At present, the gathering of SQL Server configuration information is no longer a problem— the opportunities to add value through an update and to build a stable database environment exist permanently. Most of the third party tools provide the appropriate functionality in order to capture the software market. Through this guide, you’ll figure out the ways to capture few SQL Server configurations and manipulate the data by using PowerShell.
Moreover, you will get the answers to the following questions:
- How to gather SQL Server configuration
- How to automatically discover SQL instances
- How to manually input the SQL Server instances to speed up the process
- How to transform data by using PowerShell
- And more…
Getting Started
In this article, we’ll go over an existing example of using PowerShell and SQL Server. Proper tuning up the configuration parameters will always produce a better performance. In the appendix section, you will be able to see a full-length script to query the configuration settings. The output can be used as a baseline for your instance and your databases for performance troubleshooting.
Introduction
In a moment, we’ll see how to audit the SQL Server configuration details of the database environment. In our case, we will talk about how to list XP_CMDSHELL, SQL Server Memory Settings—Max and Min memory configurations, and Traceflags property values across the SQL instances.
XP_CMDSHELL
The xp_cmdshell is a configuration property that enables the required option to execute the extended stored procedure inside the system.
Note: The xp_cmdshell is disabled by default. There are several instances where the legacy application may require this feature to be enabled. It is critical to consider this option enabled because it has several security implications and risks.
In the following PowerShell code, the configuration class of SQL Server management objects is instantiated in order to get the configvalue parameter of each SQL Server instance.
Note: the XPCmdShellEnabled property that is used to get the ConfigProperty or configvalue object, is used to configure XP_CMDSHELL configuration in our case.
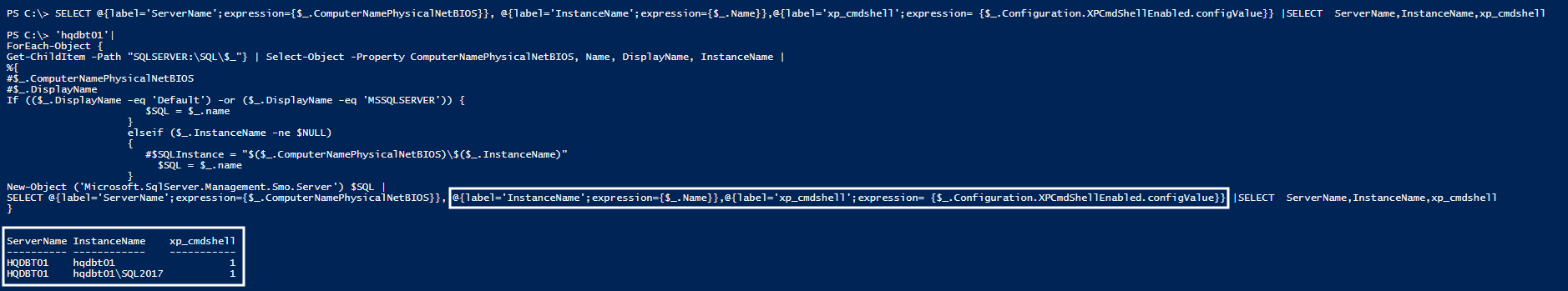
The following PowerShell code lists the configuration value for the XP_CMDSHELL property of the listed server ‘hqdbt01’:
'hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}}, @{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}},@{label='xp_cmdshell';expression= {$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}} |SELECT ServerName,InstanceName,xp_cmdshell
}
In this section, you’ll learn how to display a custom header named xp_cmdshell along with the customized value for that property. xp_cmdshell configuration is explained in detail.
Note: To get property of configuration class, you need to use $_ as it represents the current scope of SMO class ‘Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server’ in the pipeline extended with the configuration class that uses a dot membership operator to get the property of xp_cmdshell.
