Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
Mathematically, the Fibonacci Numbers are:
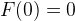
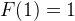
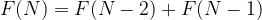
Fibonacci Number – Recursion
def f(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
if n == 1
return 1
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)
Fibonacci Number – Iterative
def f(n):
a, b = 0, 1
for i in range(n):
a, b = b, a + b
return a
Fibonacci Number – Recursion with “NoteBook”
aka. Memoization, aka Dynamic Programming:
def f(n, nb = {}):
# first look it up in notebook
if n in nb:
return nb[n]
if n == 0:
return 0
if n == 1
return 1
ans = f(n - 1, nb) + f(n - 2, nb)
# save the result in notebook
nb[n] = ans
return ans
The {} dictionary object is used as a notebook i.e. cache/meomization. The intermediate Fibonacci numbers are computed and stored as key-value pairs in the “notebook”.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
341 wordsLast Post: Two Pointer Sliding Window to Compute the Longest Substring with At Most Two Distinct Characters
Next Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Reversing a List using Stack