Given a list of positive integers nums and an integer k, return the number of subsets in the list that sum up to k.
Mod the result by 10 ** 9 + 7.
Constraints
n ≤ 300 where n is the length of nums.
k ≤ 300.
Example 1
Input
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
k = 5
Output
3
Explanation
We can choose the subsets [1,4],[2,3] and [5].Example 2
Input
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
k = 10
Output
3
Explanation
We can choose the subsets [1,4,5],[2,3,5] and [1,2,3,4].
Is this similar to 0-1 Knapsack? you need to modified Dynamic Programming (DP) transition state of 0-1 knapsack to count instead of maximizing value.
Counting the Exact Sum of Subsets using Dynamic Programming Algorithm
The Dynamic Programming (DP) transition equation is:
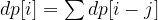 where j is the numbers in the set and if it is less or equal to i. And
where j is the numbers in the set and if it is less or equal to i. And 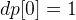
To compute the DP states, we have to compute backwards from DP[k] to DP[1].
int countExactSum(vector<int&;gt;& nums, int k) {
constexpr int M = 1e9+7;
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> dp(k + 1, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (auto &n: nums) {
for (int i = k; i > 0; -- i) {
if (i >= n) {
dp[i] = (dp[i] + dp[i - n]) % M;
}
}
}
return dp.back();
}
The time compelxity is O(KN) where N is the number of elements in the set. The space complexity is also O(KN).
Python DP code implementation:
class Solution:
def countExactSum(self, nums, k):
M = 1e9+7
n = len(nums)
dp = [0] * (k + 1)
dp[0] = 1
for i in nums:
for s in range(k, 0, -1):
if s >= i:
dp[s] += dp[s - i]
return dp[k] % M
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
422 wordsLast Post: Do you believe in Bitcoins (or other Cryptocurrencies)?
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Algorithm to Reverse Words in a Sentence