Gain a complete understanding on how to use PHP GET and POST methods with examples. Learn how to handle form data effectively with these two popular methods in PHP:
PHP supports different HTTP request methods, like GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, etc.
In this tutorial, our main concentration is on the GET and POST methods. Also, we’ll cover some of the frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to this topic.
Please note that we have used PHP version 7 in all examples.
Let’s begin!
=> Read Through the Series of PHP Tutorials
Table of Contents:
Introduction to PHP GET and PHP POST

The browser can send information to the web server using two methods.
They are,
- The GET method
- The POST method
Let’s discuss each of them in detail.
PHP GET Method
The GET method is one of the most common HTTP methods used in PHP. It is used to submit HTML form data to the server. The submitted data are collected by a special variable (superglobal) called $_GET.
Note: $_GET is case sensitive as it is a superglobal.
The GET method is the default method of submitting HTML form data. Furthermore, the GET method is used to request data from a particular resource.
The GET request to a web page is as follows:
http://www.samplesite.com/index.htm?name1=value1&name2=value2&name3=value3...
http://www.example.com/index.htm?first_name=john&last_name=doe
Note: The question mark character (?) is used to separate the page, and the encoded information, while the ampersand sign (&) is used to separate name-value pairs.
Example:
An example is shown below. You can practice this example by running the following programming code:
<form method="get" action="<?php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]; ?>?">
Name: <input type="text" id="name" name="name" value="<?php echo @$_GET['name']; ?>">
<br><br>
Age: <input type="number" id="age" name="age" value="<?php echo @$_GET['age']; ?>">
<br><br>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
<?php
echo "<h3>Output:</h3>";
echo @$_GET['name']." ".@$_GET['age'];
?>
The following screenshots show the browser output of the above programming code:
- Before entering values:

- After entering values and submitting the form:
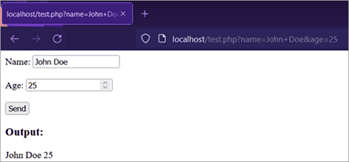
Note: The plus sign (+) is used to encode space.
PHP POST Method
The POST method is another most common HTTP method used in PHP. It is also used to submit HTML form data to the server. The submitted data are collected by a special variable (superglobal) called $_POST.
Note: $_POST is case sensitive, as it is a superglobal.
Furthermore, there are some situations where you can use POST instead of PUT.
Example:
An example is shown below. You can practice this example by running the following programming code:
<form method="post" action="<?php echo $_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]; ?>?">
Name: <input type="text" id="name" name="name" value="<?php echo @$_POST['name']; ?>">
<br><br>
Age: <input type="number" id="age" name="age" value="<?php echo @$_POST['age']; ?>">
<br><br>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
<?php
echo "<h3>Output:</h3>";
echo @$_POST['name']." ".@$_POST['age'];
?>
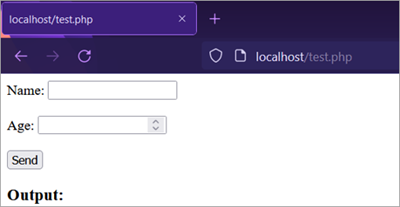
The following screenshots show the browser output of the above programming code:
- Before entering values:
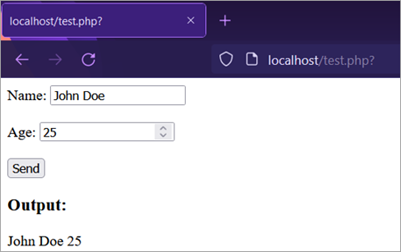
- After entering values and submitting the form:
PHP GET vs POST
Take a look at the differences between GET requests and POST requests:
| Parameter | PHP GET Request | PHP POST Request | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Visibility | Values are visible in the URL. Hence, visible to everyone. | Values are not visible in the URL. Hence, invisible to everyone. |
| 2 | Security | Comparatively less secure as values are visible in the URL. | Comparatively more secure as values are not visible in the URL. |
| 3 | Bookmark | Can be bookmarked. | Cannot be bookmarked. |
| 4 | Cache | Can be cached. | Cannot be cached. |
| 5 | Character limitation | 2048 characters. | No character limitation. |
| 6 | Data type | Cannot be used to send binary data such as images, word documents, audios, videos, etc. | Can be used to send binary data such as images, word documents, audios, videos, etc. |
| 7 | Usability | Can be used to send non-sensitive data. | Can be used to send both sensitive data (such as passwords) and non-sensitive data. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the GET & POST methods in PHP?
They are the two methods by which the browser can send information to the webserver.
2. What is a GET request used for?
It is used to request data from a particular resource.
3. Is POST more secure than GET?
Yes, POST is slightly more secure than GET because the values are not stored in the browser history, and also, the values are not visible in the URL.
4. Is POST requests slower than GET?
Usually, POST requests are slightly slower than GET requests.
5. Can I use POST instead of PUT?
Yes, you may use POST instead of PUT.
6. What is the character limit in the GET method?
The character limit is up to 2048 characters.
7. What is PHP $_ GET and PHP $_ POST?
They are PHP superglobals used to read the submitted HTML form data.
Conclusion
GET and POST are the two most commonly used HTTP request methods in PHP.
The main difference between the two methods is that values are visible in a GET request but not in a POST request. $_GET are HTTP GET variables while $_POST are HTTP POST variables.