SELECT @{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}},@{label='xp_cmdshell';expression= {$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}}
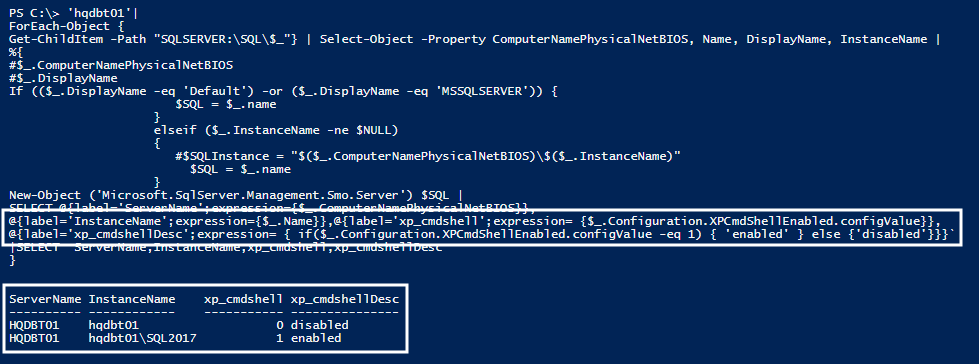
Next, you’ll learn how to use the condition statement in the expression operation. In the following code, you can see the usage of IF statement in the expression. The IF statement runs the conditional block, in this case, $_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue. It is evaluated for ‘1’ to return Enabled. For other values, it returns Disabled.
@{label='xp_cmdshellDesc';expression= { if($_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue -eq 1) { 'enabled' } else {'disabled'}}}
Let’s see the PowerShell code to retrieve the xp_cmdshell description using “if” statement in the expression.
'hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}},
@{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}},@{label='xp_cmdshell';expression= {$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='xp_cmdshellDesc';expression= { if($_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue -eq 1) { 'enabled' } else {'disabled'}}}`
|SELECT ServerName,InstanceName,xp_cmdshell,xp_cmdshellDesc
}
SQL Server Memory Settings
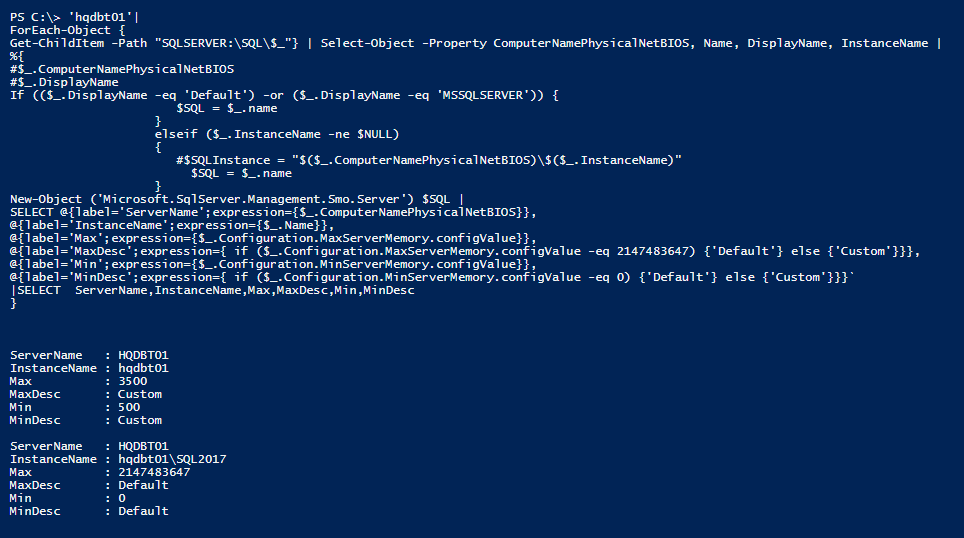
SQL Server memory settings have two options: “max_memory” setting and “min_memory” setting. Now, learn how to list the configured values of memory parameters of all the listed servers.
Note: By default, min server memory setting is configured with a 0 value, and the max server memory is configured with 2,147,483,647 MB. On another note, by default, the SQL Server engine will manage memory requirements more dynamically.
The following PowerShell code gathers the memory setting of all the SQL instances that are listed in the input servers.
'hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}},
@{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}},
@{label='Max';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='MaxDesc';expression={ if ($_.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.configValue -eq 2147483647) {'Default'} else {'Custom'}}},
@{label='Min';expression={$_.Configuration.MinServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='MinDesc';expression={ if ($_.Configuration.MinServerMemory.configValue -eq 0) {'Default'} else {'Custom'}}}`
|SELECT ServerName,InstanceName,Max,MaxDesc,Min,MinDesc
}
In the following screenshot, you can see that the memory-related properties MaxServerMemory.configValue and MinServerMemory.configValue are gathered in order to use the same method as described in the XP_CMDSHELL section.
OS and SQL Wildcard expression
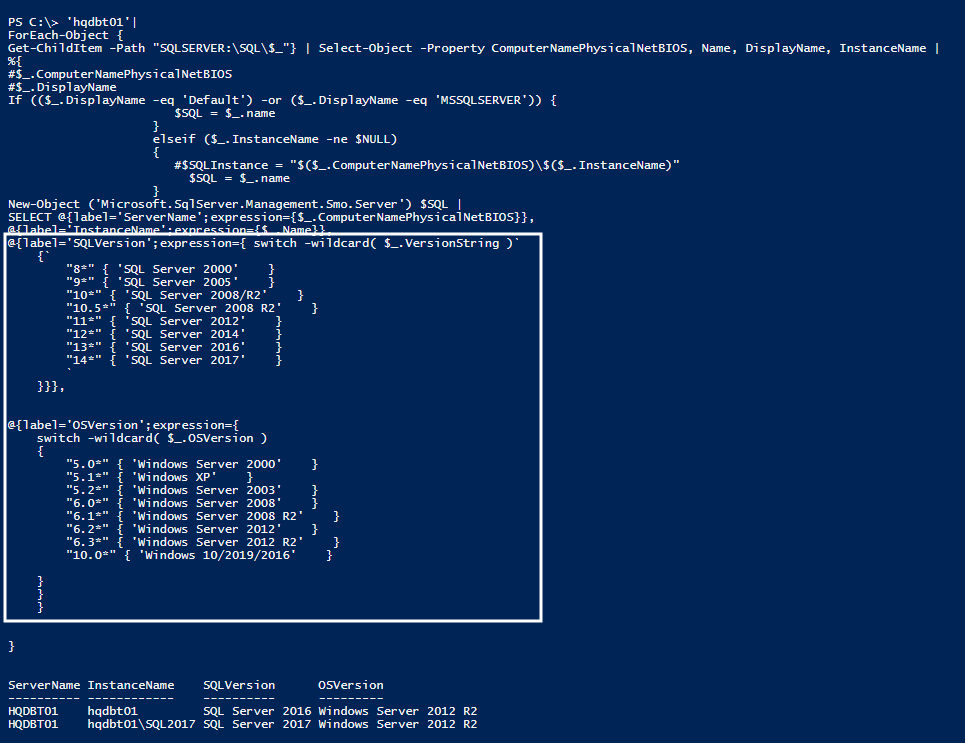
In this section, we’ll see how to use PowerShell regular expression with a “switch” statement in the expression statement.
Wildcard characters are forms of regular expression. In this case, the wildcard character is represented by an asterisk and is used to represent any character that can be repeated any number of times. In this case, you’ll see asterisk wildcard that is used with the “switch” statement.
'hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}},
@{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}},
@{label='SQLVersion';expression={ switch -wildcard( $_.VersionString )`
{`
"8*" { 'SQL Server 2000' }
"9*" { 'SQL Server 2005' }
"10*" { 'SQL Server 2008/R2' }
"10.5*" { 'SQL Server 2008 R2' }
"11*" { 'SQL Server 2012' }
"12*" { 'SQL Server 2014' }
"13*" { 'SQL Server 2016' }
"14*" { 'SQL Server 2017' }
`
}}},
@{label='OSVersion';expression={
switch -wildcard( $_.OSVersion )
{
"5.0*" { 'Windows Server 2000' }
"5.1*" { 'Windows XP' }
"5.2*" { 'Windows Server 2003' }
"6.0*" { 'Windows Server 2008' }
"6.1*" { 'Windows Server 2008 R2' }
"6.2*" { 'Windows Server 2012' }
"6.3*" { 'Windows Server 2012 R2' }
"10.0*" { 'Windows 10/2019/2016' }
}
}
}
}
The “switch” statement is an extension of IF-ELSE conditional statement. In this demo, it will retrieve a versionString and OSVersion properties of the SQL Server object and its compared values to print the respective OS and SQL Server version. The usage of the ‘*’ wildcard in the statement includes the same logic just as the LIKE operator to match each field.
