers
Elastomers form a separate materials pyramid, defined by flexibility, resilience, and the ability to recover after deformation. Unlike thermoplastics and thermosets, elastomers are selected for sealing, vibration control, and environmental resistance rather than structural strength.
Typical Advantages
- High elasticity and compression recovery
- Effective sealing and cushioning
- Available in dense and sponge formulations
Examples: EPDM, silicone, nitrile, neoprene, TPE
The Pexco Materials Pyramid
Toggle to expand to show the material table under each bullet
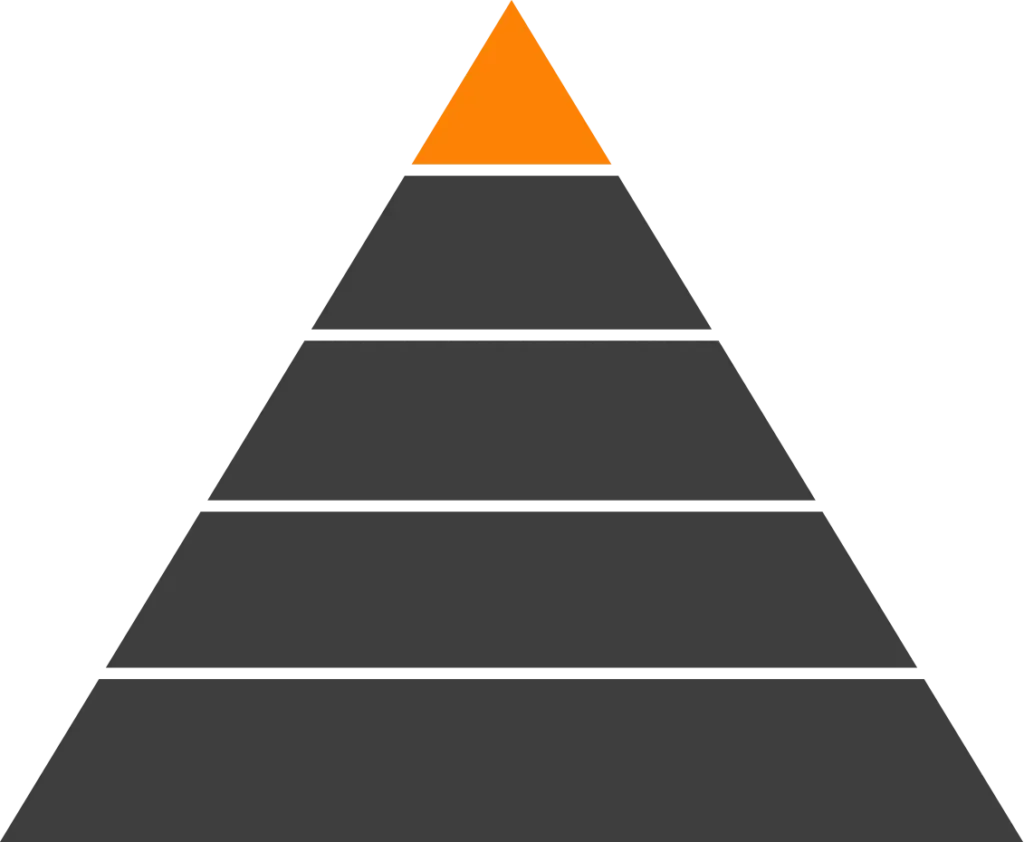
Imidized Materials represent the highest tier of polymer performance, offering exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength in environments where conventional thermoplastics fail. These materials are ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, electronics, semiconductor, and industrial processing where sustained high temperatures, dimensional stability, and long-term reliability are critical.
