File System Navigation Commands in Linux
Last Updated :
01 Nov, 2025
Linux offers an alternative to the usual Windows and icons. The terminal might seem different at first, relying on text commands instead of a mouse. Linux organizes all files and directories under this single root, creating a unified structure. This design allows for consistent navigation and management of files across the system.
Commonly Used File System Navigation Commands
These commands help you navigate, organize, and manage files and directories within the Linux file system.
Linux Commands | Functions |
|---|
pwd | Shows the current location. |
|---|
ls | List files and folders. |
|---|
cd | Change working directory. |
|---|
mkdir | Used to create new folder. |
|---|
rmdir | Remove an empty folder. |
|---|
cp | Creating a copy of a file in a new location. |
|---|
mv | Relocate files from one folder to another. |
|---|
1. pwd (print working directory)
The pwd command shows the current location in the system. It tells you which folder you're currently in.
pwd

Observation
The current directory is /home/kali/Templates
2. ls (list files and directories)
The ls command is used to list the files and directories in the current directory. It provides an overview of what is inside a folder.
ls
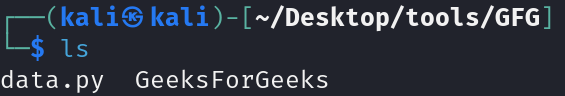
Observation
All the files and folders present inside the current folder is listed.
3. cd (change directory)
The cd command is used to move between folders. You can tell it exactly which folder you want to go to (like giving it an address), or you can use shortcuts to get around. Let's look into both the methods.
Moving around nearby folder
If you want to move into a folder that's within the one you're already in, you can just use its name. For instance, if you're in your home directory and want to reach downloads.
cd [directory name]
cd Downloads

Observation
A. checking the current directory
B. using cd command to change the directory
C. observe the updated directory
Going to a Specific Folder
Imagine telling someone the full address to find your house. Similarly, you can do the same by giving the complete path to the folder. For example, you want to access the documents folder inside the username folder.
cd [directory path]
cd /home/username/documents

Observation
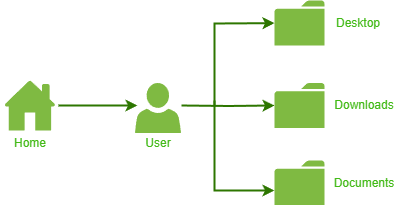 Directory Structure
Directory StructureConsidering the above directory structure, the active directory was changed from Downloads to Documents by traversing from the home directory.
4. mkdir (make directory)
The mkdir command, an abbreviation for "make directory," allows you to create new folders within your existing file system. This provides a structured way to categorize and store your files.
mkdir [directory name]
mkdir GeeksForGeeks
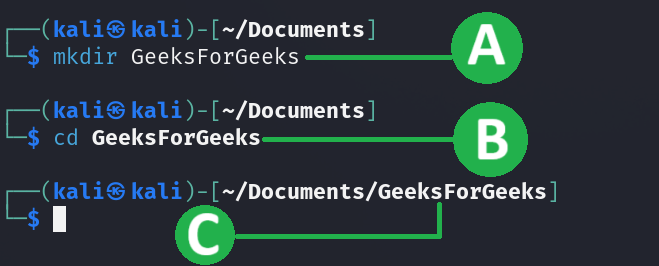
Observation
A. User tried to create a new folder named GeeksForGeeks
B. changed the directory to newly created directory
C. The active directory is updated
5. rmdir (remove empty directory)
The rmdir command, short for "remove directory," enables you to delete empty directories. This is useful for cleaning up unused folders and maintaining a streamlined file system.
The syntax for rmdir is:
rmdir [directory_name]
Note: rmdir can only delete empty directories.