Note: The Switch statement is actually a nested IF-ELSE statement.
Next, let’s put all together to retrieve a set of configuration values by using PowerShell. In the following PowerShell code, replace the input array of servers.
[expand title =”Code“]
#An array to hold the output values
$Results=@()
#Input server names for the configuration listing
'hqmesrp01','hqmesrp02','hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
$a=''
$inv=New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}}, @{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}} ,@{label='Max';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='Min';expression={$_.Configuration.MinServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='xp_cmdshell';expression= {$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='xp_cmdshell1';expression= { if($_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue -eq 1) { 'enabled' } else {'disabled'}}},
@{label='SQLVersion';expression={ switch -wildcard( $_.VersionString )`
{`
"8*" { 'SQL Server 2000' }`
"9*" { 'SQL Server 2005' }`
"10*" { 'SQL Server 2008/R2' }`
"10.5*" { 'SQL Server 2008 R2' }`
"11*" { 'SQL Server 2012' }`
"12*" { 'SQL Server 2014' }`
"13*" { 'SQL Server 2016' }`
"14*" { 'SQL Server 2017' }`
`
}}},
@{label='OSVersion';expression={
switch -wildcard( $_.OSVersion )
{
"5.0*" { 'Windows Server 2000' }
"5.1*" { 'Windows XP' }
"5.2*" { 'Windows Server 2003' }
"6.0*" { 'Windows Server 2008' }
"6.1*" { 'Windows Server 2008 R2' }
"6.2*" { 'Windows Server 2012' }
"6.3*" { 'Windows Server 2012 R2/8.1' }
"10.0*" { 'Windows 10/2019/2016' }
}
}
},
@{label='Traceflag';expression={ $_.EnumActiveGlobalTraceFlags()| % {
[string]$b=$_.status
[string]$c=$_.TraceFlag
$a+=$c.ToString() +'->'+ $b.ToString()+ ' '
}
$a
}
}
ForEach($i in $inv)
{
$Properties = @{Name=$i.ServerName
InstanceName =$i.InstanceName
MaxMemory=$i.Max
MinMemory=$i.Min
xp_cmdshell=$i.xp_cmdshell
xp_cmdshellStatus=$i.xp_cmdshell1
SQLVersion=$i.SQLVersion
OSVersion=$i.OSVersion
Traceflag=$i.Traceflag
}
$Results += New-Object psobject -Property $properties
}
}
$Results |Select Name,InstanceName,OSVersion,SQLVersion,xp_cmdshell,xp_cmdshellStatus,Traceflag,MinMemory,MaxMemory| format-table -AutoSize
[/expand]
The output is a formatted list of configuration values generated via using SQL Server Managed objects along with the data transformation using PowerShell techniques.
Summary
This guide is an effort to outline some of the SQL Server information and configuration, such as xp_cmdshell, memory settings, trace flag, os version, and SQL version. It is recommended to use the above snippets to gather other properties of your choice using SMO (SQL Server Management Object) configuration class. You’ll also learn the tips to use a conditional statement, switch statement and looping statement in the expression statement using PowerShell.
I hope you liked this article. Please, leave your feedback in the comment section.
