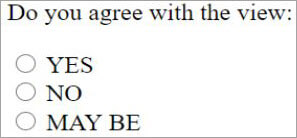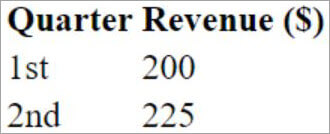Refer to this comprehensive HTML Cheat Sheet to learn about various commonly used HTML coding tags with code examples:
As we begin the tutorial, we will first understand what is HTML language and further in the tutorial, we will take a look at the various HTML tags. Here, we shall also understand some of the tags used in HTML5.
So let us get going and first understand what is HTML.
Table of Contents:
What Is HTML
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language. It is a markup language that was invented by Tim Berners-Lee in the year 1991. In simple words, we can say that this is a language that describes how the content on a web page would display. For this purpose, it uses tags within which the text to be displayed is embedded. The browser interprets those tags to display the text on the screen.
There have been many revisions to HTML, and the most recent one available is HTML5 that was released in the year 2014.
What Is An HTML Cheat Sheet
HTML Cheat Sheet is a quick reference guide that lists the commonly used HTML tags and their attributes. The tags are generally grouped category wise for easy readability.
HTML Tags
Below we have grouped the tags into various categories and we shall learn about the tags falling in each category along with examples.
Basic Tags
| Tags | Purpose |
|---|---|
| <HTML>...</HTML> | This is the parent tag (root element) for any HTML document. The entire HTML code block is embedded within this tag |
| <HEAD>...</HEAD> | This tag provides general information about the document like its title and links to style sheets(if any). This information is not displayed on the web page. |
| <TITLE>...</TITLE> | My Web Page |
| <BODY>...</BODY> | My First Web Page |
Code Snippet:
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>
My Web Page
</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
My First Web Page
</BODY>
</HTML>
Output:
My Web Page
(Displayed in the browser’s Title Bar)
My First Web Page
(Displayed as Web page content)
Meta Information Tags
| Tags | Purpose |
|---|---|
| <BASE> | This is used to specify the base URL of the website. |
| <META> | It contains information like Published date, author;s name etc. |
| <STYLE> | It contains the information related to the appearance of the web page. |
| <LINK> | It is used to indicate external links, mainly stylesheets. It is an empty tag and contains attributes only. |
| <SCRIPT> …. </SCRIPT> | Used for adding code snippets to make a web page dynamic. |
Code Snippet:
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<META name="The author" content="Rashmi">
<BASE href=”https://Webpage.com” target=”_blank”>
<TITLE> Rashmi’s Web Page </TITLE>
<LINK rel=”Stylesheet” href=”/parent.css”>
<SCRIPT src=”source.js”>
Var a=10;
</SCRIPT>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
This is Rashmi’s Web Page Content Area
</BODY>
</HTML>
Output:
Rashmi’s Web Page
(Displayed in the browser’s Title Bar)
This is Rashmi’s Web Page Content Area
(Displayed as Web page content)
Text Formatting Tags
| Tag | Purpose | Code Snippet | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| <B> .... </B> | Makes the text bold | <B>Hello</B> | Hello |
| <I> .... </I> | Makes the text Italic | <I>Hello</I> | Hello |
| <U> .... </U> | Underlines the text | <U>Hello</U> | Hello |
| <STRIKE>.... </STRIKE> | Strike out the text | <STRIKE>Hello</STRIKE> | |
| <STRONG>.... </STRONG> | Makes the text bold (Same as <B>..</B> tag) | <STRONG>Hello</STRONG> | Hello |
| <EM>.... </EM> | Makes the text Italic (Same as <I>..</I> tags) | <EM>Hello</EM> | Hello |
| <PRE> ....</PRE> | Preformatted text (spacing, line break and font are preserved) | <PRE>HELLO Sam</PRE> | HELLO Sam |
| <H#> .... </H#> | Heading Tag - # can range from 1 to 6 | <H1>Hello</H1> <H6>Hello </H6 > | HelloHello |
| <SMALL> ....</SMALL> | Makes the text small sized | <SMALL>Hello</SMALL> | Hello |
| <TT> ....</TT> | Displays text Typewriter style | <TT>Hello</TT> | Hello |
| <SUP> ....</SUP> | Displays text as Superscript | 5<SUP>2</SUP> | 5 2 |
| <SUB> ....</SUB> | Displays text as Subscript | H<SUB>2</SUB>O | H2O |
| <BLOCKQUOTE>...</BLOCKQUOTE> | Displays text as a distinct code block | <BLOCKQUOTE>Hello</BLOCKQUOTE> | Hello |
FORM
Purpose: This tag is used to accept user input.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| action | Mentions where the form data is to be sent after submitting | URL |
| autocomplete | Mentions if form has autocomplete feature or not | on off |
| target | Mentions display place of response received after form submission | _self _parent _top _blank |
| method | Specifies method used to send the form data | get post |
| name | Name of the form | text |
Code Snippet:
<FORM name=”User_Details” action=”/data.php” method=”get” autocomplete=”on” target=”_blank”> <LABEL for="name">Name:</LABEL> <INPUT type="text" id="your_name" name="your_fname">
Output:
INPUT
Purpose: This tag specifies an area to capture user input
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| alt | Mentions an alternate text to appear if image is missing | text |
| autofocus | Mentions if the input field should have focus when the form loads | autofocus |
| name | Mentions the name of the input field | text |
| required | Mentions if an input field is mandatory | required |
| size | Mentions character length | number |
| type | Mentions type of input field | button, checkbox, image, password, radio, text, time |
| value | Mentions the value of an input area | text |
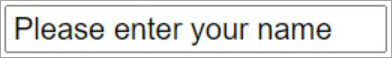
Code Snippet:
<INPUT type=text autofocus name=”user_name” required size=”50” value="Please enter your name">
Output:
TEXTAREA
Purpose: This is an input control used to capture multi-line user input.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| cols | Defines the width of the textarea | number |
| rows | Defines the number of visible lines in the textarea | number |
| autofocus | Defines if field should get autofocus on page load | autofocus |
| maxlength | Defines max characters allowed in the textarea | number |
| name | Defines the textarea name | text |
Code Snippet:
<TEXTAREA name="data" rows="4" cols="50" autofocus maxlength=”200”>
Hi! This is a textarea
</TEXTAREA>
Output:
BUTTON
Purpose: It is used to include a button (clickable) on the screen.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| name | Defines the button’s name | text |
| type | Defines the type of the button | button, reset, submit |
| value | Defines the initial value of the button | text |
| autofocus | Defines if the button should get autofocus on page load | autofocus |
| disabled | Defines if button is disabled | disabled |
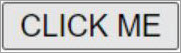
Code Snippet:
<BUTTON type=”button” name="button1" value=”Click Me” autofocus>
CLICK ME
</BUTTON>
Output:
SELECT
Purpose: This tag is mostly used along with the FORM tag to capture user input. It creates a drop-down list from which the user can select a value.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| name | Defines the name of drop down list | text |
| required | Defines if drop down selection is mandatory | required |
| form | Defines the form the drop down is associated with | form ID |
| autofocus | Defines if the drop down should get autofocus on page load | autofocus |
| multiple | Defines if more than one options can be selected | multiple |
Code Snippet:
<SELECT name="mode" form="transport_id" multiple autofocus required>
<OPTGROUP label="Transport Used">
<OPTION value="private">Private</OPTION>
<OPTION value="public">Public</OPTION>
</OPTGROUP>
Output:
OPTION
Purpose: This tag is used to define the options of a SELECT list.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| disabled | Defines the option to be disabled | disabled |
| label | Defines a short name for an option | Text |
| selected | Defines an option to be pre selected on page load | selected |
| value | Defines the value that is sent to the server | Text |
Code Snippet:
<SELECT name="mode" >
<OPTION value="private" disabled label=”PV”>Private</OPTION>
<OPTION value="public" selected>Public</OPTION>
Output:
OPTGROUP
Purpose: This tag is used to group options in a SELECT tag.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| disabled | Defines if an option group is disabled | disabled |
| Label | Defines a label for an option group | text |
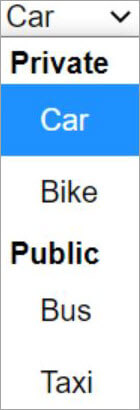
Code Snippet:
<SELECT name="mode" id="Transport">
<OPTGROUP label="Private">
<OPTION value="private1">Car</OPTION>
<OPTION value="private2">Bike</OPTION>
</OPTGROUP>
<OPTGROUP label="Public">
<OPTION value="public1">Bus</OPTION>
<OPTION value="public2">Taxi</OPTION>
</OPTGROUP>
</SELECT>
Output:
FIELDSET
Purpose: This tag is used to group related elements in a form.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| disabled | Defines if a fieldset should to be disabled | disabled |
| form | Defines the form to which the fieldset belongs | form ID |
| name | Defines a name for the fieldset | text |
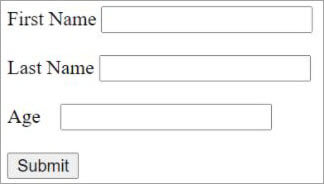
Code Snippet:
<FORM action="/action_page.php">
<FIELDSET>
First Name <INPUT type="text" id="fname" name="fname"><br><br>
Last Name <INPUT type="text" id="lname" name="lname"><br><br>
Age <INPUT type="email" id="email"
name="email"><br><br>
<INPUT type="submit" value="Submit">
</FIELDSET>
</FORM>
Output:
LABEL
Purpose: As the name suggests, this tag is used to define a label for various other tags.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| for | Defines the ID of the element, to which the label is associated | element ID |
| form | Defines the ID of the form, to which the label is related | form ID |
Code Snippet:
<P> Do you agree with the view: </P> <INPUT type="radio" name="option1" id="yes" value="YES"> <LABEL for="yes">YES</LABEL><br> <INPUT type="radio" name="option2" id="no" value="NO"> <LABEL for="no">NO</LABEL><br> <INPUT type="radio" name="option3" id="mb" value="MAY BE"> <LABEL for="may be">MAY BE</LABEL><br>
Output:
OUTPUT
Purpose: This tag is used to show the result of a calculation
Code Snippet:
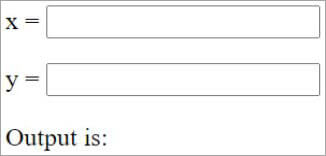
<P> x = <INPUT type="number" name="x" value=""><BR> <P> y = <INPUT type="number" name="y" value=""><BR><BR> Output is:<OUTPUT name="add"></OUTPUT>
Output:
iFRAME
Purpose: It is used to embed a document in the current HTML document. This tag was introduced in HTML5.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| allowfullscreen | Allows to set iframe to full screen mode | true, false |
| height | Mentions iframe height | pixels |
| src | Mentions link of the iframe | URL |
| width | Mentions iframe width | pixels |
Code Snippet:
<iFRAME src=”\sample.html” height=”200” width=”200” allowfullscreen=”true”> </iFRAME>
Below is the content of sample.html file used in the code snippet above:
<HTML>
<HEAD>
BODY {
Background-color: green;
}
H1 {
Color: white;
}
</HEAD>
<BODY>
Success<br>can<br>be<br>found<br>with<br>hardwork.<br>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Output:
LIST
Purpose: Lists are used to group similar items together. HTML provides two types of List tag – Ordered <OL> and Unordered <UL> lists.
| Tag | Purpose | Code Snippet | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| <OL>.... </OL> | Creates a numbered list by default. | <OL> <LI> Red </LI> <LI> Blue </LI> <LI> Green </LI> </OL> |
|
| <UL> …. </UL> | Creates a bulleted list by default. | <UL> <LI> Red </LI> <LI> Blue </LI> <LI> Green </LI> </UL> |
|
| <LI> …. </LI> | Indicates a list item for ordered as well as unordered list | <UL> <LI> Hello </LI> <LI> World </LI> </UL> |
|
IMAGE
Purpose: It allows embedding an image on a web page. It serves as a placeholder.
| Attribute | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| alt (mandatory) | Mentions text to appear if image is not displayed for some reason | text |
| src (mandatory) | Mentions path of the image | URL |
| height | Mentions height of the image | pixels |
| width | Mentions width of the image | pixels |
Code Snippet:
<IMG src="Bird.jpg" alt="Bird" width="200" height="300">
Output:
LINK
Purpose: This tag allows the user to define a link to an external document. It is placed in the <head> section of the document. It is generally used to link external style sheets.
| Attributes | Purpose | Value |
|---|---|---|
| href | Mentions the place where the link should redirect | Destination URL |
| title | Mentions information to be shown as tooltip | Text |
| target | Mentions where the link should open | _self (opens in the same window) _blank (opens in a new tab or window) _top (opens in the full screen mode from top of the window) _parent (opens link in the parent frame) |
Code Snippet:
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Link Tag</TITLE>
<LINK rel = "stylesheet" href = "stylenew.css">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<p> This text is formatted with external style sheet </p>
</BODY>
Below is the code of “stylenew.css” used above.
