Introduction to OpenCV
Machine Learning courses with 100+ Real-time projects Start Now!!
Hey there! Ever heard of OpenCV? It, short for Open Source Computer Vision Library, is a revolutionary tool that has transformed the field of computer vision and image processing tasks.
Do you know who created it? Intel started the ball rolling, but now it’s taken up by a cool bunch of developers and researchers who make up the OpenCV community. They’ve made it their mission to bring computer vision awesomeness to the world, and they’re doing a stellar job at it!
Here’s the cool thing: OpenCV speaks the language of developers everywhere. It’s primarily built using C++, but it doesn’t stop there. It’s also got your back if you prefer coding in Python or Java. Oh, and it doesn’t matter if you’re a Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, or Android fan – OpenCV plays nicely with all of them!
But wait, there’s more! OpenCV isn’t just limited to images. It dives headfirst into video analysis, computational photography, and the cutting-edge world of deep learning. They’ve got these pre-trained models that work like magic. Just imagine effortlessly detecting faces, recognizing objects, and classifying images like a pro without having to start from scratch.
Here is a quick overview of OpenCV introduction,
- What is OpenCV
- The History of OpenCV
- Cool Features of OpenCV
- The Various Applications of OpenCV
- The Architecture and Working of OpenCV
- OpenCV Constructs
What is OpenCV?
OpenCV, or Open Source Computer Vision Library, is a fantastic software library that has revolutionized the computer vision industry. For various image processing and computer vision tasks, a wide variety of tools and methods are provided.
One of the notable features of OpenCV is its versatility. It supports multiple programming languages, including C++, Python, and Java, making it accessible to a diverse range of developers. Moreover, it is designed to be cross-platform, allowing users to utilize its capabilities on different operating systems such as Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, and Android.
With its collection of pre-trained models, OpenCV simplifies complex tasks such as face detection, object recognition, and image classification. These models may be easily used and have been trained on big datasets, saving developers a lot of time and work.
Whether you’re a beginner exploring the basics of computer vision or an experienced professional pushing the boundaries of image processing, OpenCV provides a powerful framework to tackle challenges and unleash your creativity.
The History of OpenCV
The story of OpenCV, the Open Source Computer Vision Library, traces back to 1999 when a team of Intel researchers led by Gary Bradski embarked on a mission to create an open-source computer vision framework. Their vision was to provide a platform that would enable developers and researchers to collaborate and advance the field of computer vision.
In the year 2000, the first version of OpenCV was unveiled, capturing the attention of the computer vision community with its vast collection of algorithms and its open-source nature. Written in C and C++, it quickly gained popularity as a valuable resource for computer vision applications.
- 1999: Intel researchers, led by Gary Bradski, initiate the OpenCV project.
- 2000: The first version of OpenCV is released, gaining attention for its extensive algorithm collection.
- 2006: OpenCV 1.0 is launched, introducing new features, improved performance, and enhanced documentation.
- 2008: OpenCV 2.0 brings modularity and expands language support to include Python and Java.
- 2015: OpenCV 3.0 is released, featuring enhanced deep learning support, refined camera calibration techniques, and improved performance on multi-core systems.
- 2018: OpenCV 4.0 focuses on usability and performance, introducing a revamped API, better support for modern hardware platforms, and advancements in deep learning capabilities.
The collaborative efforts of the OpenCV community have been instrumental in shaping the library’s growth and making it a widely recognized and influential tool in the field of computer vision.
Features of OpenCV
OpenCV is a game-changing software library that has a variety of features. Let us now see the various features of OpenCV.
1. Algorithmic Powerhouse:
OpenCV boasts a vast collection of algorithms for image processing, computer vision, and machine learning. It supports a wide range of activities, including simple procedures and more complex ones like feature detection and object recognition.
2. Camera Calibration:
OpenCV provides tools for camera calibration, allowing precise calibration of camera parameters. This is crucial for tasks like 3D reconstruction, augmented reality, and accurate measurements.
3. Deep Learning Integration:
OpenCV seamlessly integrates with popular deep learning frameworks, enabling the use of pre-trained models for tasks like object detection, image classification, and semantic segmentation. This simplifies complex deep learning implementation.
4. Efficient Image I/O:
OpenCV supports various image file formats and provides efficient functions for image input and output operations. It allows seamless reading, writing, and manipulation of images.
5. Feature Detection and Extraction:
OpenCV offers robust algorithms for detecting and extracting features from images, such as corners, edges, and key points. These features are valuable for image matching, registration, and tracking.
6. GPU Acceleration:
OpenCV leverages GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) acceleration for computationally intensive operations, significantly improving performance. It excels in tasks like image filtering, deep learning, and more.
7. Interactive GUI:
OpenCV includes a graphical user interface (GUI) module, facilitating the development of interactive applications with image and video visualization capabilities. It simplifies algorithm testing and refinement.
8. Machine Learning Support:
OpenCV provides tools for machine learning, allowing training and application of machine learning models on image and numerical data. It enables tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, and more.
