Teaching Kids Programming: Videos on Data Structures and Algorithms
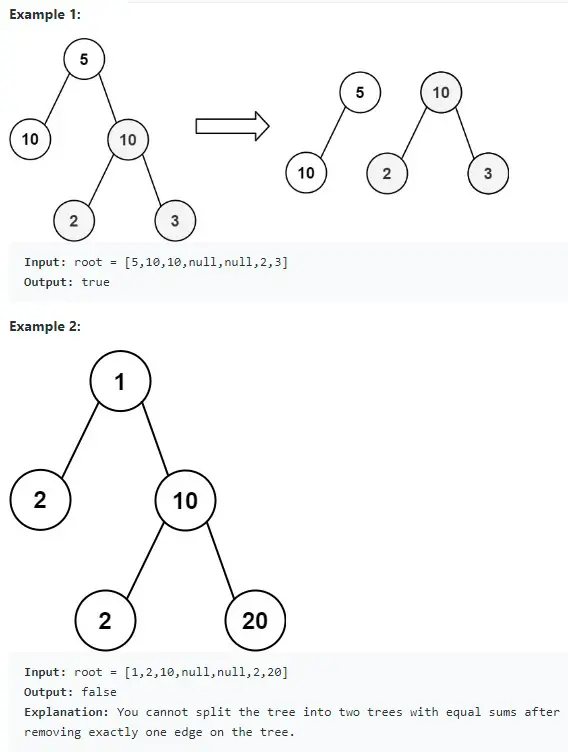
Given the root of a binary tree, return true if you can partition the tree into two trees with equal sums of values after removing exactly one edge on the original tree.
Equal Tree Partition via Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm
We already learn how to compute the sum of a binary tree using Recursive Depth First Search Algorithm. We can store all the sums for all the subtrees one by one in a list. And then the last element should be the sum of the entire tree. If there is a way to split the binary tree into half, the half of the sum should be in the list.
class Solution(object):
def checkEqualTree(self, root):
seen = []
def dfs(node):
if not node:
return 0
s = dfs(node.left) + dfs(node.right) + node.val
seen.append(s)
return s
total = dfs(root)
seen.pop()
return total / 2.0 in seen
The time complexity is O(N) as we need to visit all the nodes in the binary tree. The space complexity is O(N) as we need to use a list/array to store all the sums, and also due to implicit stack usage from Recursion.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
345 wordsLast Post: Teaching Kids Programming - Dynamic Programming Algorithms to Count the Number of Unique Binary Search Trees (Catalan Numbers)
Next Post: One-line Python Lambda Function to Hexify a String/Data (Converting ASCII code to Hexadecimal)