Imidized Materials Overview Table
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| PBI | Polybenzimidazole (Celazole®) | Extreme thermal stability up to 340°C sustained, outstanding chemical resistance, very high mechanical strength, and low creep under load | Aerospace seals, semiconductor tooling, hot gas filtration, high-temperature insulation |
| PI | Polyimide | Wide operating temperature range from cryogenic conditions (−270°C) to approximately 300°C, excellent electrical insulation, and dimensional stability | Flexible circuits, electrical insulation films, aerospace components |
| PAI | Polyamide-imide (Torlon®) | Exceptional mechanical strength, thermal resistance up to 260°C sustained, excellent chemical and wear resistance, and high load-bearing capability | Bearings, bushings, aerospace components, automotive and industrial parts |
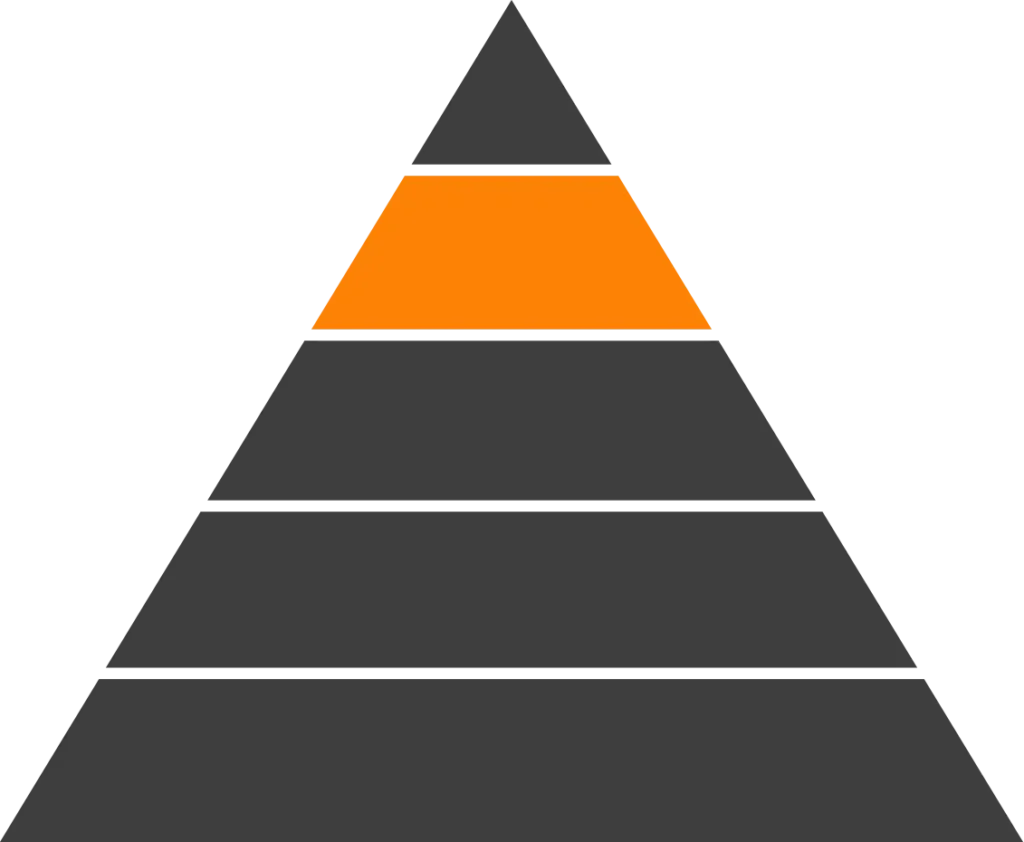
Advanced Fluoropolymers are crystalline materials known for exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and purity, making them ideal for aggressive chemical environments and high-reliability applications. Pexco’s fluoropolymer portfolio includes injection molded and extruded solutions, with specialized expertise in injection molding PFA and FEP, a capability that differentiates Pexco from many competitors. Proprietary Pexco brands such as Altaflo® and Enflon® support high-purity and precision applications across semiconductor, medical, aerospace, and industrial markets.