BODY {
Background-color: powderblue;
}
H1 {
Color: white;
}
Output:
TABLE
Purpose: This tag is used to define a table structure.
| Tags | Purpose |
|---|---|
| <TABLE> …. </TABLE> | To define a table structure |
| <TH> …. </TH> | To define table header |
| <TR> …. <TR> | To define row |
| <TD> …. </TD> | To define table data |
Code Snippet:
<TABLE>
<TR>
<TH> Quarter </TH>
<TH> Revenue ($) </TH>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD> 1st </TD>
<TD> 200 </TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TD> 2nd </TD>
<TD> 225 </TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
Output:
HTML5 Tags
| Tags | Purpose | Code Snippet | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| <ARTICLE> | To display an independent piece of article | <ARTICLE> <H3> TOURISM </H3> <P>This industry has been greatly impacted by the pandemic. </P> </ARTICLE> | TOURISMThis industry has been greatly impacted by the pandemic. |
| <ASIDE> | To display text not much relevant to the web page content | <H4> TOURISM </H4> Travel for pleasure or business. <ASIDE> <H6>Travel</H6> <P> Tourism is a dynamic and competitive industry. </P> | TOURISMTravel for pleasure or business. |
| <AUDIO> | To include an audio file | <P>Click to play:</P> <AUDIO controls> <SOURCE src="rythm.mp3" type="audio/mp3"> </AUDIO> | Click to play: |
| <CANVAS> | To render an instant graphic such as a graph | <CANVAS id=”mycanvas” width=”50” height=”10”> The browser does not support the canvas tag </CANVAS> |  |
| <DETAILS> | To display additional information that the user can obtain if required | <DETAILS> <P> This is a website marketed by GIPS group </P> <SUMMARY> Welcome to this webpage </SUMMARY> </DETAILS> | This is a website marketed by GIPS group Welcome to this webpage |
| <EMBED> | To include external content or plugin | <EMBED src=”sound.html” width=”10” height=”20”> | Sound.html This file lists the various type of sounds (Above was the content of the src file ‘sound.html” as mentioned in the code) |
| <FIGURE> | To display information that is treated as a single unit and is self contained | <FIGURE> <IMG src=”bird.gif”> </FIGURE> |  |
| <FOOTER> | To display information as footer | <FOOTER> <P> URL: SoftwareTestingHelp <BR> <A HREF=”https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/ ”> SoftwareTestingHelp.com </A> </FOOTER> | |
| <HEADER> | To display information as header | <HEADER> <H1> This is Heading 1 </H1> <P>This is the information section</P> </HEADER> | This is Heading 1This is the information section |
| <MARK> | To highlight text which is to be referenced in another section | <P>Below text is <MARK>encrypted <MARK> </P> | Below text is encrypted |
| <METER> | To represent a measurement unit | <P> Your Progress status is: </P> <METER id="status_id" value="0.5">60%</METER> | Your Progress status is: |
| <NAV> | To reference a section to be used for navigation | <P> E-commerce websites=> Tech websites </P> <A href="https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/ ">SoftwareTestingHelp</A> <BR> <A href="https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/practical-software-testing-new-free-ebook-download/">Free eBook</A> <BR> | E-commerce websites:Tech websites SoftwareTestingHelp Free eBook |
| <OUTPUT> | To display the result of a calculation | <FORM oninput="add.value=parseInt(x.value)+add(y.value);"> <P> x = <INPUT type="number" name="x" value=""/><BR> <P> y = <INPUT type="number" name="y" value=""><BR><BR> Output is:<OUTPUT name="add"></OUTPUT> </FORM> | |
| <PROGRESS> | To display the progress of a task | <P> Transfer status : <PROGRESS id="data" value="50" max="100"> 25% </PROGRESS> | Transfer status : |
| <SECTION> | To distinguish a document part as a separate section | <SECTION> <H4>Section 1</H4> <P>Hi! This is section 1.</P> </SECTION> <H4>Section 2</H4> <P>Hi! This is section 2.</P> </SECTION> | Section 1Hi! This is section 1. Section 2Hi! This is section 2. |
| <TIME> | To display date/ time | <P> Current time is <TIME> 5:00 PM </TIME> </P> | Current time is |
| <VIDEO> | To represent a video | <VIDEO width="320" height="240" controls> <SOURCE src="seasons.mp4" type="video/mp4"> </VIDEO> | |
| <WBR> | To include a line break | <P> Line is broken in two <WBR>lines</P> | Line is broken in two |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q #1) What are the four basic HTML tags?
Answer: The four basic tags used in HTML are:
<HTML>..</HTML> <HEAD>..</HEAD> <TITLE>..</TTILE> <BODY>..</BODY>
Q #2) What are the 6 heading tags?
Answer: HTML provides us with 6 heading tags as below:
<H1>..</H1> <H2>..</H2> <H3>..</H3> <H4>..</H4> <H5>..</H5> <H6>..</H6>
The content written within the heading tag appears as a distinct text as a heading where H1 is the biggest and H6 the smallest sized heading.
Q #3) Is HTML case sensitive?
Answer: No, it is not case sensitive. The tags and their attributes can be written in either upper or lower case.
Q #4) How do I align text in HTML?
Answer: Text in HTML can be aligned using the <P> paragraph tag. This tag uses the attribute Style to align the text. The CSS property text-align is used to align the text.
Refer code snippets below:
<P style="text-align:right"> <P style="text-align:left"> <P style="text-align:center">
Q #5) How to set Heading alignment in HTML?
Answer: Similar to text, alignment for Heading can also be set using the text-align property of CSS. The Style attribute can be used with the heading tag as below:
<H1 style="text-align:right"> <H1 style="text-align:left"> <H1 style="text-align:center">
Q #6) What is the difference between HTML elements and tags?
Answer: An HTML element comprises the start tag, some content, and the end tag
Example:
<H1 style="text-align:right"> Heading </H1>
On the other hand, the start or end tag is what we refer to as the HTML tag.
Example: <H1> or <H1> or <P> or </P> each of these are referred to as tags. However, it should be noted that often the two terms are used interchangeably.
Q #7) What are the 2 types of tags in HTML?
Answer: There are two types of tags in HTML Paired and Unpaired or Singular tags.
Paired Tags – As the name suggests, these are tags comprising 2 tags. One is called the opening tag and the other is called the closing tag. For example: <HTML> </HTML>, <TITLE> </TITLE> etc.
Unpaired Tags – These tags are single tags and only have the opening tag and no closing tag. For example: <BR>, <IMG> etc.
Q #8) What is the difference between a container tag and an empty tag?
Answer:
Container tags are those tags that have an opening tag followed by content and a closing tag. For example: <DIV> </DIV>, <SPAN>
Empty tags are the tags that do not have any content and/or closing tag. For example: <BR>, <HR> etc.
Q #9) What is the largest heading tag?
Answer: <H1> is the largest heading tag in HTML tag.
Q #10) What is the select tag in HTML?
Answer: A <SELECT> tag is used for creating a drop-down list. It is most commonly used in forms where user input is to be collected. Below is a code snippet along with the output of the tag. It also shows the common attributes of this tag.
Code Snippet:
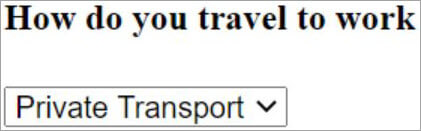
<H4>How do you travel to work</H4>
<SELECT name="travel" id="mode">
<OPTION value="Private Transport">Private Transport</OPTION>
<OPTION value="Public Transport">Public Transport</OPTION>
</SELECT>
Output:
Conclusion
Hope this article has provided you with an understanding of what exactly an HTML cheat sheet is. The aim was to share with our readers a quick reference guide of various frequently used HTML tags.
We have also seen Basic Tags, Meta Information tags, Text Formatting tags, Forms, Frames, Lists, Images, Links, Tables, and Input tags. Some tags, generally used along with the FORM tag like Select and Button, is also covered in this article. We also learned about the tags introduced with HTML5.
For each of the tags, we learned about the most common attributes used along with the tags and also saw its related code and output.