C Arithmetic operators are used to perform mathematical operations. There are five fundamental arithmetic operators supported by C language, which are addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(-), division(/) and modulus(%) of two numbers.
All arithmetic operators compute the result of specific arithmetic operation and returns its result.
| Operator | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Adds two numbers | a + b | 15 + 5 = 20 |
| – | Subtracts two numbers | a – b | 15 – 5 = 10 |
| * | Multiplies two numbers | a * b | 15 * 5 = 75 |
| / | Divides numerator by denominator | a / b | 15 / 5 = 3 |
| % | Returns remainder after an integer division | a % b | 15 % 5 = 0 |
C Program to perform Arithmetic Operations on Two Numbers
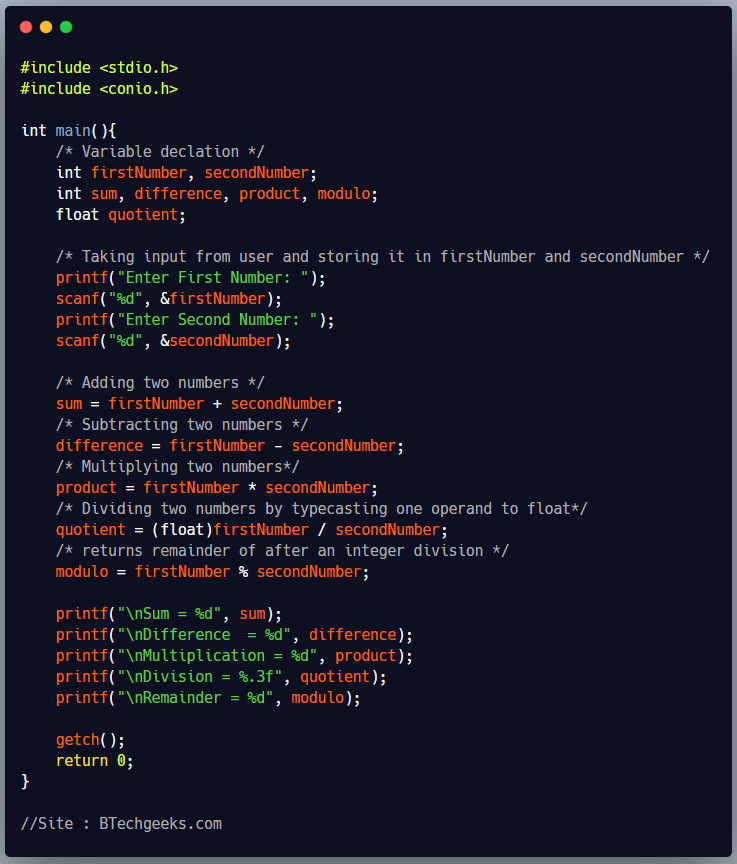
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main(){
/* Variable declation */
int firstNumber, secondNumber;
int sum, difference, product, modulo;
float quotient;
/* Taking input from user and storing it in firstNumber and secondNumber */
printf("Enter First Number: ");
scanf("%d", &firstNumber);
printf("Enter Second Number: ");
scanf("%d", &secondNumber);
/* Adding two numbers */
sum = firstNumber + secondNumber;
/* Subtracting two numbers */
difference = firstNumber - secondNumber;
/* Multiplying two numbers*/
product = firstNumber * secondNumber;
/* Dividing two numbers by typecasting one operand to float*/
quotient = (float)firstNumber / secondNumber;
/* returns remainder of after an integer division */
modulo = firstNumber % secondNumber;
printf("\nSum = %d", sum);
printf("\nDifference = %d", difference);
printf("\nMultiplication = %d", product);
printf("\nDivision = %.3f", quotient);
printf("\nRemainder = %d", modulo);
getch();
return 0;
}
Output
Enter First Number: 25 Enter Second Number: 4 Sum = 29 Difference = 21 Multiplication = 100 Division = 6.250 Remainder = 1
