Docker-compose is a tool of docker, but before understanding what is the docker-compose let us explain what is a Docker? Docker is a virtual container that is used to combine the applications with their dependencies to run on any operating system. Docker supports a tool which is known as Docker-compose and is used to handle multi-container applications.
The Docker-compose uses the YAML files for configuration and it manages all the services from the CLI (command-line interface) either it is to start the service or to create the process, all the processes can be handled easily using this tool.
In this write-up, we will learn the installation procedure of its installation in Debian 11 and also discuss some basic commands of its uses.
How to install Docker-Compose on Debian 11
As the package of Docker-Compose is not comes along with the repository of Debian 11, so we will directly install it from Github and use the flag -o as output and store the output at the path provided, to do so we will execute the command:
$ sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.0.1/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose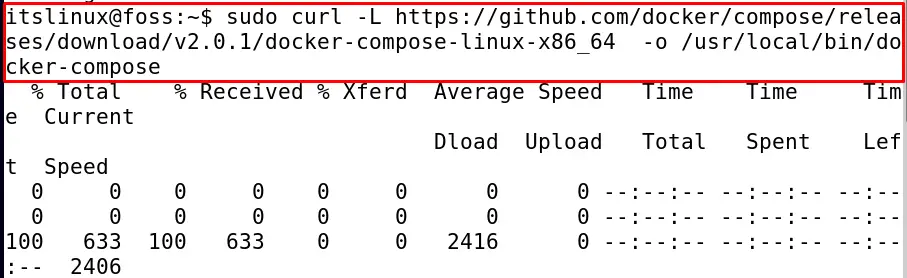
Once the Docker-Compose has been downloaded and installed, we will change the access permissions of the file using the chmod:
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose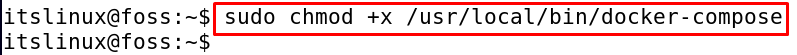
To confirm the installation, we will check the version of the Docker-Compose using the command:
$ docker-compose --version
From the output, it has been verified the Docker-Compose has been installed successfully.
How to use Docker-compose in Debian 11
Here we will discuss some basic commands to use Docker-compose in Debian 11. First, we will create a directory and switch to it lets say we create a directory with the name of Hello-itslinux by executing the commands:
$ mkdir Hello-itslinux
$ cd Hello-itslinux
Then we will create a YML file here with the help of the nano editor using a command:
$ nano docker-compose.yml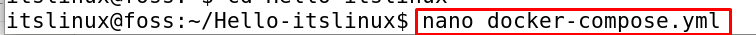
Type some content here let’s say we are going to initialize two services db and WordPress, both the services will create their own images when executed by the Docker-Compose. The code of this will be as:
version: '3'
services:
db:
image: mysql:5.7
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: somewordpress
MYSQL_DATABASE: wordpress
MYSQL_USER: wordpress
MYSQL_PASSWORD: wordpress
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
image: wordpress:latest
ports:
- "8000:80"
restart: always
