Image Transformations Operations using OpenCV
Machine Learning courses with 100+ Real-time projects Start Now!!
In the realm of image processing, the power to decode an image’s essence lies in techniques that go beyond mere pixel values. Welcome to the world of Laplacian and Distance Transformations – two potent operators that unravel hidden intricacies and pave the way for advanced image analysis.
In this journey, we will dive into the heart of these operations, discovering their role in edge detection, distance calculations, and the captivating interplay between mathematics and visual interpretation. Buckle up as we embark on a voyage to reveal the essence of images, guided by the tools of OpenCV’s Laplacian and Distance Transformations.
Laplacian Operator in OpenCV: Discerning Image Edges
The Laplacian operator is a pivotal tool in OpenCV’s image-processing arsenal, primarily designed for edge detection. It achieves this by pinpointing sudden changes in pixel intensity, which often signify the presence of edges or boundaries within an image.
In mathematical terms, the Laplacian operator employs a convolution kernel that embodies the essence of second derivatives. When applied through OpenCV’s cv2.Laplacian() function, this kernel highlights regions of rapid intensity alterations, effectively bringing image edges to the forefront.
The Laplacian operator’s significance extends beyond mere edge detection. It is crucial for jobs like feature extraction when locating important or distinguishing features in a picture is necessary.
By embracing this operator, OpenCV enthusiasts gain access to a powerful tool that enhances their ability to interpret and manipulate visual information effectively.
Mathematically, the Laplacian operator can be denoted as a convolution operation using the following kernel:
0 1 0 1 -4 1 0 1 0
This kernel is convolved with the image to compute the second derivative of pixel intensities. The resulting output highlights regions of rapid intensity changes, revealing edges and transitions within the image.
Role in Image Processing in OpenCV:
The Laplacian operator is fundamental for detecting edges and key features in an image. It helps in uncovering subtle nuances that contribute to object recognition, scene understanding, and more. Its capacity to amplify intensity changes grants it a pivotal role in image enhancement and manipulation.
Applications:
- Edge Detection: The Laplacian operator excels at edge detection, where identifying boundaries is crucial.
- Feature Extraction: It aids in extracting features like corners and key points that form the foundation of various computer vision tasks.
In the realm of OpenCV, the Laplacian operator serves as a guide that directs us to the heart of image structure, allowing us to perceive the world through the lens of intensity changes.
The Laplacian operator operates on the concept of detecting rapid intensity changes in an image, which often correspond to edges or boundaries. Mathematically, it calculates the second derivative of pixel intensities, emphasizing transitions and discontinuities.
