Importing Data in R Script
Last Updated :
14 Jul, 2025
We can read external datasets and operate with them in our R environment by importing data into an R script. R programming language offers a number of functions for importing data from various file formats. For this demonstration, we will use two examples of a single dataset, one in .csv form and another .txt
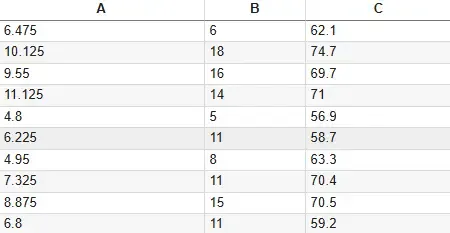 Dataset
DatasetYou can download the files from here.
1. Reading a Comma-Separated Value(CSV) File
CSV files are a widely used format for tabular data and R offers built-in functions to read them easily.
Method 1: Using read.csv() Function Read CSV Files into R
The function has two parameters:
- file.choose(): It opens a menu to choose a CSV file from the desktop.
- header: It is to indicate whether the first row of the dataset is a variable name or not. Apply T/True if the variable name is present else put F/False.
Example:
R
data1 <- read.csv(file.choose(), header=T)
data1
Output:
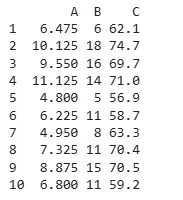 Output
Output
Method 2: Using read.table() Function
This function specifies how the dataset is separated, in this case we take sep=", " as an argument.
Example:
R
data2 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep=", ")
data2
Output:
 Output
Output
2. Reading a Tab-Delimited(txt) File
Tab-delimited files are commonly used for data exchange and R supports reading them with built-in methods.
Method 1: Using read.delim() Function
The function has two parameters:
- file.choose(): It opens a menu to choose a csv file from the desktop.
- header: It is to indicate whether the first row of the dataset is a variable name or not. Apply T/True if the variable name is present else put F/False.
Example:
R
data3 <- read.delim(file.choose(), header=T)
data3
Output:
 Output
OutputMethod 2: Using read.table() Function
This function specifies how the dataset is separated, in this case we take sep="\t" as the argument.
Example:
R
data4 <- read.table(file.choose(), header=T, sep="\t")
data4
Output:
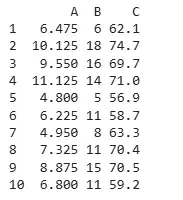 Output
Output3. Using R-Studio
Here we are going to import data through R studio with the following steps.
Steps:
- From the Environment tab click on the Import Dataset Menu.
.png) Importing Data in R Script
Importing Data in R Script- Select the file extension from the option.
.png) Importing Data in R Script
Importing Data in R Script- In the third step, a pop-up box will appear, either enter the file name or browse the desktop.
- The selected file will be displayed on a new window with its dimensions.
- In order to see the output on the console, type the filename.
4. Reading JSON Files in R
In order to work with JSON files in R, one needs to install the “rjson” package.
- fromJSON(): This function reads and parses a JSON file into an R object.
JSON file for demonstration:
{
"ID":["1","2","3","4","5"],
"Name":["Mithuna","Tanushree","Parnasha","Arjun","Pankaj"],
"Salary":["722.5","815.2","1611","2829","843.25"],
"StartDate":["6/17/2014","1/1/2012","11/15/2014","9/23/2013","5/21/2013"],
"Dept":["IT","IT","HR","Operations","Finance"]
}
R
library("rjson")
result <- fromJSON(file = "/content/example.json")
print(result)
Output:
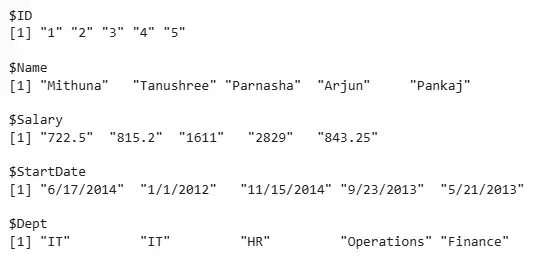 Output
OutputThe output shows the JSON data successfully read into R, with fields such as ID, Name, Salary, StartDate and Dept stored as vectors. This data can now be converted into a data frame for further analysis or manipulation.
Explore
Introduction
Fundamentals of R
Variables
Input/Output
Control Flow
Functions
Data Structures
Object Oriented Programming
Error Handling
File Handling