Advanced Fluoropolymers Overview Table – High Performance Fluoropolymers
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| ECTFE | Ethylene Chlorotrifluoroethylene | Excellent chemical resistance, high mechanical strength, good permeation resistance, and durability in harsh environments | Chemical processing components, wire and cable insulation, corrosion-resistant linings |
| ETFE | Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene | High impact resistance, wide temperature capability, excellent weatherability, and good electrical insulation | Aerospace wire coatings, cable jacketing, industrial tubing |
| FEP | Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (Altaflo®) (Insultab®) | Outstanding chemical resistance, low friction, high transparency, and flexibility with melt-processability | High-purity tubing, wire insulation, injection molded fluid handling components |
| PFA | Perfluoroalkoxy (Altaflo®) | Superior chemical resistance, high temperature capability, low extractables, and excellent mechanical integrity | Semiconductor fluid handling, injection molded fittings, high-purity tubing |
| HP PFA | High Purity Perfluoroalkoxy (Altaflo®) | Enhanced purity with reduced ionic contamination, excellent thermal and chemical resistance, and dimensional stability | Semiconductor wet benches, ultra-clean fluid distribution systems |
| UHP PFA | Ultra-High Purity Perfluoroalkoxy (Altaflo®) | Ultra-low extractables and metals content, exceptional chemical resistance, and high-temperature performance | Advanced semiconductor manufacturing, critical process fluid components |
| PCTFE | Polychlorotrifluoroethylene | Low moisture absorption, excellent dimensional stability, good chemical resistance, and low gas permeability | Cryogenic seals, valve seats, semiconductor components |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene (Altaflo®) (Enflon®) | Extremely low coefficient of friction, outstanding chemical inertness, and wide temperature resistance | Seals, gaskets, liners, bearings, and chemical processing components |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride (Kynar®) (Altaflo®) | Excellent chemical resistance, good mechanical strength, and resistance to UV and radiation | Chemical piping systems, wire insulation, fluid handling components |
| THV | Terpolymer of Tetrafluoroethylene, Hexafluoropropylene, and Vinylidene Fluoride | High flexibility, low processing temperature, good chemical resistance, and transparency | Flexible tubing, cable insulation, specialty fluid handling |
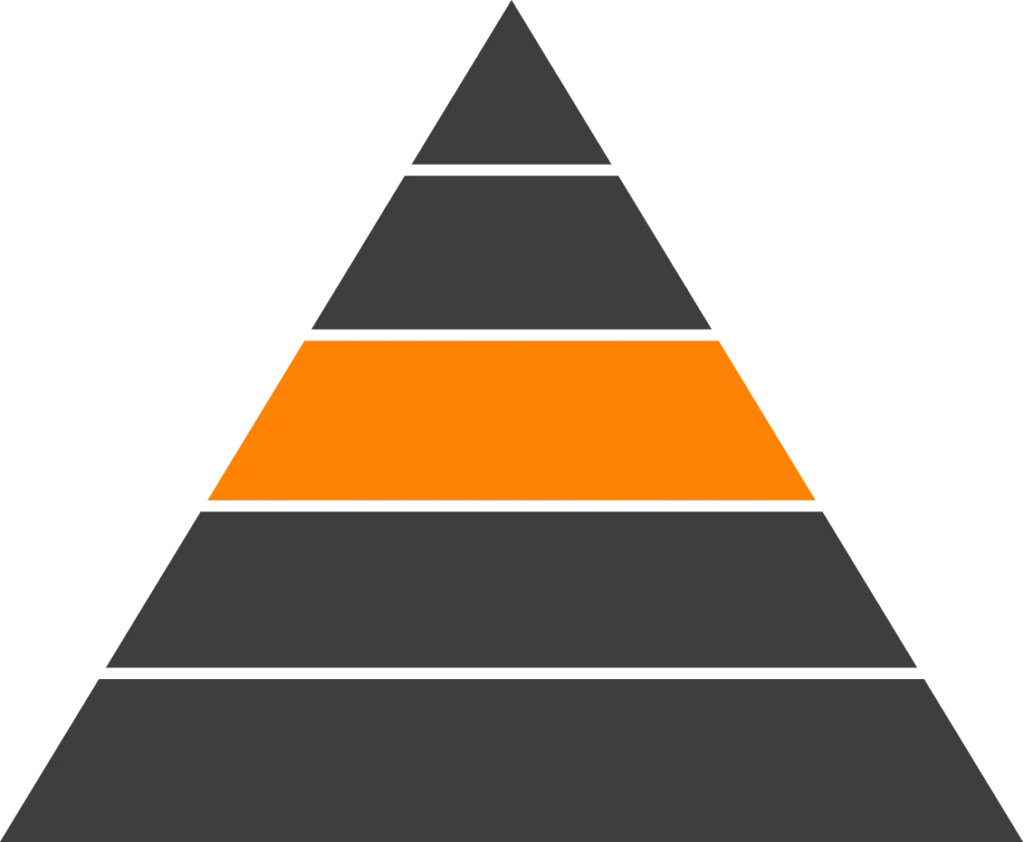
Advanced Thermoplastics offer an optimal balance of mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and processability, serving as a critical bridge between engineering plastics and ultra-high-performance polymers. This category includes both amorphous and crystalline thermoplastics, allowing engineers to select materials based on transparency, toughness, chemical resistance, and temperature performance across aerospace, medical, electrical, and industrial applications.
Advanced Thermoplastics Overview Table – High-Performance Thermoplastics
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| PEI | Polyetherimide (Ultem®) | Amorphous thermoplastic with high heat resistance, excellent strength-to-weight ratio, flame retardancy, and good electrical insulation | Aerospace interior components, medical device housings, electrical connectors |
| PES | Polyethersulfone | Amorphous polymer with high thermal stability, excellent hydrolytic resistance, and good chemical resistance | Medical device components, filtration housings, electrical insulation |
| PPSU | Polyphenylsulfone | Tough, amorphous material with outstanding impact resistance, high temperature capability, and excellent resistance to repeated sterilization | Medical device components, plumbing fittings, aerospace interiors |
| PSU | Polysulfone (Udel®) | Amorphous thermoplastic with good mechanical strength, transparency, thermal stability, and hydrolytic resistance | Medical components, electrical housings, industrial fluid handling |
| PEEK | Polyether Ether Ketone | Crystalline thermoplastic with exceptional mechanical strength, high temperature resistance up to 260°C, and outstanding chemical resistance | Aerospace components, semiconductor parts, medical implants, bearings |
| PPS | Polyphenylene Sulfide (Ryton®) | Crystalline polymer with excellent chemical resistance, dimensional stability, inherent flame retardancy, and high stiffness | Electrical connectors, automotive components, industrial pump parts |
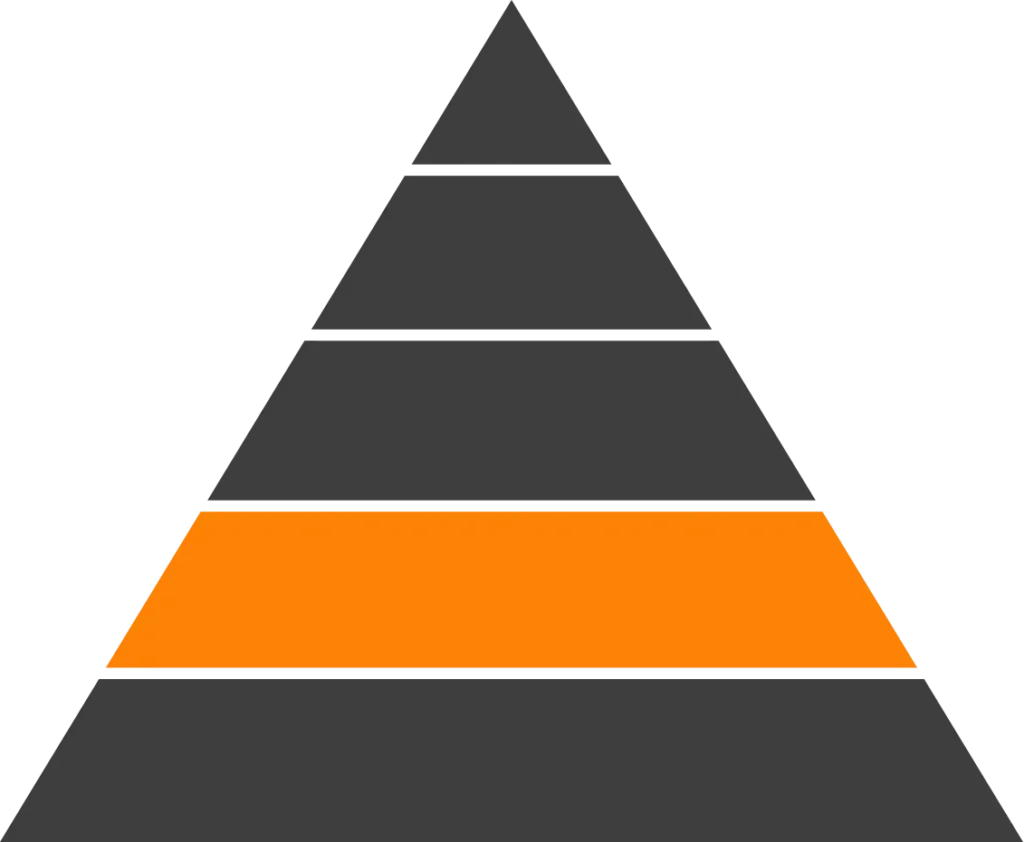
Engineering Grade Plastics provide a versatile balance of strength, toughness, chemical resistance, and cost efficiency for a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. This category includes both amorphous and crystalline thermoplastics, enabling engineers to select materials based on impact resistance, dimensional stability, moisture resistance, and ease of processing while maintaining reliable performance across diverse environments.