9. Real-time Video Processing:
OpenCV empowers real-time video processing, enabling capture, processing, and analysis of video streams. It finds application in areas like video surveillance, object tracking, and augmented reality.
10. Versatile Language Support:
OpenCV supports multiple programming languages, including C++, Python, Java, and more. It accommodates diverse developer preferences and facilitates seamless integration into various projects.
Applications of OpenCV
Here are some of the key applications of OpenCV,
- OpenCV is widely used for object identification and recognition in both still photos and moving films. It enables applications like face detection, object tracking, and object classification.
- Image and video processing: OpenCV provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for image and video processing tasks. It allows tasks such as image filtering, image enhancement, noise reduction, and video stabilization.
- Camera calibration: OpenCV offers tools for camera calibration, which is essential for tasks like 3D reconstruction, augmented reality, and accurate measurements. It helps to obtain precise geometric parameters of a camera.
- Medical imaging: OpenCV is utilized in medical imaging applications for tasks like image analysis, segmentation, and feature extraction. It assists in diagnosing diseases, detecting anomalies, and facilitating medical research.
- Robotics: OpenCV plays a crucial role in robotics applications, including object detection and tracking, robot navigation, and human-robot interaction. It helps robots perceive and interact with their environment.
- Augmented reality (AR): OpenCV enables the development of augmented reality applications by providing tools for marker detection, image tracking, and 3D object rendering. It enhances real-world environments with digital information and virtual objects.
- Video surveillance: OpenCV is widely used in video surveillance systems for activities like motion detection, object tracking, and facial recognition. It aids in security monitoring, behavior analysis, and anomaly detection.
- Automotive industry: OpenCV contributes to the automotive industry by enabling features like lane detection, pedestrian detection, and driver monitoring systems. It enhances safety and assists in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS).
- Biometrics: OpenCV supports biometric applications, including face recognition, fingerprint recognition, and iris recognition. It aids in secure authentication and identification systems.
- Sports analytics: OpenCV is employed in sports analytics for tasks like player tracking, ball tracking, and gesture recognition. It helps extract valuable insights from sports videos and enhances coaching and analysis.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of OpenCV. Its versatility, extensive feature set, and open-source nature make it a popular choice for various industries and research fields.
Apple integrates OpenCV in their products and development tools. It finds application in computer vision tasks within Apple’s software, including features like face detection and augmented reality capabilities.
OpenCV has been used by Toyota in their research and development of autonomous driving technologies, including object detection and tracking algorithms.
Intel has integrated OpenCV into their computer vision software development kits (SDKs) and platforms, such as the Intel RealSense technology, used for depth sensing and gesture recognition.
Sony has employed OpenCV in their computer vision projects, including camera technologies, augmented reality applications, and image processing algorithms.
These are just a few examples of companies that utilize OpenCV. OpenCV’s versatility and extensive functionality make it a popular choice.
Architecture and Working of OpenCV
OpenCV follows a modular architecture designed to be highly flexible and efficient. Its core components consist of the following modules:
1. Core Module: The Core module provides essential data structures and basic functionalities used throughout OpenCV. It includes matrix operations, data handling, and utility functions.
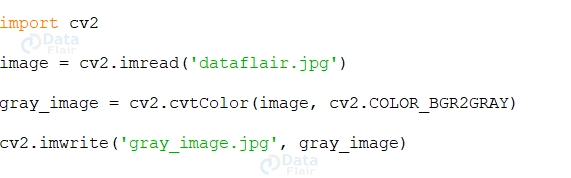
For Example:
Consider the following function cv2.imread(): This function is used to save an image to a file.
2. Image Processing Module: The many image processing algorithms covered by this topic include filtering, morphological operations, histogram equalization, and geometric transformations.
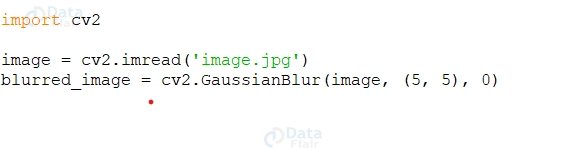
For Example: Image Filtering: Image filtering involves modifying an image using filters to enhance or extract specific features. OpenCV provides functions for common filter types, such as Gaussian, Median, and Sobel filters. For example, here’s how to apply a Gaussian filter:
3. Feature Detection and Extraction Module: This module focuses on algorithms for feature detection and extraction, including corner detection (e.g., Harris corner detector), edge detection (e.g., Canny edge detector), and keypoint extraction (e.g., SIFT, SURF, ORB).
For Example, Feature detection algorithms aim to identify distinctive points or regions in an image that can be easily tracked or matched across multiple images. FAST (Features from Accelerated Segment Test): Detects corners and features using a high-speed corner detection algorithm.
Here’s an example of using the FAST feature detection algorithm:
4. Object Detection and Recognition Module: OpenCV offers powerful algorithms for object detection and recognition. It includes popular techniques like Haar cascades, HOG (Histogram of Oriented Gradients), and deep learning-based models (e.g., using the DNN module)
For Example, Object recognition aims to identify and classify objects within images or video frames. OpenCV provides methods to perform object recognition using machine learning techniques, such as Support Vector Machines (SVM) or Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN).