Appendix
[expand title =”Code“]
#Output file to hold the list
$Outputfile='c:\output.csv'
#An array to hold the output values
$Results=@()
'hqmesrp01','hqmesrp02','hqdbt01'|
ForEach-Object {
Get-ChildItem -Path "SQLSERVER:\SQL\$_"} | Select-Object -Property ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS, Name, DisplayName, InstanceName |
%{
#$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS
#$_.DisplayName
If (($_.DisplayName -eq 'Default') -or ($_.DisplayName -eq 'MSSQLSERVER')) {
$SQL = $_.name
}
elseif ($_.InstanceName -ne $NULL)
{
#$SQLInstance = "$($_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS)\$($_.InstanceName)"
$SQL = $_.name
}
$inv=New-Object ('Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server') $SQL |
SELECT @{label='ServerName';expression={$_.ComputerNamePhysicalNetBIOS}}, @{label='InstanceName';expression={$_.Name}} ,@{label='Max';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='Min';expression={$_.Configuration.MinServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='AdHocDistributedQueriesEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.AdHocDistributedQueriesEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='Affinity64IOMask';expression={$_.Configuration.Affinity64IOMask.configValue}},
@{label='Affinity64Mask';expression={$_.Configuration.Affinity64Mask.configValue}},
@{label='xp_cmdshell';expression= {$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='xp_cmdshell1';expression= { if($_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue -eq 1) { 'enabled' } else {'disabled'}}},
@{label='AgentXPsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.AgentXPsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='AllowUpdates';expression={$_.Configuration.AllowUpdates.configValue}},
@{label='AweEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.AweEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='BlockedProcessThreshold';expression={$_.Configuration.BlockedProcessThreshold.configValue}},
@{label='C2AuditMode';expression={$_.Configuration.C2AuditMode.configValue}},
@{label='CommonCriteriaComplianceEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.CommonCriteriaComplianceEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='ContainmentEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.ContainmentEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='CostThresholdForParallelism';expression={$_.Configuration.CostThresholdForParallelism.configValue}},
@{label='CrossDBOwnershipChaining';expression={$_.Configuration.CrossDBOwnershipChaining.configValue}},
@{label='CursorThreshold';expression={$_.Configuration.CursorThreshold.configValue}},
@{label='DatabaseMailEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.DatabaseMailEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='DefaultBackupCompression';expression={$_.Configuration.DefaultBackupCompression.configValue}},
@{label='DefaultFullTextLanguage';expression={$_.Configuration.DefaultFullTextLanguage.configValue}},
@{label='DefaultLanguage';expression={$_.Configuration.DefaultLanguage.configValue}},
@{label='DefaultTraceEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.DefaultTraceEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='DisallowResultsFromTriggers';expression={$_.Configuration.DisallowResultsFromTriggers.configValue}},
@{label='ExtensibleKeyManagementEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.ExtensibleKeyManagementEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='FilestreamAccessLevel';expression={$_.Configuration.FilestreamAccessLevel.configValue}},
@{label='FillFactor';expression={$_.Configuration.FillFactor.configValue}},
