Python Fidget Spinner – Snipe Your Stress Away
Master Python with 70+ Hands-on Projects and Get Job-ready - Learn Python
In this project, we will be building a Fidget Spinner Simulator using the Pygame library in Python. We will be using it to create the graphical interface for our Fidget Spinner Simulator.
About Python Fidget Spinner
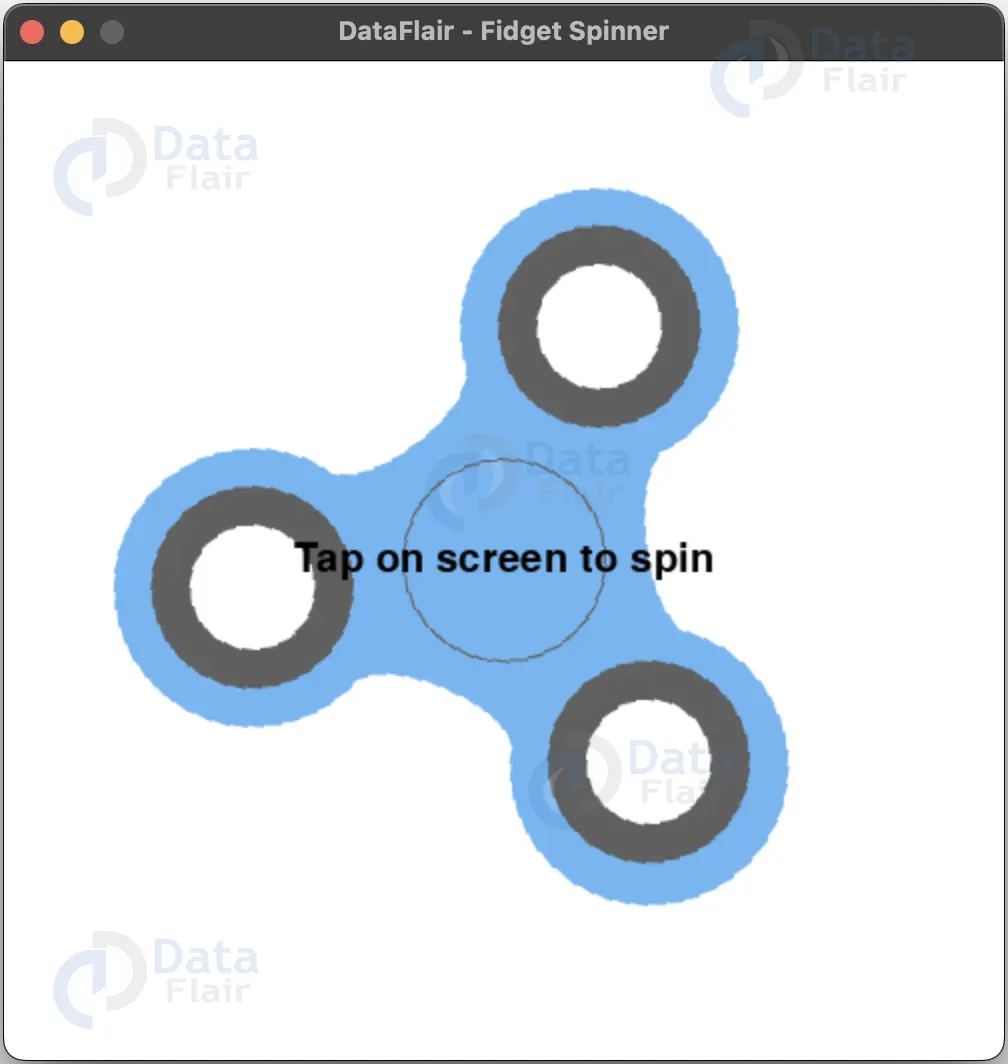
The objective of this project is to create a Fidget Spinner Simulator that can be spun with the mouse and slows down over time, displaying a message “Tap on screen to spin” when it stops.
Prerequisites for Fidget Spinner using Python
Basic knowledge of Python programming language
Pygame library installed in your system
Download Python Fidget Spinner Project
Please download the source code of python Fidget Spinner project from the following link: Python Fidget Spinner Project Code
Steps to Create Fidget Spinner using Python
Following are the steps for developing the python fidget spinner project:
Step 1: Importing Libraries
The first step to create a fidget spinner is importing the necessary libraries. In this case, we will be using the Pygame library. Import it at the top of your code as shown below:
# Importing pygame library import pygame
Step 2: Initializing Pygame
Next, we will initialize Pygame using the pygame.init() function. This function initializes all the pygame modules required for our program.
# Initialize Pygame pygame.init()
Step 3: Setting the window size and creating the window
We will set the size of the window in which our Fidget Spinner Simulator will be displayed. In this case, the size is set to 500×500 pixels.
# Set the window size size = (500, 500) screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size)
Step 4: Setting the title of the window
We will set the title of the window using the pygame.display.set_caption() function.
# Set the title of the window
pygame.display.set_caption("DataFlair - Fidget Spinner")
Step 5: Loading the fidget spinner image
We will load the fidget spinner image using the pygame.image.load() function.
# Load the fidget spinner image
spinner_image = pygame.image.load("fidget_spinner.png").convert_alpha()
Note: Make sure the image file is in the same directory as the python file or provide the full path of the image
Step 6: Resizing the image to fit the window
We will resize the image to fit the window using the pygame.transform.scale() function. In this case, we are scaling the image to 80% of the window size.
# Resizing the image of the fidget spinner # to fit the window size i.e. 80% of the window size spinner_image = pygame.transform.scale(spinner_image, (int(size[0]*0.8), int(size[1]*0.8)))
Step 7: Getting the rect of the fidget spinner image
We will get the rect of the fidget spinner image using the spinner_image.get_rect() function.
