Pointers to structure: The pointers to a structure in C in very similar to the pointer to any in-built data type variable.
The syntax for declaring a pointer to structure variable is as follows:
struct structure_name *pointer_variable
For Example
struct Employee
{
char name[50];
int age;
float salary;
}employee_one;
struct Employee *employee_ptr;
We can use addressOf operator(&) to get the address of structure variable.
struct Employee *employee_ptr = &employee_one;
To access the member variable using a pointer to a structure variable we can use arrow operator(->). We can access member variable by using pointer variable followed by an arrow operator and then the name of the member variable.
To access a member variable of structure using variable identifier we use dot(.) operator whereas we use arrow(->) operator to access member variable using structure pointer.
employee_ptr->salary;
C Program to print the members of a structure using Pointer and Arrow Operators
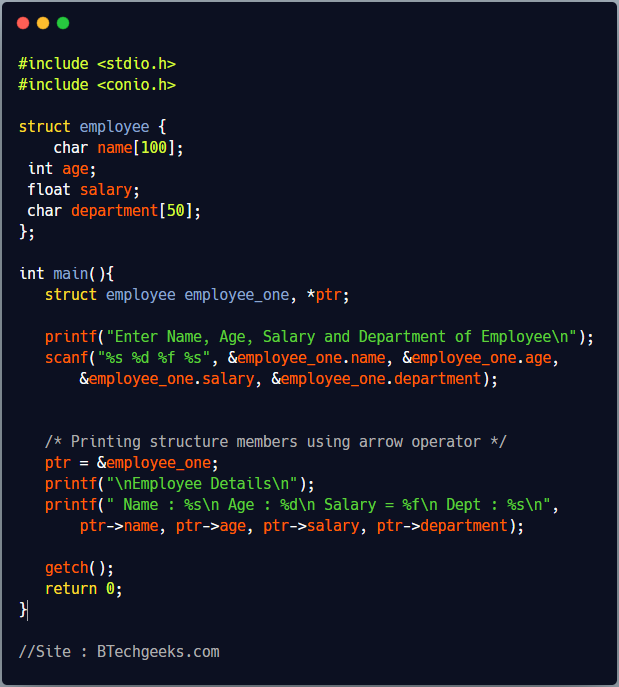
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
struct employee {
char name[100];
int age;
float salary;
char department[50];
};
int main(){
struct employee employee_one, *ptr;
printf("Enter Name, Age, Salary and Department of Employee\n");
scanf("%s %d %f %s", &employee_one.name, &employee_one.age,
&employee_one.salary, &employee_one.department);
/* Printing structure members using arrow operator */
ptr = &employee_one;
printf("\nEmployee Details\n");
printf(" Name : %s\n Age : %d\n Salary = %f\n Dept : %s\n",
ptr->name, ptr->age, ptr->salary, ptr->department);
getch();
return 0;
}
Output
Enter Name, Age, Salary and Department of Employee Jack 30 1234.5 Sales Employee Details Name : Jack Age : 30 Salary = 1234.500000 Dept : Sales
