Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
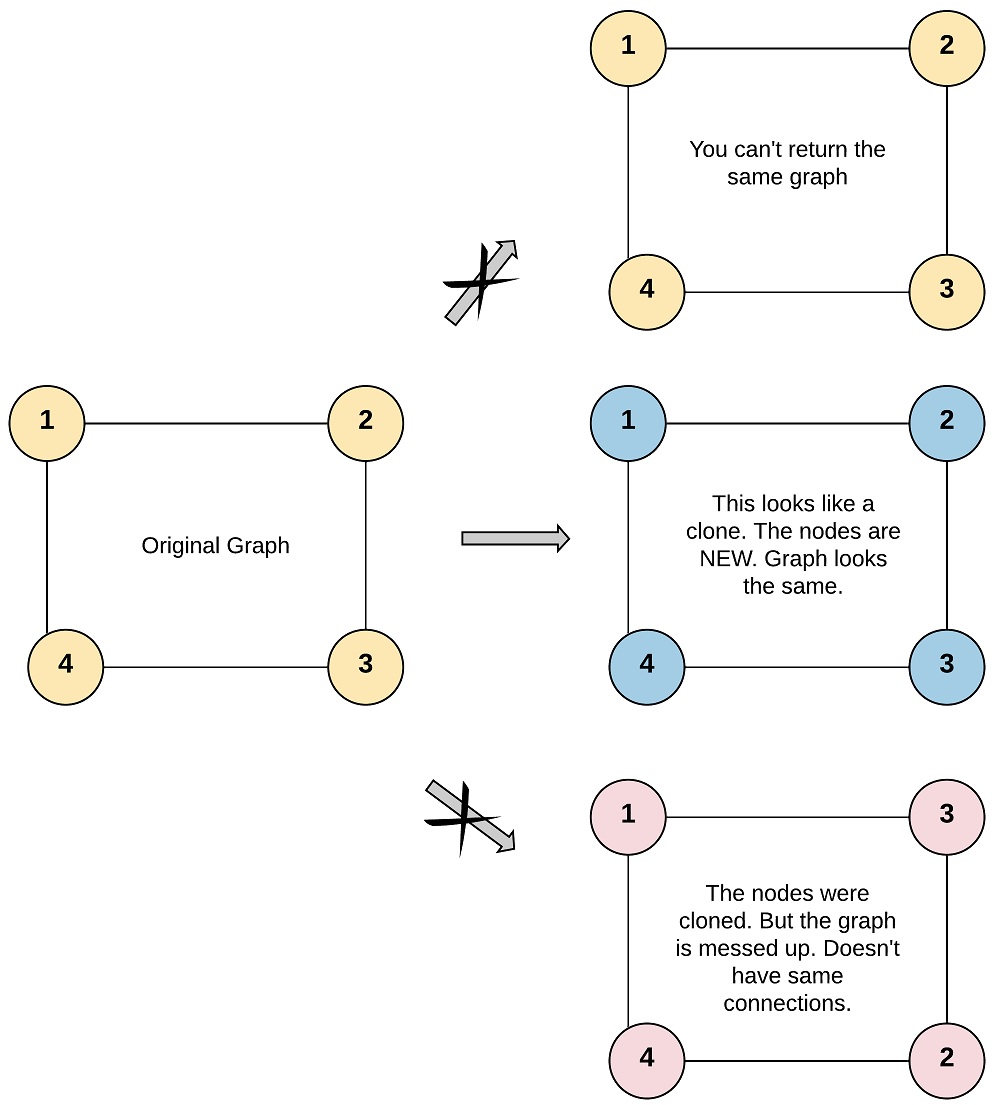
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph. Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; }Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)’s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)’s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).Example 2:
Input: adjList = [[]]
Output: [[]]
Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.Example 3:
Input: adjList = []
Output: []
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.Constraints:
The number of nodes in the graph is in the range [0, 100].
1 <= Node.val <= 100
Node.val is unique for each node.
There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Clone a Graph using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
A Graph is a collections of vertices and edges and can be noted as 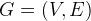
We can use the Depth First Search Algorithm (usually implemented in Recursion Manner) to traverse and clone the Graph. The pitfall here is that we need a hash table to remember the nodes that we have visited, and that needs to be marked immediately once a vertex is visited but before its neighbour vertices are cloned.
We use a Stack to implement the Depth First Search Algorithm, and this can be done simply via Recursion (the compilers maintain a stack for us)
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, neighbors):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors
"""
class Solution(object):
def cloneGraph(self, node):
def clone(node, memo = {}):
if not node:
return node
if node in memo:
return memo[node]
clone_node = Node(node.val, [])
memo[node] = clone_node
clone_node.neighbors = [clone(kid) for kid in node.neighbors]
return clone_node
return clone(node)
The time complexity is O(N+M) where N is the number of vertices and M is the number of edges. And the space complexity is O(N) because of Recursion that uses implicit stack and also the hash map to keep tracking of the cloned vertices. The runtime space/time complexity is the same as: Teaching Kids Programming – Clone (Deep Copy) a Undirected Connected Graph using Breadth First Search Algorithm
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
809 wordsLast Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Estimate the Math Continued Fraction Value in Python (Recursion and Iterative Algorithm)
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Clone (Deep Copy) a Undirected Connected Graph using Breadth First Search Algorithm