# Get the rect of the fidget spinner image spinner_rect = spinner_image.get_rect()
Step 8: Centering the rect on the screen
We will center the rect on the screen using the spinner_rect.center property.
# Center the rect on the screen spinner_rect.center = (size[0]//2, size[1]//2)
Step 9: Setting the spin angle and spin speed
We will set the initial spin angle and spin speed for the fidget spinner.
# Set the spin angle spin_angle = 0 # Set the spin speed spin_speed = 15
Step 10: Setting the clock
In this step, we will set the clock variable. This variable is used to limit the number of frames per second that the animation is displayed at. This is important for performance and smoothness of the animation. In our case, we want the animation to run at 60 frames per second, so we set the clock variable as follows:
# Set the clock clock = pygame.time.Clock() FPS = 60 # Set the font and size for the message font = pygame.font.Font(None, 30)
Step 11: Main Loop
The main loop of the program is where the animation and event handling takes place. We use a while loop to keep the program running until the done variable is set to True. Within the loop, we check for any events that have occurred, such as the user clicking the X button to close the window.
# Main loop
done = False
while not done:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
done = True
elif event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
spin_speed = 15
Step 12: Clear the screen
Before we start drawing the fidget spinner, we need to clear the screen. We do this by filling the screen with a white color.
# Clear the screen screen.fill((255, 255, 255))
Step 13: Rotate the fidget spinner
In this step, we rotate the fidget spinner by a certain angle. The angle is determined by the spin_angle variable which we increase by the spin_speed variable in each iteration of the loop. We also update the rect of the rotated image so that it stays centered on the screen.
# Rotate the fidget spinner spin_angle += spin_speed rotated_image = pygame.transform.rotate(spinner_image, spin_angle) rotated_rect = rotated_image.get_rect(center=spinner_rect.center)
Step 14: Draw the fidget spinner
Now that the fidget spinner is rotated, we can draw it on the screen. We use the blit() function to draw the rotated image on the screen at the position specified by the rotated_rect variable.
# Draw the fidget spinner screen.blit(rotated_image, rotated_rect)
Step 15: Check if the fidget spinner stops
We check if the spin_speed variable is less than or equal to 0, indicating that the fidget spinner has stopped spinning. If it has, we display a message on the screen instructing the user to tap the screen to spin the fidget spinner again.
# check if fidget spinner stops
if spin_speed <= 0:
# render the message 'tap on screen to spin'
message = font.render("Tap on screen to spin", True, (0, 0, 0))
message_rect = message.get_rect(center=(size[0]//2, size[1]//2))
screen.blit(message, message_rect)
else:
# reduce the spin speed by 0.01 every frame
spin_speed -= 0.01
Step 16: Update the display
After all the drawing and event handling is done, we update the display to show the current frame of the animation.
# Update the display pygame.display.flip()
Step 17: Limit to 60 frames per second
Finally, we limit the number of frames per second that the animation is displayed at by using the tick() function of the clock variable.
# Limit to 60 frames per second clock.tick(60)
Step 18: Exit Pygame
At the end of the program, we need to exit Pygame using the pygame.quit() function. This function will clean up all the resources and exit the program.
# Exit Pygame pygame.quit()
Complete Code:
# Importing pygame library
import pygame
# Initialize Pygame
pygame.init()
# Set the window size
size = (500, 500)
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(size)
# Set the title of the window
pygame.display.set_caption("DataFlair - Fidget Spinner")
# Load the fidget spinner image
spinner_image = pygame.image.load("fidget_spinner.png").convert_alpha()
# Resizing the image of the fidget spinner
# to fit the window size i.e. 80% of the window size
spinner_image = pygame.transform.scale(spinner_image, (int(size[0]*0.8), int(size[1]*0.8)))
# Get the rect of the fidget spinner image
spinner_rect = spinner_image.get_rect()
# Center the rect on the screen
spinner_rect.center = (size[0]//2, size[1]//2)
# Set the spin angle
spin_angle = 0
# Set the spin speed
spin_speed = 15
# Set the clock
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
FPS = 60
# Set the font and size for the message
font = pygame.font.Font(None, 30)
# Main loop
done = False
while not done:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
done = True
elif event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
spin_speed = 15
# Clear the screen
screen.fill((255, 255, 255))
# Rotate the fidget spinner
spin_angle += spin_speed
rotated_image = pygame.transform.rotate(spinner_image, spin_angle)
rotated_rect = rotated_image.get_rect(center=spinner_rect.center)
# Draw the fidget spinner
screen.blit(rotated_image, rotated_rect)
# check if fidget spinner stops
if spin_speed <= 0:
# render the message 'tap on screen to spin'
message = font.render("Tap on screen to spin", True, (0, 0, 0))
message_rect = message.get_rect(center=(size[0]//2, size[1]//2))
screen.blit(message, message_rect)
else:
# reduce the spin speed by 0.01 every frame
spin_speed -= 0.01
# Update the display
pygame.display.flip()
# Limit to 60 frames per second
clock.tick(60)
# Exit Pygame
pygame.quit()Python Fidget Spinner Output
Summary
In this project, we walk you through the process of creating a Fidget Spinner Simulator using the Pygame library in Python. The simulator allows users to interact with the spinner by clicking on the screen, simulating the spinning motion, and slowing down over time.
The project includes instructions on how to import necessary libraries, set up the window, display the spinner image, and implement the spinning motion using Pygame’s functions. We hope you enjoyed this tutorial.
Did you like our efforts? If Yes, please give DataFlair 5 Stars on Google