Here’s an example of using an SVM classifier for object recognition:
5. Video Analysis Module: The Video Analysis module provides tools for video processing and analysis. It includes functions for video capture, optical flow estimation, background subtraction, and object tracking.
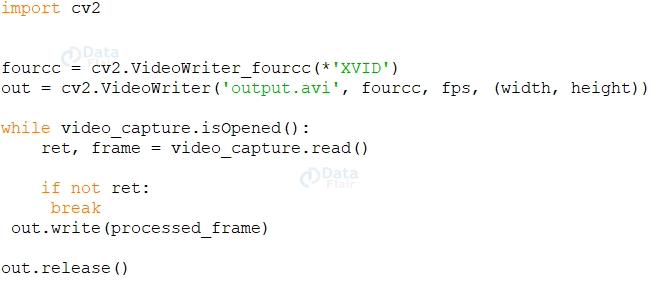
For Example, You can save the processed video frames as a new video file using the `cv2.VideoWriter()` class.
OpenCV follows a straightforward workflow for processing images and videos. Here’s a general outline of its working:
1. Input Acquisition: OpenCV provides APIs to acquire input from various sources, such as image files, video streams, or cameras. It abstracts the complexities of input acquisition, allowing developers to focus on the subsequent processing steps.
2. Preprocessing: Before applying specific algorithms, preprocessing steps may be necessary, such as resizing, color space conversion, noise removal, and normalization. OpenCV offers functions to facilitate these preprocessing tasks.
3. Algorithm Application: OpenCV provides a vast collection of algorithms for different computer vision tasks. Developers can choose the appropriate algorithms based on their requirements and apply them to the input data. For example, object detection algorithms can be applied to identify specific objects within an image or video stream.
4. Postprocessing and Visualization: After the algorithmic processing, post-processing steps can be performed, such as result refinement, data analysis, or visualization. OpenCV provides functions to aid in these steps, including result rendering, drawing bounding boxes, or saving the processed data.
Image Thresholding:
5. Output Display or Storage: OpenCV enables developers to display the processed results in a graphical user interface (GUI), show them on a screen, or store them in files for further analysis or distribution.
Throughout the workflow, OpenCV leverages its underlying architecture and modules to process and manipulate images and videos efficiently, making it a powerful tool for computer vision applications.
It’s important to note that OpenCV’s architecture and workflow can be extended and customized as per specific requirements, allowing developers to build tailored solutions for their applications.
OpenCV Constructs
Here’s a concise explanation of key constructs in OpenCV, organized with subheadings:
1. Matrices (cv::Mat):
- Matrices are fundamental data structures in OpenCV.
- Represented by the `cv::Mat` class.
- Used to store and manipulate image data and numerical information.
2. Core Operations:
- OpenCV provides essential core operations for matrices.
- Includes creating, accessing, and modifying matrix elements.
- Supports arithmetic and logical operations on matrices.
3. Image I/O:
- OpenCV offers functions for reading and writing images.
- Supports various file formats for image input and output.
- Enables loading, displaying, and saving images.
4. Image Processing:
- OpenCV provides functions for image processing tasks.
- Includes operations like filtering, transformations, and color space conversions.
- Enables image enhancement, manipulation, and analysis.
5. Feature Detection and Description:
- OpenCV offers algorithms for detecting and describing image features.
- Includes methods like corner detection, edge detection, and keypoint extraction.
- Crucial for tasks like image matching, object recognition, and tracking.
6. Object Detection and Recognition:
- OpenCV provides algorithms and pre-trained models for object detection and recognition.
- Includes Haar cascades, HOG, and deep learning-based models.
- Enables identification and localization of objects in images or video streams.
7. Video Processing and Analysis:
- OpenCV supports video processing and analysis.
- Allows reading, writing, and accessing video files and streams.
- Includes operations like video stabilization, optical flow estimation, and background subtraction.
These constructs form the foundation of OpenCV and provide developers with powerful tools for image and video manipulation, processing, and analysis.
Interesting OpenCV Interview Questions
Below are some of the frequently asked OpenCV questions,
1. What is OpenCV, and what are its key features?
2. Explain the role of matrices in OpenCV and their importance in image processing.
3. What are some core operations provided by OpenCV for working with matrices?
4. How does OpenCV support image I/O operations? Give examples of file formats it can handle.
5. What are some common image processing tasks that can be performed using OpenCV?
Summary
Explore the power of OpenCV, the Open Source Computer Vision Library, with its robust constructs for image and video processing. Manipulate image data using matrices, perform essential computations with core operations, and effortlessly read and save images using the image I/O capabilities. Detect features and recognize objects using advanced algorithms while also leveraging video processing functionalities for stabilization and optical flow estimation. You can not empower developers to create cutting-edge computer vision applications with OpenCV’s versatile constructs.
Your 15 seconds will encourage us to work even harder
Please share your happy experience on Google








Great start