Observation
Observe that the empty directory was removed.
6. cp (copy)
The cp command acts like a duplicator, creating a copy of a file in a new location.
cp [source_file] [location]
For instance, to copy "image.jpg" from Downloads to Pictures while keeping the original, you'd use
cp ~/Downloads/image.jpg ~/Pictures
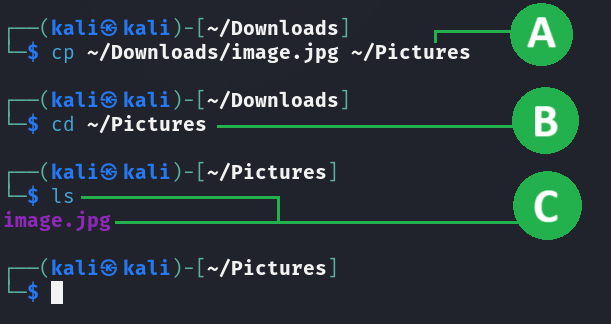
Obervation
A. Executing the copying command.
B. Changing the current active directory for checking.
C. Using the list command, we can observe that the image.jpg was copied.
7. mv (move)
The mv command is like a handy mover, allowing you to relocate files from one folder to another.
mv [source_file] [location]
For instance, to move a file named "image.jpg" from your Downloads folder to Documents, you'd use
mv ~/Downloads/image.jpg ~/Pictures
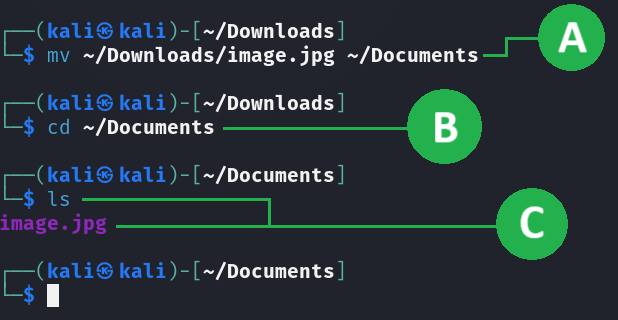
Observation
A. Executing the mv (move) command.
B. Changing the current active directory.
C. After executing ls (list) command, we can observe that the file has been transferred.
Difference between Windows and Linux File System
Windows and Linux differ significantly in how they organize, access, and manage files within their operating systems.
Feature | Windows | Linux |
|---|
Structure | Drives (C:, D:, etc.) and folders | Single, unified tree structure starting from root (/) |
|---|
Case Sensitivity | Not case-sensitive | Case-sensitive |
|---|
File Permissions | Simpler (user accounts) | More granular control (user, group, others) |
|---|
File System | Primarily NTFS | Ext4 (most common) FAT32, NTFS (sometimes) |
|---|
Overall Remarks | User-friendly, familiar interface | Flexible, powerful for advanced users |
|---|
Additional Shortcut Tips
These quick symbols help you navigate the Linux file system more efficiently.
Serial No | Symbol | Symbol Name | Function |
|---|
1 | ~ | tilde | shortcut to your home base |
|---|
2 | . | dot | the folder you're in right now |
|---|
3 | .. | double dot | the folder one level above |
|---|
1. ~ (tilde) - shortcut in Linux
This symbol is like a shortcut to your home base. No matter where you are, typing tilde will always bring you back to your home folder.
cd ~
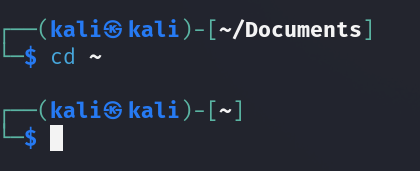
The active directory was updated to home.
2. . (dot) - shortcut in Linux
This simply means the folder you're in right now. If you're already inside a folder and want to work with something there, you can use the dot symbol.
3. .. (double dot) - shortcut in Linux
This means the folder one level above the one you're in, like going up a floor in a building. If you're deep inside folders and want to go back a step, this will take you to the bigger folder that contains the one you're in.
cd ..
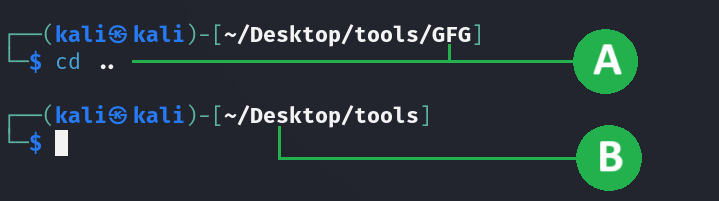
Observation
A. The current directory is visible, and we execute the command.
B. The active directory is updated.
4. tree - seeing the bigger picture in Linux
This command isn't exactly for moving around, but it helps you see all the folders at once. It shows how all the folders are connected, like a family tree, so you can understand the bigger picture.
tree
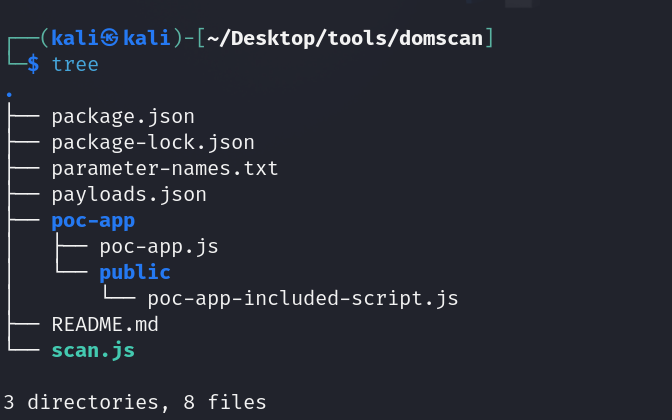
All the files and folders of the active directory is listed.
Which command shows your exact current directory path in the Linux filesystem?
Explanation:
pwd displays your present working directory so you always know where you are in the file tree.
You are inside /home/user/docs and want to go one level up to /home/user. Which shortcut should you use?
Explanation:
.. moves you exactly one directory upward from the current location.
What happens when you run rmdir testfolder?
-
It deletes the folder even if it has files
-
It only deletes an empty directory
-
It asks for confirmation before removal
-
It moves the folder to trash
Explanation:
rmdir can remove a directory only if no files are inside it.
Which command would correctly copy file.txt from Downloads to Documents without removing the original?
-
mv ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents
-
cp ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents
-
move ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents
-
copy ~/Downloads/file.txt ~/Documents
Explanation:
cp duplicates a file to a new location while keeping the original intact.
In Linux, what does the symbol ~ represent when used with cd?
Explanation:
~ is a direct shortcut to your user home directory from anywhere in the filesystem.
Quiz Completed Successfully
Your Score : 2/5
Accuracy : 0%
Login to View Explanation
1/5
1/5
< Previous
Next >
Explore
Getting Started with Linux
Installation with Linux
Linux Commands
Linux File System
Linux Kernel
Linux Networking Tools
Linux Process
Linux Firewall
Shell Scripting & Bash Scripting
Linux Administrator System