Java StringBuffer capacity() method returns the current capacity of StringBuffer object. In this tutorial, we will discuss the capacity() method in detail with the help of examples.
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); //default capacity 16 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(34); //capacity 34
Syntax of capacity() method
int cp = sb.capacity() //returns the capacity of sb
Here, sb is an object of StringBuffer class.
capacity() Description
public int capacity(): Returns the current capacity. If the current capacity is exhausted by adding new elements, the capacity is automatically increased using the following formula:
New Capacity = (Old Capacity*2)+2
capacity() Parameters
- It does not take any parameter.
capacity() Return Value
- It returns an integer value, which represents the current capacity of StringBuffer object.
Example 1: Capacity of different char sequences
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("Nice Guide");
/* Capacity of newly created StringBuffer instance
* = length of string "Nice Guide" + 16
* i.e 10+16 =26
*/
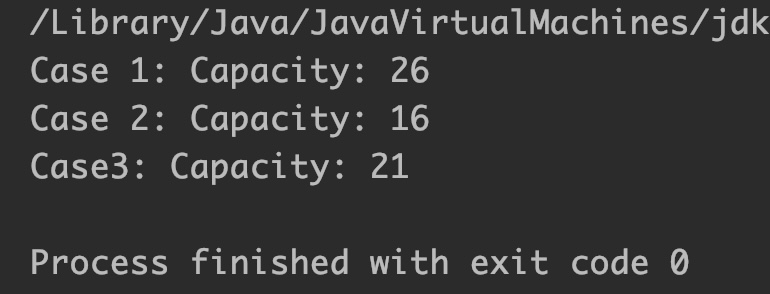
System.out.println("Case 1: Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
StringBuffer sb2 = new StringBuffer(); //default 16
System.out.println("Case 2: Capacity: "+sb2.capacity());
StringBuffer sb3 = new StringBuffer("Hello");
/* Capacity = length of String "Hello"+ default capacity
* i.e 5+16 =21
*/
System.out.println("Case3: Capacity: "+sb3.capacity());
}
}
Output:
Example 2: Capacity automatically increased
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
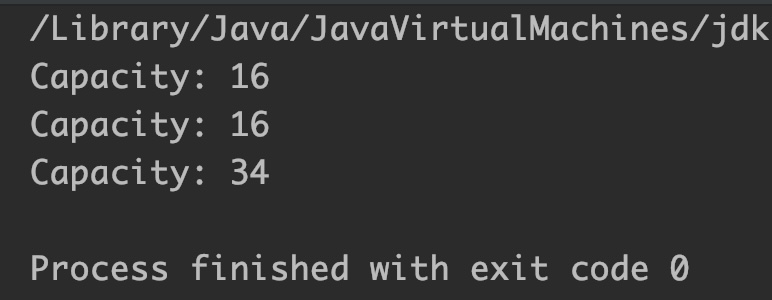
System.out.println("Capacity: "+sb.capacity()); //default 16
sb.append("Welcome"); // capacity is not exhausted
System.out.println("Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
//appending 17 new chars in the sequence
//so sequence now has 24 chars, which cant be adjusted
// in default capacity so capacity is increased
// new capacity = (16*2)+2 = 34
sb.append(" to beginnersbook");
System.out.println("Capacity: "+sb.capacity());
}
}
Output:
Example 3: Trim non utilized capacity
To trim the free capacity, we can use StringBuffer trimToSize() method as shown below:
class JavaExample{
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("Welcome to BeginnersBook.com"); //16*2+2 = 34
System.out.println("Capacity: "+sb.capacity()); //34
//we appended 28 characters, capacity is increased from 16 to 34
//if we want to trim extra capacity and free memory
sb.trimToSize();
System.out.println("Capacity after trim: "+sb.capacity());
}
}
Output:
