Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
You are given a binary array nums. We call a subarray alternating if no two adjacent elements in the subarray have the same value. Return the number of alternating subarrays in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,1,1,1]
Output: 5
Explanation:
The following subarrays are alternating: [0], [1], [1], [1], and [0,1].Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,0]
Output: 10
Explanation:
Every subarray of the array is alternating. There are 10 possible subarrays that we can choose.Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5
nums[i] is either 0 or 1.
Hints:
Try using dynamic programming.
Let dp[i] be the number of alternating subarrays ending at index i.
The final answer is the sum of dp[i] over all indices i from 0 to n – 1.
Count Alternating Subarrays
We can bruteforce all the pairs of subarrays using O(N^2) time, i.e. the subarrays of size one is C(N, 1) and the subarray of more than 1 element can be counted via C(N, 2) where we pick two different indices, one for the left and another for the right.
Thus, the total number of subarrays is 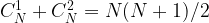 i.e. O(N^2) time
i.e. O(N^2) time
Checking if any given subarray is alternating requires O(N) time thus O(N^3) overall.
class Solution:
def countAlternatingSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
## check if the subarray[L:R+1] is alternative O(N) time
def check(L, R):
for i in range(L, R):
if nums[i] == nums[i + 1]:
return 0
return 1
n = len(nums)
ans = 0
## Bruteforce all pairs O(N^2)
for R in range(n):
for L in range(R + 1):
## O(N)
ans += check(L, R)
return ans
Count Alternating Subarrays via Bottom Up Dynamic Programming Algorithms
If we let dp[i] be the number of alternating subarrays that end at index i, thus when we iterate from left to right, we check the neighbour elements, if it differs, then we conclude the 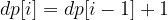 otherwise, we reset the counter i.e.
otherwise, we reset the counter i.e. 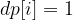
The DP algorithm is O(N) time and the space complexity is O(N) due to the dp array.
class Solution:
def countAlternatingSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
## Bottom Up Dynamic Programming - O(N) time/space
ans = 1
n = len(nums)
dp = [1] + [0] * (n - 1)
for i in range(1, n):
if nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
dp[i] = 1
else:
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + 1
ans += dp[i]
return ans
We can optimize the space by using a counter to represent the number of subarrays that end at current index. We don’t need to store previous dp[i] values.
class Solution:
def countAlternatingSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
## Bottom Up Dynamic Programming - O(N) time, O(1) space
ans = size = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
size = 1
else:
size += 1
ans += size
return ans
The time complexity is O(N) and the space is optimized to O(1) constant.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
710 wordsLast Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Latest Time You Can Obtain After Replacing Characters (Decision Tree)
Next Post: Rust Cargo Manifest Files Explained: What are the the Cargo.lock and Cargo.toml files?