Top Talent On Demand
AI EngineersAndroid DevelopersAngularJS DevelopersBigCommerce DevelopersC# DevelopersC++ DevelopersData Visualization DevelopersDrupal DevelopersFront-end DevelopersHTML5 DevelopersiOS DevelopersJava DevelopersKubernetes DevelopersMagento DevelopersMobile App DevelopersNode.js DevelopersOdoo DevelopersPHP DevelopersPython DevelopersQA EngineersReact.js DevelopersRemote DevelopersRuby on Rails DevelopersSalesforce ConsultantsSalesforce DevelopersShopify DevelopersSoftware DevelopersSquarespace DevelopersSvelte DevelopersTechnical WritersWeb DevelopersWebRTC DevelopersWooCommerce DevelopersWordPress DevelopersWPF Developers
Toptal connects the top 3% of freelance developers all over the world.
Selection Sort
Animation, code, analysis, and discussion of selection sort on 4 initial conditions.
How to use: Press "Play all", or choose the 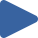 button.
button.
ALGORITHM
for i = 1:n,
k = i
for j = i+1:n, if a[j] < a[k], k = j
→ invariant: a[k] smallest of a[i..n]
swap a[i,k]
→ invariant: a[1..i] in final position
end
DISCUSSION
From the comparions presented here, one might conclude that selection sort should never be used. It does not adapt to the data in any way (notice that the four animations above run in lock step), so its runtime is always quadratic.
However, selection sort has the property of minimizing the number of swaps. In applications where the cost of swapping items is high, selection sort very well may be the algorithm of choice.
KEY
- Black values are sorted.
- Gray values are unsorted.
- A red triangle marks the algorithm position.
PROPERTIES
- Not stable
- O(1) extra space
- Θ(n2) comparisons
- Θ(n) swaps
- Not adaptive






