bzip2 command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
04 Nov, 2025
bzip2 command in Linux is used to compress and decompress the files i.e. it helps in binding the files into a single file which takes less storage space than the original file used to take. It has a slower decompression time and higher memory use. It uses the Burrows-Wheeler block sorting text compression algorithm and Huffman Coding. Each file is replaced by a compressed version of itself, with the name original name of the file followed by the extension bz2.
Consider this example using bzip2.
Command:
bzip2 -k file1.txt
Output:
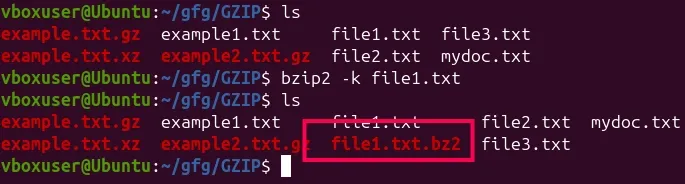
What it does:
- Creates input.txt.bz2 while keeping file1.txt due to -k; without -k, file1.txt would be removed after compression.
Syntax
bzip2 [OPTIONS] filenames ...
Each provided file is compressed individually to file.bz2; to decompress, use bunzip2 or bzip2 -d.
Commonly Used Options in bzip2
1. Compress a File (-z Option)
The -z option forces compression, though it is the default action of the bzip2 command. When you run this command, the original file is replaced by the compressed version.
$ bzip2 -z input.txt
 Compress a File
Compress a File2. Keep the Original File (-k Option)
Normally, bzip2 deletes the original file after compression, but the -k option ensures the original file is preserved alongside the compressed version.
$ bzip2 -k input.txt
 Keep the Original File
Keep the Original File3. Decompress a File (-d Option)
The -d option is used for decompressing files that were previously compressed using bzip2.
$ bzip2 -d input.txt.bz2
 Decompress a File
Decompress a File4. Integrity Check (-t Option)
If you want to check whether a .bz2 file is corrupted without decompressing it, the -t option comes in handy. It checks the integrity of the file and informs you if it's corrupted.
$ bzip2 -t input.txt.bz2
 Integrity Check
Integrity Check5. Verbose Mode (-v Option)
The -v option enables verbose mode, where the command shows additional information, such as compression ratios and other diagnostics, during the compression process.
$ bzip2 -v input.txt
 Verbose Mode
Verbose ModeOther Available Options
| Option | Description |
|---|
-h, --help | Displays the help message and exits. |
|---|
-L, --license | Displays the software version, license terms, and conditions. |
|---|
-V, --version | Displays the software version and exits. |
|---|
-q, --quiet | Suppresses non-essential warning messages. Critical messages like I/O errors are still displayed. |
|---|
-f, --force | Forces overwriting of output files without confirmation. |
|---|
The bzip2 command is an essential tool for compressing files in Linux, especially when storage space is a concern. While it offers excellent compression ratios, its higher memory usage and slower decompression times make it better suited for specific use cases, such as long-term storage or data transfers where space efficiency is critical.
Explore
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Linux Administrator System