Syntax and Parameters:
The cv2.Laplacian() function is used to apply the Laplacian operator:
laplacian_image = cv2.Laplacian(src, ddepth, ksize)
- Src: The input image.
- The required depth of the produced image is depth.
- ksize: The size of the Laplacian kernel (usually 1, 3, 5, or 7).
Code and Explanation:
To apply the Laplacian operator and highlight edges in an image, consider the following code snippet:
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Read the image
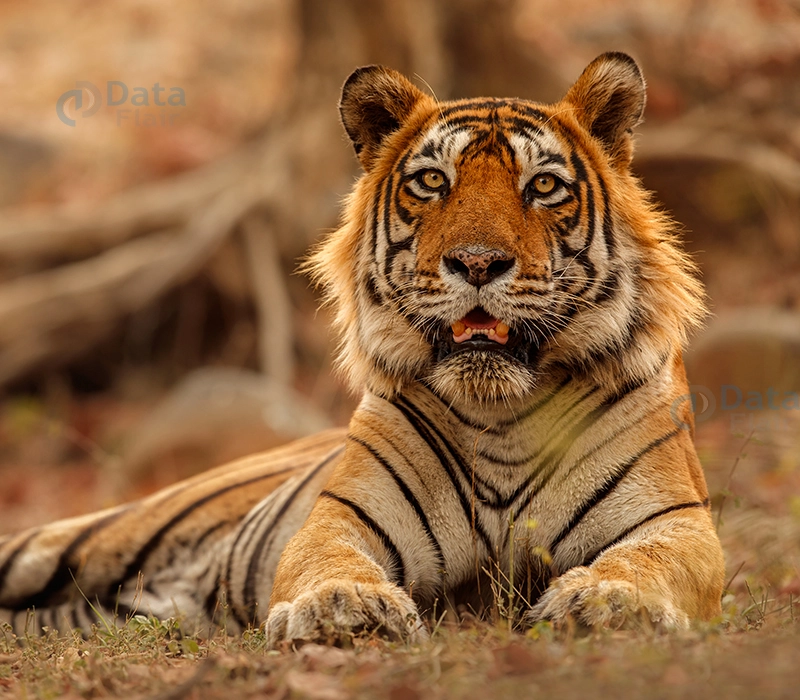
image = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\DataFlair\OneDrive\Desktop\OpenCV Data Flair\opencv transformation operations\wildlife-tiger.jpg")
# Apply the Laplacian operator
laplacian_image = cv2.Laplacian(image, cv2.CV_64F)
# Display the original and Laplacian images
plt.subplot(121), plt.imshow(image, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Original Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122), plt.imshow(laplacian_image, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Laplacian Image'), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()Original Image:
Laplacian Image:
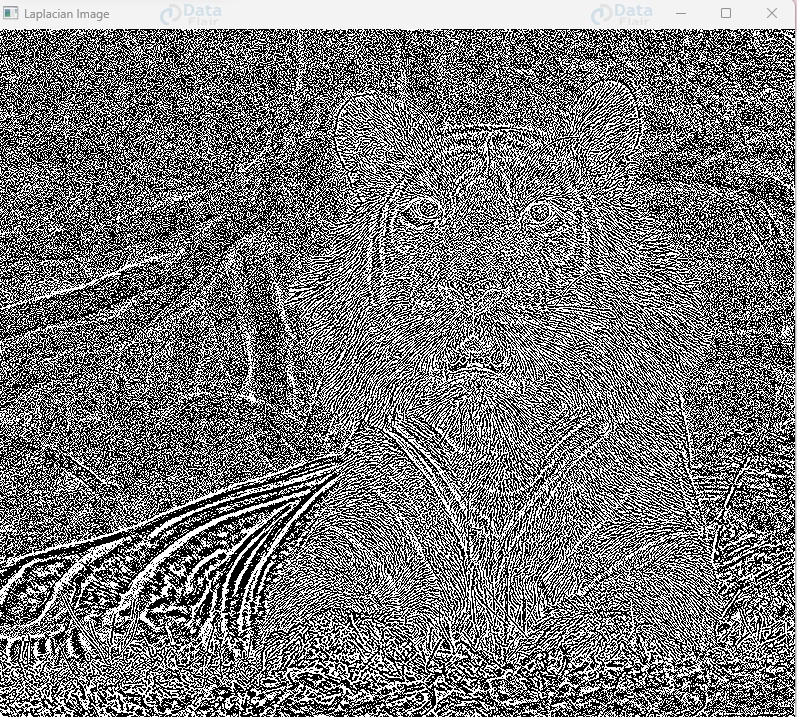
In this code, the Laplacian operator is applied using `cv2.Laplacian()` on the grayscale input image. The cv2.CV_64F argument specifies the output image depth as a 64-bit floating point.
Grayscale to Laplacian Conversion :
import cv2
# Read the image in grayscale
image = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\DataFlair\OneDrive\Desktop\OpenCV Data Flair\opencv transformation operations\wildlife-tiger.jpg", cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# Apply the Laplacian operator
laplacian_image = cv2.Laplacian(image, cv2.CV_64F)
# Display the original image
cv2.imshow('Original Image', image)
# Display the Laplacian image
cv2.imshow('Laplacian Image', laplacian_image)
# Wait for a key press and close the windows
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()Original Image :
Laplacian Image :
This operator serves as an indispensable tool for detecting edges and significant features within images, shaping the foundation of edge detection techniques.
Let’s Know About Image Scaling
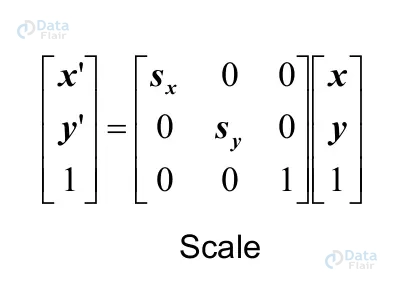
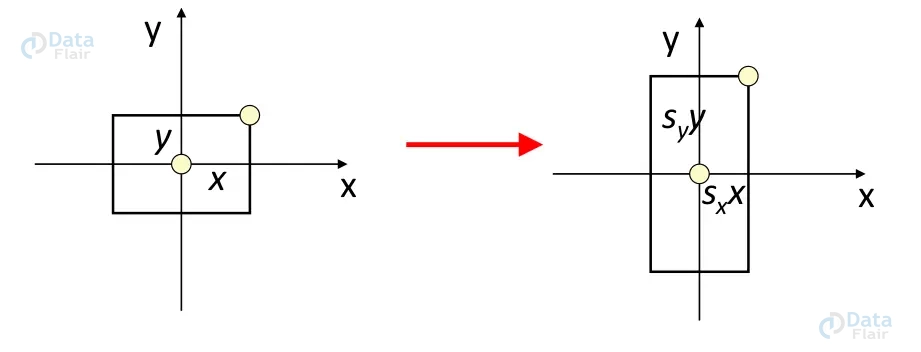
A digital image can be resized using the image scaling technique. Although the built-in OpenCV method cv2.resize() exists, we will still execute the change using matrix multiplication. The scaling matrix is displayed below:
The scaling factors for the x-axis and y-axis, respectively, are Sx and Sy.
Distance Transformation Operator in OpenCV: Unveiling Spatial Distances
Distance Transformation, a fundamental technique in OpenCV, delves into the intricate spatial relationships within images. It quantifies the distance of each pixel from a specified point or region, culminating in a distance map that captures the essence of spatial arrangement.