Engineering Grade Plastics Overview Table
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| CPVC | Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride | Amorphous material with improved temperature and chemical resistance compared to PVC, good flame retardancy, and corrosion resistance | Industrial piping, fluid handling components, chemical processing systems |
| PC | Polycarbonate | Amorphous polymer with high impact strength, optical clarity, good heat resistance, and dimensional stability | Protective housings, lighting components, electrical enclosures |
| PC-ABS | Polycarbonate–ABS Blend | Tough, amorphous blend combining impact resistance, strength, and improved processability | Electronic housings, automotive interiors, industrial enclosures |
| PC/PBT | Polycarbonate Polyester Blend | Balanced toughness and chemical resistance with improved dimensional stability over PC alone | Electrical connectors, appliance components, industrial parts |
| PPO | Polyphenylene Oxide | Amorphous thermoplastic with low moisture absorption, good dimensional stability, and electrical insulation properties | Electrical housings, structural components, fluid handling applications |
| PU | Polyurethane | Versatile polymer offering flexibility or rigidity depending on formulation, with good abrasion resistance and durability | Wheels, rollers, protective components, industrial parts |
| PA | Polyamide (Nylon) | Crystalline thermoplastic with excellent wear resistance, good mechanical strength, and resistance to fatigue | Gears, bearings, structural components, industrial hardware |
| POM | Polyoxymethylene (Acetal) | Crystalline polymer with low friction, excellent dimensional stability, and good mechanical strength | Precision gears, valve components, bushings |
| PBT | Polybutylene Terephthalate (Co-Polyester) | Crystalline thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and dimensional stability | Electrical connectors, appliance components, automotive parts |
| PE | Polyethylene | Crystalline polymer with good chemical resistance, impact strength, and flexibility across grades | Containers, tubing, liners, industrial components |
Commodity Plastics provide cost-effective, highly versatile solutions for high-volume and everyday applications where ease of processing, durability, and availability are key priorities. This category includes both amorphous and crystalline thermoplastics, offering a wide range of flexibility, impact resistance, chemical resistance, and formability for consumer, industrial, and infrastructure products.
