Expert-led Online Courses: Elevate Your Skills, Get ready for Future - Enroll Now!
In this article, we will be discussing about Node.js web Module, web server, how to create a web server, how to create a web client in detail with code and examples.
Web server and its working:
Web servers are programs that deal with http requests. The http requests sent by the client are handled by the web server and it then gives a response to the clients. A web server generally provides the html, stylesheets, and images.
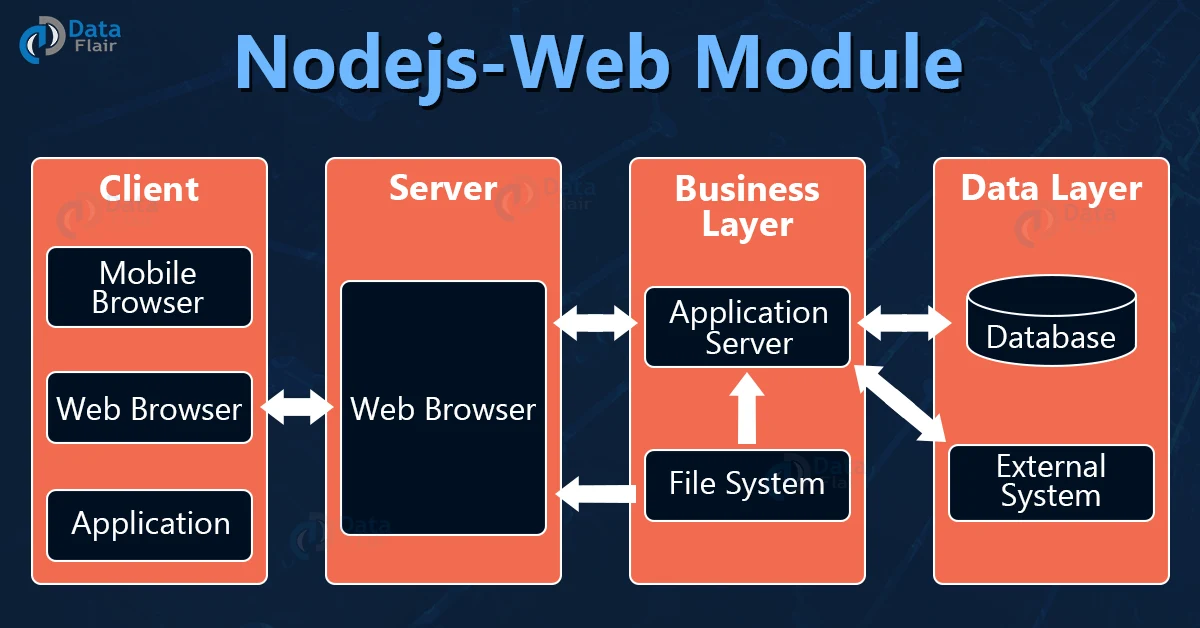
Web Server Architecture:
1. Client:
Browsers and other applications that make http requests to the server are known as clients.
2. Server:
This layer takes the requests made by the client and sends them a response.
3. Business:
This layer contains all the logics and functions required in the application, it also interacts with the data layer using databases.
4. Data:
This layer contains the data required by the application. The data is generally stored in the databases.
Create a Web server:
We will be creating a nodejs server using http which is a builtin module of node js.
Code for creating a web server:
const http = require('http');
http.createServer(function (request, response) {
response.write("Welcome to DataFlair");
response.end();
}).listen(3000);
console.log('Server is running on port 3000');
Output:
Making a request to node server:
Open your browser and go to localhost:3000 you will see like the below image:
Output at terminal:
Creating web client:
Till now, we have seen creating a web server. Now we will see how to create a web client, here we will be creating the web client using the built in http module. In order to make a request from the web client to our web server we will be running the below code from a different terminal and make sure that your web server is running before making a request from your web client.
Code for creating a web Client:
const http = require('http');
const options = {
host: 'localhost',
port: '3000',
path: '/'
};
const callback = function (response) {
var body = '';
response.on('data', function (data) {
body += data;
});
response.on('end', function () {
console.log(body);
});
}
var req = http.request(options, callback);
req.end();
Output
Conclusion:
In this article, we have seen Nodejs web modules in detail. Hope you liked it.