This lesson mainly focuses on how to manage Database transactions while working with the MySQL database in Python. Learn Python MySQL transaction management using commit and rollback using ‘Mysql connector python’ module.
Further Reading:
Table of contents
What is Database Transaction
The database transaction represents a single unit of work. Any operation which modifies the state of the MySQL database is a transaction. Let see in detail what is database transaction. For example, take a sample of a Bank amount transfer, which involves two significant transactions.
- Withdrawal of money from account A
- Deposit Money to Account B
If the first Transaction is executed successfully but the second failed, in this case, we need to re-deposit money back to account A. To manage such instances, we need transaction management.
Using ACID properties, we can study transaction management well. ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, isolation, and durability.
- Atomicity: means all or nothing. Either all transactions are successful or none. You can group SQL statements as one logical unit, and if any query fails, the whole transaction fails.
- Consistency: It ensures that the database remains in a consistent state after performing a transaction.
- Isolation: It ensures that the transaction is isolated from other transactions.
- Durability: It means once a transaction has been committed, it persists in the database irrespective of power loss, error, or restart system.
Python MySQL Commit(), rollback() and setAutoCommit() to manage transactions
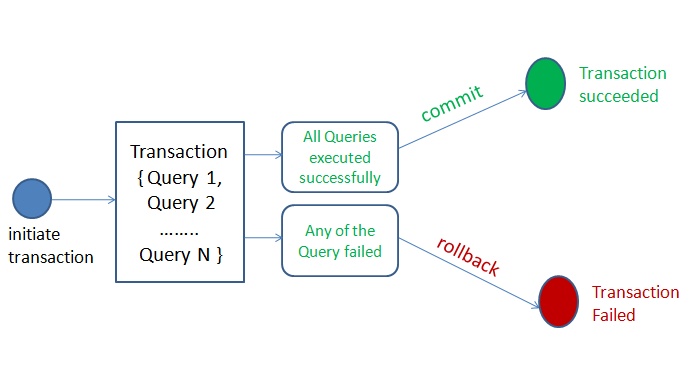
Please follow the below steps to manage MySQL transactions in Python: –
- Create MySQL database connections in Python.
- Prepare the SQL queries that you want to run as a part of a transaction. For example, we can combine two SQL queries(withdrawal money and deposit money query) in a single transaction.
- Set an auto-commit property of MySQL connection to false.
- Execute all queries one by one using the cursor.execute()
- If all queries execute successfully, commit the changes to the database
- If one of the queries failed to execute, then rollback all the changes.
- Catch any SQL exceptions that may occur during this process
- Close the cursor object and MySQL database connection
Methods to manage MySQL Database Transactions in Python
Python MySQL Connector provides the following method to manage database transactions.
commit():MySQLConnection.commit()method sends a COMMIT statement to the MySQL server, committing the current transaction. After the successful execution of a query make changes persistent into a database using the commit() of a connection class.rollback():MySQLConnection.rollbackrevert the changes made by the current transaction. When one of the transactions fails to execute, and you want to revert or undo all your changes, call a rollback method of MySQL connection object.autoCommit():MySQLConnection.autocommitvalue can be as True or False to enable or disable the auto-commit feature of MySQL. By default its value is False.
Python example to manage MySQL transactions using commit and rollback
Output if the query executes successfully.
Record Updated successfully
You should get the following output if a query fails to execute.
Failed to update record to database rollback
Let’s understand the above code: –
- We imported the MySQL connector python module so we can use its API to communicate with MySQL Database.
- After a successful MySQL connection, we set
auto-committoFalse, i.e., we need to commit the transaction only when both the transactions complete successfully. - We prepared two update SQL queries as a part of a single transaction to deposit money to account B from account A.
- We executed both the queries one by one using a
cursor.execute()method. - After successful execution of both the queries, we committed our changes to the database using a
conn.commit(). - In case of an exception or failure of one of the queries, we can revert our changes using a
conn.rollback(). - We placed all our code in the
try-exceptblock to catch the database exceptions that may occur during the process.
Next Steps:
To practice what you learned in this article, Please solve a Python Database Exercise project to Practice and master the Python Database operations.

Hi, how many executed queries can be done in one commit?
necesito hacer reversión a través de un procedimiento desde Python. “Python rollback SQL transactions”.
Hi Vishal,
Let’s say I created a database with some tables and some sample data using Python, and then I have a simple user interface that allows the user to insert, delete, and update some data into my database.
And let’s say the database is deleted, if I want the transactions that the user inserted/deleted/updated to stay in the database upon recreation in my code, how do I do that?
A short example would be great. Thank you.
Sorry, really new to both Python and mySQL.
Jeff
This is amazing, thanks man.
hi,
is there any way to do a
commit()on a cursor and not on a DB connection?No. Can you please let me know the problem you are facing
no problem actually, i saw in a course that you can do a commit() on a cursor in sqlite3 on python and i was just wondering if there is any equivalent way in mysql.
Okay. but I don’t think that is possible. Can you please ping me the link
Could you show how this same transaction could be done using a ‘with’ statement to handle the closing of the database?
Hi Johno, I will add that
Please fix your example: replace “false” with “False”