Commodity Plastics Overview Table
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene | Amorphous polymer with good impact resistance, toughness, and ease of processing | Consumer housings, enclosures, industrial components |
| ABS-GF | Glass-Filled ABS (10% and 20%) | Improved stiffness and strength, and lower co-efficient of expansion compared to standard ABS | Structural housings, equipment covers, reinforced components |
| PS | Polystyrene | Amorphous material with good rigidity, clarity, and ease of molding | Disposable products, packaging, housings |
| HIPS | High-Impact Polystyrene | Modified polystyrene offering improved impact resistance and toughness | Appliance housings, signage, consumer products |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride | Amorphous thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, flame retardancy, and durability | Pipe, profiles, industrial components |
| FPVC | Flexible Polyvinyl Chloride | Plasticized PVC offering flexibility, abrasion resistance, and good chemical resistance | Tubing, jacketing, protective coverings |
| Foamed PVC | Foamed Polyvinyl Chloride | Lightweight PVC with good stiffness, insulation properties, and machinability | Signage, panels, decorative and structural elements |
| RPVC | Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride | Unplasticized PVC with improved stiffness, strength, and dimensional stability | Pipe, conduit, structural profiles |
| PMMA | Polymethyl Methacrylate (Acrylic) | Amorphous polymer with excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and surface hardness | Lighting components, displays, lenses |
| HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene | Crystalline polymer with high strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and impact durability | Containers, piping, industrial components |
| LDPE | Low-Density Polyethylene | Crystalline polymer with flexibility, toughness, and good chemical resistance | Films, tubing, liners |
| LLDPE | Linear Low-Density Polyethylene | Improved tensile strength and puncture resistance compared to LDPE | Films, flexible packaging, tubing |
| Poly-O / PO | Polyolefin | Crystalline family offering chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and flexibility across grades | Industrial packaging, molded and extruded components |
| PP | Polypropylene | Crystalline thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, and low density | Automotive components, containers, industrial parts |
Elastomers form a distinct materials pyramid, ranging from high-performance formulations engineered for sealing, cushioning, and vibration control to economical rubber compounds. Unlike rigid thermoplastics, elastomers are defined by their flexibility, resilience, and ability to recover after compression. They are essential for applications requiring environmental resistance, fluid sealing, and long-term durability across industrial, automotive, medical, and infrastructure markets.
Elastomers Overview Table
| Material (Chemical Abbreviation) | Full Name (Key Brand Names) | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| EPDM (Dense, Sponge) | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer | Excellent resistance to weathering, ozone UV exposure, and aging | Outdoor seals, automotive tubing and seals, electrical insulation |
| VMQ (Dense, Sponge) | Silicone Rubber (Polysiloxane) | Exceptional temperature tolerance, flexibility, and material purity | Food-grade gaskets, medically compliant components, high-temperature seals |
| CR (Dense) | Chloroprene Rubber | Balanced resistance to chemicals, oils, weathering, and abrasion | Industrial seals, vibration isolation components |
| NBR (Dense) | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber | Outstanding resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons | Automotive seals, hydraulic seals, fuel system components |
| SBR (Dense) | Styrene Butadiene Rubber | Cost-effective material with good abrasion resistance | General-purpose seals, gaskets, industrial applications |
| IR (Sponge) | Polyisoprene or Isoprene Rubber | Soft, flexible elastomer with properties similar to natural rubber | Cushioning components, vibration pads, protective applications |
| TPE | Thermoplastic Elastomer | Combines rubber-like flexibility with thermoplastic processability | Seals, weatherstripping, flexible extruded components |
Pexco’s materials engineers assist customers in:
- Selecting the right polymer for mechanical, thermal, and chemical requirements
- Designing for manufacturability and cost optimization
- Meeting compliance standards (ISO 9001:2015, AS9100, ISO 13485:2016, SEMI F57, SEMI C-90, FDA Regulations, FST, USP Class VI, FAR 25.853, UL94, MASH-16, NCHRP 350)
- Managing transitions between materials (e.g., upgrading from PPS to PEEK or from PVDF to PFA)