@{label='FullTextCrawlBandwidthMax';expression={$_.Configuration.FullTextCrawlBandwidthMax.configValue}},
@{label='FullTextCrawlBandwidthMin';expression={$_.Configuration.FullTextCrawlBandwidthMin.configValue}},
@{label='FullTextCrawlRangeMax';expression={$_.Configuration.FullTextCrawlRangeMax.configValue}},
@{label='FullTextNotifyBandwidthMax';expression={$_.Configuration.FullTextNotifyBandwidthMax.configValue}},
@{label='FullTextNotifyBandwidthMin';expression={$_.Configuration.FullTextNotifyBandwidthMin.configValue}},
@{label='IndexCreateMemory';expression={$_.Configuration.IndexCreateMemory.configValue}},
@{label='InDoubtTransactionResolution';expression={$_.Configuration.InDoubtTransactionResolution.configValue}},
@{label='IsSqlClrEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.IsSqlClrEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='LightweightPooling';expression={$_.Configuration.LightweightPooling.configValue}},
@{label='Locks';expression={$_.Configuration.Locks.configValue}},
@{label='MaxDegreeOfParallelism';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxDegreeOfParallelism.configValue}},
@{label='MaxServerMemory';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='MaxWorkerThreads';expression={$_.Configuration.MaxWorkerThreads.configValue}},
@{label='MediaRetention';expression={$_.Configuration.MediaRetention.configValue}},
@{label='MinMemoryPerQuery';expression={$_.Configuration.MinMemoryPerQuery.configValue}},
@{label='MinServerMemory';expression={$_.Configuration.MinServerMemory.configValue}},
@{label='NestedTriggers';expression={$_.Configuration.NestedTriggers.configValue}},
@{label='NetworkPacketSize';expression={$_.Configuration.NetworkPacketSize.configValue}},
@{label='OleAutomationProceduresEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.OleAutomationProceduresEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='OpenObjects';expression={$_.Configuration.OpenObjects.configValue}},
@{label='OptimizeAdhocWorkloads';expression={$_.Configuration.OptimizeAdhocWorkloads.configValue}},
@{label='Parent';expression={$_.Configuration.Parent.configValue}},
@{label='PrecomputeRank';expression={$_.Configuration.PrecomputeRank.configValue}},
@{label='PriorityBoost';expression={$_.Configuration.PriorityBoost.configValue}},
@{label='Properties';expression={$_.Configuration.Properties.configValue}},
@{label='ProtocolHandlerTimeout';expression={$_.Configuration.ProtocolHandlerTimeout.configValue}},
@{label='QueryGovernorCostLimit';expression={$_.Configuration.QueryGovernorCostLimit.configValue}},
@{label='QueryWait';expression={$_.Configuration.QueryWait.configValue}},
@{label='RecoveryInterval';expression={$_.Configuration.RecoveryInterval.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteAccess';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteAccess.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteDacConnectionsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteDacConnectionsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteDataArchiveEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteDataArchiveEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteLoginTimeout';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteLoginTimeout.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteProcTrans';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteProcTrans.configValue}},
@{label='RemoteQueryTimeout';expression={$_.Configuration.RemoteQueryTimeout.configValue}},
@{label='ReplicationMaxTextSize';expression={$_.Configuration.ReplicationMaxTextSize.configValue}},
@{label='ReplicationXPsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.ReplicationXPsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='ScanForStartupProcedures';expression={$_.Configuration.ScanForStartupProcedures.configValue}},
