What is Swift Inheritance
Job-ready Online Courses: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
Inheritance is an important concept associated with Object-Oriented Programming. We can create child classes which inherit entities from a parent class. In this article, we’ll learn about inheritance in Swift and what base classes and subclasses are. We will also go through concepts related to inheritance, such as overriding and superclass.
Why Inheritance?
Inheritance enables us to reuse our code. It allows the child classes to inherit the properties and methods of its parent class. For example, we can have a parent class called Animals, and it has a property name and a method sound. It can have child classes called Dog and Cat. These child classes can inherit the sound method from its parent class.
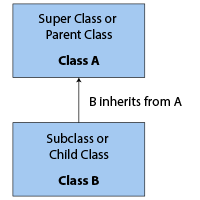
Basics of Inheritance
We can classify the classes in inheritance into subclasses or superclasses. The subclass is the child class that inherits behaviour from its parent class. This parent class from which the subclass inherits is called a Super Class.
is-a relationship
We can use inheritance only when there is a is-a relationship between the classes. For example,
Car is a Vehicle
Mango is a Fruit.
Hexagon is a Shape
Defining a Base class in Swift
A base class is a class that doesn’t inherit anything from another class. We define a base class like we define a class.
class ClassName{
//code
}For example, here we have the base class as Animal. Other classes will inherit entities from this base class Animal.
class Animal{
var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
func sound(){
print("\(name) makes sound")
}
}Subclassing in Swift
Subclassing is when we base a new class on an existing class. The subclass inherits properties, methods and functions from the superclass. We can also add new properties, methods or functions to this subclass.
Syntax to define a subclass.
class SubClassName: SuperClassName {
//code
}For example,
class Animal{
var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
func sound(){
print("\(name) makes sound")
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var breed: String
init(name: String, breed: String){
self.breed = breed
super.init(name: name)
}
override func sound(){
print("\(name) barks.")
}
func play(){
print("\(name) plays.")
}
}Here, we defined a subclass Dog of the class Animal. The subclass has its own property and methods. It also inherits the properties and methods from its superclass.
Overriding in Swift
An object of a subclass can access methods defined in its class as well as its superclass. But it can also define the same method in it. To do so, we override the method from the parent class. The override keyword informs the compiler that we are overriding a property or method.
The syntax to override a method is as follows.
override func functionName(){
//code
}Method Overriding
When we override a method of the superclass in the subclass, we call it method overriding. For example,
class Animal{
var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
func sound(){
print("\(name) makes sound")
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var color: String
init(name: String, color: String){
self.color = color
super.init(name: name)
}
override func sound(){
print("\(name) barks.")
}
}
var dog = Dog(name: "Louis", color: "Brown")
dog.sound()Output:
Louis barks.
Here, the method from the superclass is overridden.
Property Overriding
We can override a superclass property in a subclass. In this way, we can either customize or extend the property’s usage. We can use property overriding with inherited stored and computed properties by using a custom getter and setter.
We cannot override inherited constant stored and inherited read-only properties.
For example,
class Animal{
var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
var description: String{
return "This is Animal \(name)."
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var color: String
init(name: String, color: String){
self.color = color
super.init(name: name)
}
override var description: String{
return "Overridden property. This is Dog \(name)."
}
}
var dog = Dog(name: "Louis", color: "Brown")
print(dog.description)Output:
Overridden property. This is Dog Louis.
Here, the property description is an overriding property.
Overriding Property Observers
We can also use property overriding to add property observed to inherited properties. It will notify us when the inherited value changes. Note that we cannot add these observers to inherited read-only computed property or inherited constant stored property as we cannot set their values.
Final Keyword in Swift
If we don’t want subclasses to override class properties or methods, we can use the final keyword. We can use the final keyword to prevent subclassing if we don’t want a class to have a subclass. If we try to override even when the final keyword is used, then the Swift compiler throws an error. If we try to create a subclass from a final class, then also the Swift compiler generates errors.
In the example, we have a final method sound() in the Animal class. If we try to override the final method, the Swift compiler gives an error.
class Animal{
final var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
final func sound(){
print("\(name) makes sound")
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var color: String
init(name: String, color: String){
self.color = color
super.init(name: name)
}
override func sound(){
super.sound()
print("\(name) barks.")
}
}Output:
swift:20:20: error: instance method overrides a ‘final’ instance method
override func sound(){
^
swift:8:16: note: overridden declaration is here
final func sound(){
^
In the given example, we made the Animal class as final. When we try to subclass this method, we encounter errors.
final class Animal{
final var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var color: String
init(name: String, color: String){
self.color = color
super.init(name: name)
}
}Output:
swift:8:8: error: inheritance from a final class ‘Animal’
class Dog: Animal{
^
Super keyword in Swift
We can override a method in the subclass from the superclass. But if we want to access a method from the superclass in the subclass, then we use the super keyword. For example,
class Animal{
var name: String
init(name: String){
self.name = name
}
func sound(){
print("\(name) makes sound")
}
}
class Dog: Animal{
var color: String
init(name: String, color: String){
self.color = color
// calling the method from superclass using the super keyword
super.init(name: name)
}
override func sound(){
// calling the method from superclass using the super keyword
super.sound()
print("\(name) barks.")
}
}
var dog = Dog(name: "Louis", color: "Brown")
dog.sound()Output:
Louis makes sound
Louis barks.
The following table depicts how we can access the entities from the superclass in a subclass.
| Overriding Entity | Syntax |
| Methods | super.exampleMethod() |
| Properties | super.exampleProperty() |
| Subscripts | super[exampleIndex] |
Conclusion
Swift is an object-oriented programming language. Hence, it allows inheritance. Inheritances enable us to reuse our code. It allows the subclasses to inherit entities from its superclass.
In this article, we’ve seen the basics of swift inheritance and how we define a base class and subclass. We have also understood concepts of overriding and the usage of keywords like final, super, and override in swift inheritance. We have also gone through relevant concepts to each of these concepts.
Did we exceed your expectations?
If Yes, share your valuable feedback on Google