Understanding the Concept:
The Distance Transformation operator calculates the distance of every pixel in an image from a defined reference point. This measurement is not solely geometric; it encompasses the context of the image structure and spatial layout.
Types of Distance Calculation:
OpenCV provides different types of distance calculations to suit various scenarios:
- Euclidean Distance (cv2.DIST_L2): Measures the straight-line distance between two points.
- City Block Distance (cv2.DIST_L1): Computes the distance along grid lines (Manhattan distance).
- Chessboard Distance (cv2.DIST_C): Calculates the maximum of the horizontal and vertical distances.
These methods offer flexibility in understanding spatial relationships, depending on the context of the image.
Distance Transformation has a broad range of applications, from image segmentation to skeletonization. By quantifying distances and encapsulating spatial patterns, this operator offers a profound perspective on image structures and their intricate arrangements.
The section on “Distance Transformation Operator in OpenCV” invites us to explore an essential technique for calculating distances within images, transcending mere pixel values. OpenCV’s cv2.distanceTransform() function is our gateway to comprehending spatial relationships and distances across image structures.
Understanding the Distance Transformation:
The Distance Transformation operator is a powerful tool used to compute the distance of each pixel from a specified point or region in an image. Unlike simple geometric distances, this operator delves into the very fabric of an image, generating a “distance map” that quantifies the spatial relationships.
Syntax and Parameters :
The cv2.distanceTransform() function performs the distance transformation operation :
distance_map = cv2.distanceTransform(src, distanceType, maskSize, dstType)
- Src: The input binary image (single-channel, 8-bit or 32-bit floating point).
- distanceType: The type of distance calculation to be performed (e.g., cv2.DIST_L2, cv2.DIST_C, etc.).
- mask size: The size of the distance transform mask (default is 0).
- dstType: The type of the output distance map (e.g., cv2.CV_32F).
Code and Explanation:
To demystify the Distance Transformation, consider the following code example :
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Read a color image
color_image = cv2.imread(r"C:\Users\DataFlair\OneDrive\Desktop\OpenCV Data Flair\opencv transformation operations\wildlife-tiger.jpg")
# Convert the color image to grayscale
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(color_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Apply thresholding to create a binary image
_, binary_image = cv2.threshold(gray_image, 128, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Perform the distance transformation
distance_map = cv2.distanceTransform(binary_image, cv2.DIST_L2, 5)
# Display the original color image, binary image, and distance map
cv2.imshow('gray Image', gray_image)
cv2.imshow('Binary Image', binary_image)
# Display the distance map using a colormap
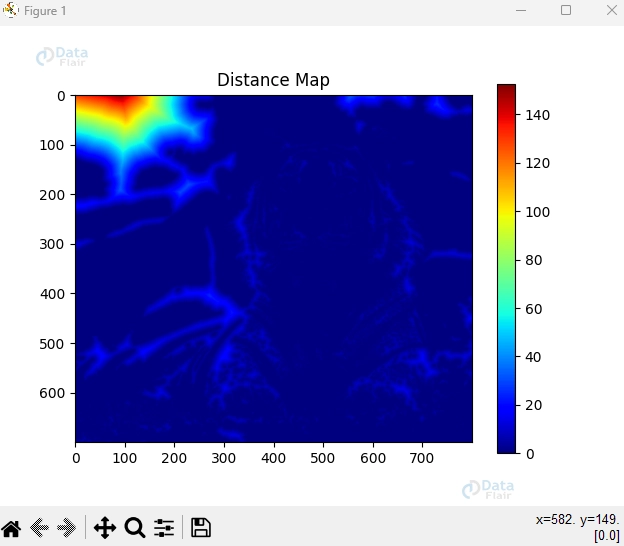
plt.imshow(distance_map, cmap='jet')
plt.title('Distance Map')
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
# Wait for a key press and close the windows
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()Original Image:
Binary Image:
Distance Transformation:
In this code, a binary image with a white object on a black background is created. The cv2.distanceTransform() function is then applied to calculate the distance map. The cv2.DIST_L2 argument specifies the Euclidean distance calculation.
The Distance Transformation operator opens doors to diverse applications, from image segmentation to object recognition, as it quantifies spatial relationships and unveils hidden spatial patterns within images.
Summary
In the realm of image processing, we’ve uncovered the significance of Laplacian and Distance Transformations. These OpenCV-powered techniques have illuminated edges, gradients, spatial relationships, and distances within images.
The Laplacian operator, a beacon for edge detection, has revealed the hidden contours that define objects. Meanwhile, the Distance Transformation operator has quantified spatial connections, enriching our understanding of layouts and arrangements. Equipped with these insights, we’re primed to navigate the intricate landscapes of image processing, armed with the transformative potential of Laplacian and Distance Transformations.
Did you know we work 24x7 to provide you best tutorials
Please encourage us - write a review on Google