@{label='ServerTriggerRecursionEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.ServerTriggerRecursionEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='SetWorkingSetSize';expression={$_.Configuration.SetWorkingSetSize.configValue}},
@{label='ShowAdvancedOptions';expression={$_.Configuration.ShowAdvancedOptions.configValue}},
@{label='SmoAndDmoXPsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.SmoAndDmoXPsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='SqlMailXPsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.SqlMailXPsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='TransformNoiseWords';expression={$_.Configuration.TransformNoiseWords.configValue}},
@{label='TwoDigitYearCutoff';expression={$_.Configuration.TwoDigitYearCutoff.configValue}},
@{label='UserConnections';expression={$_.Configuration.UserConnections.configValue}},
@{label='UserInstancesEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.UserInstancesEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='UserInstanceTimeout';expression={$_.Configuration.UserInstanceTimeout.configValue}},
@{label='UserOptions';expression={$_.Configuration.UserOptions.configValue}},
@{label='WebXPsEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.WebXPsEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='XPCmdShellEnabled';expression={$_.Configuration.XPCmdShellEnabled.configValue}},
@{label='SQLVersion';expression={ switch -wildcard( $_.VersionString )`
{`
"8*" { 'SQL Server 2000' }`
"9*" { 'SQL Server 2005' }`
"10*" { 'SQL Server 2008/R2' }`
"10.5*" { 'SQL Server 2008 R2' }`
"11*" { 'SQL Server 2012' }`
"12*" { 'SQL Server 2014' }`
"13*" { 'SQL Server 2016' }`
"14*" { 'SQL Server 2017' }`
`
}}},
@{label='OSVersion';expression={
switch -wildcard( $_.OSVersion )
{
"5.0*" { 'Windows Server 2000' }
"5.1*" { 'Windows XP' }
"5.2*" { 'Windows Server 2003' }
"6.0*" { 'Windows Server 2008' }
"6.1*" { 'Windows Server 2008 R2' }
"6.2*" { 'Windows Server 2012' }
"6.3*" { 'Windows Server 2012 R2/8.1' }
"10.0*" { 'Windows 10/2019/2016' }
}
}
},
@{label='Traceflag';expression={ $_.EnumActiveGlobalTraceFlags()| % {
[string]$b=$_.status
[string]$c=$_.TraceFlag
$a+=$c.ToString() +'->'+ $b.ToString()+ ' '
}
$a
}
}
ForEach($i in $inv)
{
$Properties = @{Name=$i.ServerName
InstanceName =$i.InstanceName
MaxMemory=$i.Max
MinMemory=$i.Min
xp_cmdshell=$i.xp_cmdshell
xp_cmdshellStatus=$i.xp_cmdshell1
SQLVersion=$i.SQLVersion
OSVersion=$i.OSVersion
Traceflag=$i.Traceflag
AdHocDistributedQueriesEnabled=$i.AdHocDistributedQueriesEnabled
Affinity64IOMask=$i.Affinity64IOMask
Affinity64Mask=$i.Affinity64Mask
AffinityIOMask=$i.AffinityIOMask
AffinityMask=$i.AffinityMask
AgentXPsEnabled=$i.AgentXPsEnabled
AllowUpdates=$i.AllowUpdates
AweEnabled=$i.AweEnabled
BlockedProcessThreshold=$i.BlockedProcessThreshold
C2AuditMode=$i.C2AuditMode
CommonCriteriaComplianceEnabled=$i.CommonCriteriaComplianceEnabled
ContainmentEnabled=$i.ContainmentEnabled
CostThresholdForParallelism=$i.CostThresholdForParallelism
CrossDBOwnershipChaining=$i.CrossDBOwnershipChaining
CursorThreshold=$i.CursorThreshold
DatabaseMailEnabled=$i.DatabaseMailEnabled
DefaultBackupCompression=$i.DefaultBackupCompression
DefaultFullTextLanguage=$i.DefaultFullTextLanguage
DefaultLanguage=$i.DefaultLanguage
DefaultTraceEnabled=$i.DefaultTraceEnabled
DisallowResultsFromTriggers=$i.DisallowResultsFromTriggers
ExtensibleKeyManagementEnabled=$i.ExtensibleKeyManagementEnabled
FilestreamAccessLevel=$i.FilestreamAccessLevel
FillFactor=$i.FillFactor
FullTextCrawlBandwidthMax=$i.FullTextCrawlBandwidthMax
FullTextCrawlBandwidthMin=$i.FullTextCrawlBandwidthMin
FullTextCrawlRangeMax=$i.FullTextCrawlRangeMax
FullTextNotifyBandwidthMax=$i.FullTextNotifyBandwidthMax
FullTextNotifyBandwidthMin=$i.FullTextNotifyBandwidthMin
IndexCreateMemory=$i.IndexCreateMemory
InDoubtTransactionResolution=$i.InDoubtTransactionResolution
IsSqlClrEnabled=$i.IsSqlClrEnabled
LightweightPooling=$i.LightweightPooling
Locks=$i.Locks
MaxDegreeOfParallelism=$i.MaxDegreeOfParallelism
MaxServerMemory=$i.MaxServerMemory
MaxWorkerThreads=$i.MaxWorkerThreads
MediaRetention=$i.MediaRetention
MinMemoryPerQuery=$i.MinMemoryPerQuery
MinServerMemory=$i.MinServerMemory
NestedTriggers=$i.NestedTriggers
NetworkPacketSize=$i.NetworkPacketSize
OleAutomationProceduresEnabled=$i.OleAutomationProceduresEnabled
OpenObjects=$i.OpenObjects
OptimizeAdhocWorkloads=$i.OptimizeAdhocWorkloads
Parent=$i.Parent
PrecomputeRank=$i.PrecomputeRank
PriorityBoost=$i.PriorityBoost
ProtocolHandlerTimeout=$i.ProtocolHandlerTimeout
QueryGovernorCostLimit=$i.QueryGovernorCostLimit
QueryWait=$i.QueryWait
RecoveryInterval=$i.RecoveryInterval
RemoteAccess=$i.RemoteAccess
RemoteDacConnectionsEnabled=$i.RemoteDacConnectionsEnabled
RemoteDataArchiveEnabled=$i.RemoteDataArchiveEnabled
RemoteLoginTimeout=$i.RemoteLoginTimeout
RemoteProcTrans=$i.RemoteProcTrans
RemoteQueryTimeout=$i.RemoteQueryTimeout
ReplicationMaxTextSize=$i.ReplicationMaxTextSize
ReplicationXPsEnabled=$i.ReplicationXPsEnabled
ScanForStartupProcedures=$i.ScanForStartupProcedures
ServerTriggerRecursionEnabled=$i.ServerTriggerRecursionEnabled
SetWorkingSetSize=$i.SetWorkingSetSize
ShowAdvancedOptions=$i.ShowAdvancedOptions
SmoAndDmoXPsEnabled=$i.SmoAndDmoXPsEnabled
SqlMailXPsEnabled=$i.SqlMailXPsEnabled
TransformNoiseWords=$i.TransformNoiseWords
TwoDigitYearCutoff=$i.TwoDigitYearCutoff
UserConnections=$i.UserConnections
UserInstancesEnabled=$i.UserInstancesEnabled
UserInstanceTimeout=$i.UserInstanceTimeout
UserOptions=$i.UserOptions
WebXPsEnabled=$i.WebXPsEnabled
XPCmdShellEnabled=$i.XPCmdShellEnabled
}
$Results += New-Object psobject -Property $properties
}
}
$Results |Select Name,InstanceName,OSVersion,SQLVersion,xp_cmdshell,xp_cmdshellStatus,Traceflag,MinMemory,MaxMemory,AdHocDistributedQueriesEnabled,Affinity64IOMask,Affinity64Mask,AffinityIOMask,AffinityMask,AgentXPsEnabled,AllowUpdates,AweEnabled,BlockedProcessThreshold,C2AuditMode,CommonCriteriaComplianceEnabled,ContainmentEnabled,CostThresholdForParallelism,CrossDBOwnershipChaining,CursorThreshold,DatabaseMailEnabled,DefaultBackupCompression,DefaultFullTextLanguage,DefaultLanguage,DefaultTraceEnabled,DisallowResultsFromTriggers,ExtensibleKeyManagementEnabled,FilestreamAccessLevel,FillFactor,FullTextCrawlBandwidthMax,FullTextCrawlBandwidthMin,FullTextCrawlRangeMax,FullTextNotifyBandwidthMax,FullTextNotifyBandwidthMin,IndexCreateMemory,InDoubtTransactionResolution,IsSqlClrEnabled,LightweightPooling,Locks,MaxDegreeOfParallelism,MaxServerMemory,MaxWorkerThreads,MediaRetention,MinMemoryPerQuery,MinServerMemory,NestedTriggers,NetworkPacketSize,OleAutomationProceduresEnabled,OpenObjects,OptimizeAdhocWorkloads,Parent,PrecomputeRank,PriorityBoost,Properties,ProtocolHandlerTimeout,QueryGovernorCostLimit,QueryWait,RecoveryInterval,RemoteAccess,RemoteDacConnectionsEnabled,RemoteDataArchiveEnabled,RemoteLoginTimeout,RemoteProcTrans,RemoteQueryTimeout,ReplicationMaxTextSize,ReplicationXPsEnabled,ScanForStartupProcedures,ServerTriggerRecursionEnabled,SetWorkingSetSize,ShowAdvancedOptions,SmoAndDmoXPsEnabled,SqlMailXPsEnabled,TransformNoiseWords,TwoDigitYearCutoff,UserConnections,UserInstancesEnabled,UserInstanceTimeout,UserOptions,WebXPsEnabled,XPCmdShellEnabled| Export-Csv $outputfile
[/expand]
Tags: powershell, sql, sql server Last modified: September 22, 2021