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: wordpress
volumes:
db_data: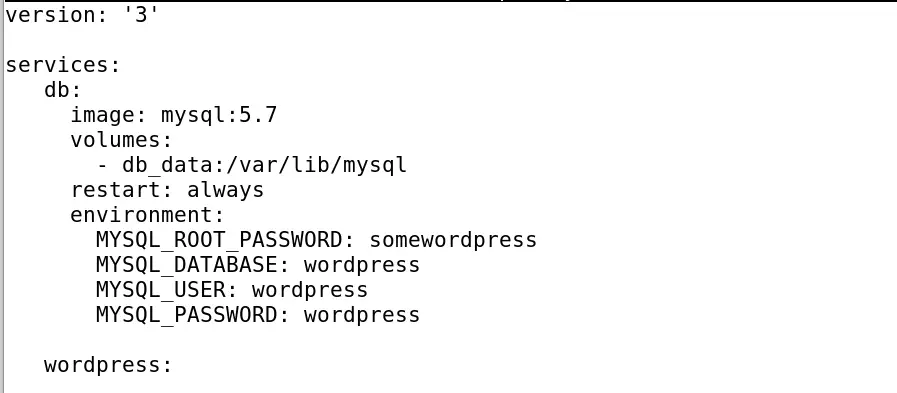
Press CTRL+S to save the file and CTRL+X to exit the editor, now execute the file using the docker-composer as:
$ sudo docker-compose up -d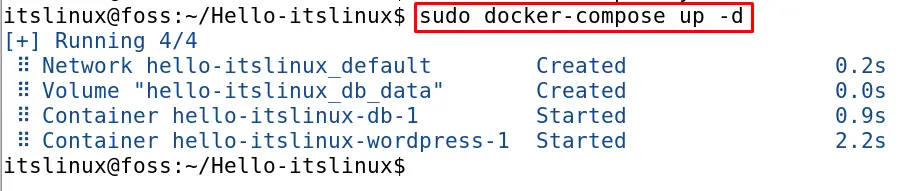
Now the above command will build up both; db and WordPress containers and also run them. Now if we want to remove and stop the containers using the docker-compose, execute the command:
$ sudo docker-compose down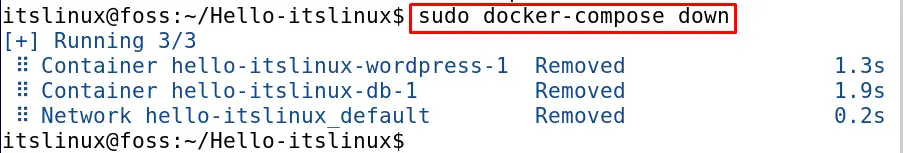
We can also build a multi-container application using the Docker-Compose, a simple example is being considered for this purpose, again open a file using the nano editor and insert a new code in it.
$ nano docker-compose.yml
Now edit the code in which each section of the “Services” section will create a separate entry on the execution of the docker-compose as:
version: '3'
services:
distro:
image: alpine
restart: always
container_name: Alpine_Distro
entrypoint: tail -f /dev/null
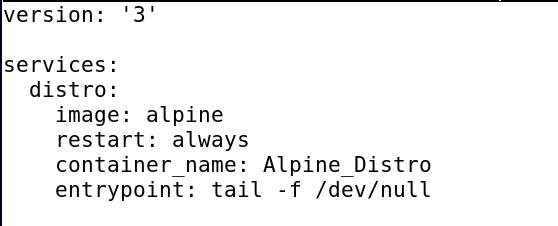
Save the file by pressing CTRL+S and exit the editor by pressing CTRL+X. Once the editor is closed, execute the command to build the containers.
$ sudo docker-compose up -d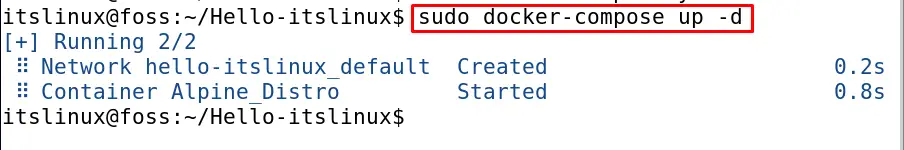
The containers have been buildup, to check the status of the containers executes the command:
$ sudo docker ps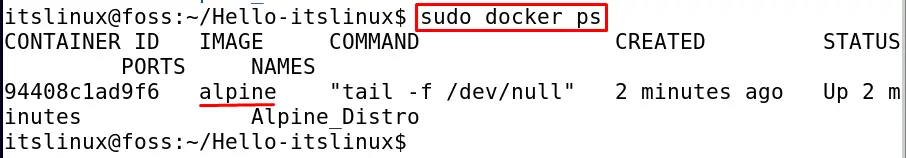
Now to remove them, we will use the down command as:
$ sudo docker-compose down
There are a lot of other advanced commands too with the help of which we can perform many other tasks. If we want to remove the Docker-Compose from Debian 11, run the command:
$ sudo rm /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
The Docker-compose has been removed from Debian 11 successfully.
Conclusion
Multi environments can be hosted from a single machine using the Docker-compose, which is the tool of the Dockers. It is very secure while communicating the information between the containers as it keeps the information in the form of a swarm. In this write-up, we first discussed the method of installation of Docker-Compose in Debian 11 directly from Github, and then we discuss its uses by building the two services db and WordPress and also building a simple application using the Docker-compose.

Saryia is a professional writer with a passion for simplifying complex topics. Specializing in Linux, programming, and technology, Saryia creates in-depth tutorials and articles designed to educate and empower readers.
