3D Scatter Plotting in Python using Matplotlib
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2025
A 3D Scatter Plot is a mathematical diagram that visualizes data points in three dimensions, allowing us to observe relationships between three variables of a dataset. Matplotlib provides a built-in toolkit called mplot3d, which enables three-dimensional plotting. To create a 3D Scatter Plot, we use the ax.scatter3D() function from Matplotlib's mplot3d module. This function requires three sets of values—X, Y, and Z coordinates—to define the position of each point in the 3D space. Example:
The following example demonstrates how to create a simple 3D scatter plot using ax.scatter3D().
Python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
np.random.seed(42)
x = np.random.rand(50)
y = np.random.rand(50)
z = np.random.rand(50)
# Create a figure and 3D axis
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Create scatter plot
ax.scatter3D(x, y, z, color='red', marker='o')
# Labels
ax.set_xlabel('X Axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Axis')
ax.set_title('Basic 3D Scatter Plot')
plt.show()
Output:

Explanation: In this example, we generate three sets of random data and use scatter3D() to visualize them in a 3D space. The points are marked in red with circular markers.
Installation and setup
Before proceeding, ensure you have Matplotlib installed. If not, install it using:
pip install matplotlib
Now, let's explore various examples to understand how 3D scatter plots work.
Example 1: 3D Scatter Plot with Color Mapping
To enhance visualization, we can use color mapping based on the Z-values of the data points.
Python
x = np.random.rand(100)
y = np.random.rand(100)
z = np.random.rand(100)
colors = z # Color mapped to z-values
# Create figure and 3D axis
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Scatter plot with color mapping
sc = ax.scatter3D(x, y, z, c=colors, cmap='viridis', marker='^')
plt.colorbar(sc, ax=ax, label='Z Value')
# Labels
ax.set_xlabel('X Axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Axis')
ax.set_title('3D Scatter Plot with Color Mapping')
plt.show()
Output:

Explanation: In this example, colors of the points are assigned based on the Z-values using the viridis colormap, making it easier to interpret variations in the dataset.
Example 2: 3D Scatter Plot with Different Markers and Sizes
To improve visualization, we can use different markers and vary the size of the points based on another dataset.
Python
x = np.random.rand(100)
y = np.random.rand(100)
z = np.random.rand(100)
sizes = 100 * np.random.rand(100) # Size of markers
colors = np.random.rand(100) # Color variation
# Create figure and 3D axis
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Scatter plot with varying marker size and colors
sc = ax.scatter3D(x, y, z, s=sizes, c=colors, cmap='coolwarm', alpha=0.7, marker='D')
plt.colorbar(sc, ax=ax, label='Color Mapping')
# Labels
ax.set_xlabel('X Axis')
ax.set_ylabel('Y Axis')
ax.set_zlabel('Z Axis')
ax.set_title('3D Scatter Plot with Different Markers and Sizes')
plt.show()
Output:

Explanation: Here, we adjust marker sizes randomly to improve visualization and use the coolwarm colormap to enhance the color distribution.
Example 3: Customization and additional features
This example demonstrates how to create a 3D surface plot using matplotlib and numpy while incorporating customization options to enhance visualization. The code plots a 3D function and applies various modifications, such as adjusting the viewing angle, enabling the grid and changing the background color.
Python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
Z = np.sin(np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2))
# Plot surface
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, cmap='viridis')
# Customization
ax.view_init(elev=30, azim=60) # Adjust view angle
ax.grid(True) # Add grid
ax.set_facecolor('lightgray') # Set background color
plt.show()
Output:
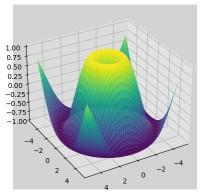 Customization and additional features
Customization and additional featuresExplanation: This code creates a 3D surface plot using Matplotlib. It generates X, Y coordinates using meshgrid. The surface is plotted with a viridis colormap. Customizations include adjusting the viewing angle, enabling the grid and changing the background color for better visualization.
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice