In this article, we will help you understand how to read and write binary files in Java. File handling in Java is an important topic that helps you to store and manipulate data.
If you have just started your Java programming journey, binary file handling in Java is a topic that you should not skip. This article will help you to grasp the concept of file handling in Java with ease.
So, without waiting any further, let us start learning!
TL;DR: Read And Write Binary Files In Java
Aspect | Summary |
What Are Binary Files? | Binary files store raw bytes (not characters) and are used for images, audio, video, compiled code, and structured data. Compact, fast, and efficient for non-text data. |
Importance | Used in game development, media apps, data serialization, networking, and IoT due to fast access, no encoding issues, and the ability to store any structured data. |
Reading Binary Files | To read binary files, use the FileInputStream and DataInputStream. Some common methods are readInt(), readDouble(), readUTF(). |
Writing Binary Files | To write binary files, use FileOutputStream and DataOutputStream. Some common methods are writeInt(), writeDouble(), writeUTF(). |
Best Practices | Handle exceptions like IOException, FileNotFoundException, use buffering like BufferedInputStream, and BufferedOutputStream. |
Introduction To Binary Files In Java
Nowadays, we are surrounded by a lot of data. Have you ever wondered if the images, audio files, and videos that you play are stored in which format?
These are examples of binary files. While reading text files written in Notepad or MS Word is easy and human-comprehensible, we cannot read binary data as it is difficult for humans to understand.
Binary files store data in the form of raw bytes, not characters that we see in .txt files or .csv files. From images to compiled code, binary files can store anything.
In programming, binary files are efficient, compact, and provide fast access to structured data. This allows us to use them effectively for low-level operations. Let us also see why binary files are essential in Java programming.
Importance of Binary File Handling in Java Applications
Although binary files are only machine-readable, they play an important role in software development. They have a simple format and perform fast reading and writing operations.
Moreover, there are no encoding issues as the data is stored in raw bytes. Binary files can store almost any kind of structured data. Let us see how it is essential in some of the Java applications.
- Game Development: Games utilize different kinds of structured data. Images, sounds, or effects are some of the structured data that is stored in binary files for faster access and processing.
- Media Applications: Image or video editing software and even audio streaming platforms utilize binary files to manipulate the data. These applications need to process larger data, and therefore, binary files are useful for better execution in such cases.
- Data Serialization and Networking: Binary files are also used in data serialization. Serialization converts Java objects to binary files which makes it simpler to transmit between systems. Byte streams can also be transmitted over HTTP in networking.
Understanding Java I/O Streams: Byte Stream
A byte stream is essentially a sequence of bytes. The I/O stream is a representation of input and output sources. These streams are used to read and write data to different sources like files, sockets, or memory.
Java mainly has two kinds of I/O streams – the character stream and the byte stream. In this article, we will learn about the byte stream.
The byte stream is used to handle binary data. These include images, videos, audio, or any kind of non-text files. The byte stream uses the InputStream and the OutputStream classes to operate.
Let us have a look at some of their basic functions to see how we can read and write binary files. The table given below represents the same.
InputStream | OutputStream | ||
Method Name | Description | Method Name | Description |
read() | Reads one byte at a time | write(int b) | Writes one byte at a time |
read(byte[] b) | Reads bytes in the buffer | write(byte[] b) | Writes an array of bytes |
close() | Closes the stream | close() | Closes the stream |
The InputStream and OutputStream classes are abstract. We can use their subclasses for more specific functions. To read and write in a binary file, we make use of the FileInputStream and the FileOutputStream classes.
In the next section, we will learn about their role in binary files and see how to read and write them in Java. Keep reading to know more!
How To Read A Binary File In Java? Read Below
To read a binary file, we make use of the FileInputStream and the DataInputStream classes. These classes are used to read byte streams and primitive data types in Java. Below, we will see an example program to help you understand how to read from a binary file.
Here, we will use the following methods to fetch the data from the binary file. Look at the table below to see them.
Method | Description |
readInt() | Reads integer data from the binary file |
readDouble() | Reads double data type data from the binary file |
readUTF() | Reads character strings or data encoded in UTF format |
In the program given below, we are reading the “ExampleFile.bin” binary file. This file contains some primitive data types. Our program will use the DataInputStream class methods to read this data and print it in the terminal.
Have a look at the example program given below.
Program:
// import classes
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadBinaryFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// storing the name of the binary file in a string for simplicity
String fileName = "ExampleFile.bin";
// using exception handling
// creating a DataInputStream object named reading
try (DataInputStream reading = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileName))) {
// storing the fetched data
int id = reading.readInt();
double salary = reading.readDouble();
String name = reading.readUTF();
System.out.println("Data Successfully Read from file:");
System.out.println("ID: " + id);
System.out.println("Salary: " + salary);
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error reading from file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Explanation Of The Program:
- In the above program, we first imported all the necessary classes and packages that are needed to read data from a binary file in Java.
- We have created a data input stream object called reading and allocated the file name to it so that it is able to read the data from that particular file.
- To handle unexpected errors, we are using the IO exception.
- We are using the above methods to fetch the data from the binary file.
- Next, we are storing the data that is fetched from the file in new variables, which are then printed in the terminal.
Output:
How To Write In A Binary File In Java? Read Below
To write in a binary file, we make use of the FileOutputStream and the DataOutputStream classes. These classes are used to write byte streams and primitive data types in binary files in Java. Below, we will see an example program to help you understand how to write in a binary file.
Here, we will use the following methods to output the data in the binary file. Look at the table below to see them.
Method | Description |
writeInt() | Writes integer data from the binary file |
writeDouble() | Writes double data type data from the binary file |
writeUTF() | Writes character strings or data encoded in UTF format |
In the program given below, we are writing the data in the “ExampleFile.bin” binary file. Our program will use the DataOutputStream class methods to print this data in the file and print the message of success or failure in the terminal.
Have a look at the example program given below.
Program:
// import classes
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WriteBinaryFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// storing file name in a string
String fileName = "ExampleFile.bin";
// using exception handling
// creating an object of the DataOutputStream named writing
try (DataOutputStream writing = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName))) {
// declare the data that is to be written
int id = 101;
double salary = 75000.50;
String name = "Alice";
// methods for writing data
writing.writeInt(id);
writing.writeDouble(salary);
writing.writeUTF(name);
System.out.println("Data written to " + fileName);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error writing to file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Explanation Of The Program:
- In the above program, we first imported all the necessary classes and packages that are needed to write data in a binary file in Java.
- We have created a data output stream object called writing and allocated the file name to it so that it is able to read the data from that particular file.
- To handle unexpected errors, we are using the IO exception.
- Then, we are storing some values having primitive datatype in variables.
- We are using the above methods for writing the data in the binary file.
- When the data is written in the file, a status message is printed in the terminal.
Output:
What Is The Efficient Way To Read Large Binary Files?
Now, if you are dealing with some very large binary files, then using the methods mentioned above will not help you a lot. In that case, to read large binary files, the efficient way will be to use Memory-mapping.
Memory-mapping is the optimized way to deal with files having a size in GB. We will implement the code using the Java NIO FileChannel. Let us check how to do that.
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Trying To Access Extremely Large File 'Zap.bin'
try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("Zap.bin", "r");
FileChannel channel = file.getChannel())
{
// File Will Be Loaded And Extremely Fast Read By MappedByteBuffer
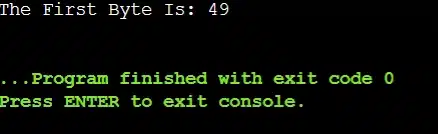
MappedByteBuffer buffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, channel.size());
System.out.println("The First Byte Is: " + buffer.get()); // Print The First Byte
}
}
}
Explanation Of The Program:
- At first, a Try-Catch Block will be implemented, which will try to access the large file ‘Zap.bin’.
- Now, if it can access the file, it will be loaded using the Java NIO FileChannel.
- Then, the program will extremely fast read the data using the MappedByteBuffer, and the first byte will be printed.
Output:
Comparison Table Between Java NIO FileChannel Vs InputStream:
We have seen that, for reading normal binary files, the InputStream is used. And for large binary files, the Java NIO (New IO) FileChannel is required. So, with both of them, we can read the binary file.
The confusion is which one is the best and which one you have to use. To clarify, let us check the following table.
Criteria | FileChannel | InputStream |
Speed | Faster | Slower |
Access Mode | Random | Sequential |
Buffer Usage | Mandatory | Optional |
File Size | Large | Moderate |
Thread Safety | Low | High |
How To Do Object Serialization To A File In Java?
Normally, an Object is stored in a memory location, which gets deleted when we close the program. However, if you want to save that object, you have to do Object Serialization to a File, which will convert the object to bytes.
Let us check the following code, which has been developed with the help of the ObjectOutputStream example.
Import java.io.*;
class Student implements Serializable // Class Will Be Serialized
{
int id;
String name;
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student s = new Student(); // Creating The Java Object
s.id = 25;
s.name = “Zap”;
// Trying To Perform Serialization With ObjectOutputStream
try (ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(“Temp.ser”))) {
out.writeObject(s);
// Data Will Be Saved In Temp. ser File
System.out.println(“Object Serialization Is Completed”); // Confirmation Message
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Explanation Of The Program:
- At first, a Student Class has been implemented, which will be serialized later.
- Now, we will create an object with the Student Class.
- Then, the Try-Catch will be used with ObjectOutputStream to convert the Student Object into bytes and store it in the Temp.ser file.
Output:
Comparison Table Between DataOutputStream Vs ObjectOutputStream:
So, in summation, we can write binary files using both DataOutputStream and ObjectOutputStream. The DataOutputStream is used for normal binary files, and the ObjectOutputStream for object serialization.
If you are confused about both of these, then you can refer to the following comparison table to clarify the concept.
Criteria | DataOutputStream | ObjectOutputStream |
Data Type | All Primitive Data Types | Only Objects |
Readability | High | Low |
File Size | Small | Large |
Speed | Fast | Slow |
Compatibility | Wide | Limited |
Best Practices For Reading and Writing Binary Files in Java
Now that we have learned how to read and write binary files in Java, let us also get to know some of the best practices that you should follow to handle binary files efficiently. Read below to learn more!
- Use Exception Handling to Catch Common Errors: If you noticed in the above programs, we are using the IO Exception in our Java code. This is to handle the binary file operations so that no error results in program termination.
Common binary file errors like FileNotFoundException and IO Exception occur when the file that we need is not created or is inaccessible and when there are errors in writing or reading from a file.
- Buffering For Performance: FileInputStream and FileOutputStream can only read and write one byte at a time. In larger systems, this leads to slower execution and performance inefficiency.
To tackle this, we can use the BufferedInputStream and the BufferedOutputStream classes. The syntax for declaring the objects of these classes is given below.
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("file.bin"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("file.bin"));
- Close Streams and Resources: When reading and writing in a file, it is important to close them once the job is done. This not only helps in saving the content but also prevents memory leaks and file locks. The close() function can be used for the same.
In this article, we saw how to read and write binary files in Java and learned about the best practices for writing better code. Binary files in Java help us store and manipulate data quickly and effectively.
If you have difficulty understanding the above approaches, you can always ask for help with file I/O in your Java assignment to clarify all your doubts.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding how to read and write binary files in Java is essential for processing different
types of data in Java. Besides the discussed approaches, another method for reading and writing
binary files is using `DataInputStream` and `Data OutputStream`.
So now when you come across image files or audio files, you know that these are an example of binary files, and you can use them in your Java project. Also, if you have any doubts in Java, feel free to reach out to us.
Takeaways:
- Binary files in Java can be accessed with the help of the InputStream and OutpStream abstract classes and their subclasses.
- To read or write data in a binary file, you can also use the BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream and the DataInputStream/DataOutputStream.
- Remember to follow the best practices while manipulating binary files to make the code cleaner and efficient.