RoboDK tools for simulating and programming industrial robots (implements the RoboDK API)
Project description
RoboDK API for Python
The robodk package implements the RoboDK API for Python.
The RoboDK API allows you to create simulations for industrial robots, mechanisms and generate vendor-specific programs for robots. With the RoboDK API for Python you can simulate and program any industrial robot using Python programming language. The RoboDK API provides an alternative to using vendor-specific programming languages.
While RoboDK's graphical user interface can be used to create programs, it is possible to extend the robot controller limitations by using a universal programming language such as Python. The following page provides an overview of the RoboDK API using Python: https://robodk.com/offline-programming.
The robodk package is available on PyPi.
RoboDK can be used for a wide range of robot manufacturing applications, such as robot machining, 3D printing, synchronizing multiple robots, pick and place, and so on.
Important: The RoboDK API is not the same as the RoboDK Plug-In interface.
Documentation
The robodk package includes the following modules:
- The
robolinkmodule is the link between RoboDK and Python. Any item from the RoboDK item tree can be retrieved. Items are represented by the object Item. An item can be a robot, a reference frame, a tool, an object or a specific project. - The
robomathmodule is a robotics toolbox, inspired from Peter Corke's Robotics Toolbox. For instance, matrix operations, projection, timers, etc. - The
robodialogsmodule is a dialogs toolbox. For instance, open and save file dialogs, message prompts, etc. - The
robofileiomodule is a file operation toolbox. File properties, CSV, FTP, etc. - The
roboappsmodule is a RoboDK Apps toolbox. More information can be found in our App loader documentation.
You can find more information about RoboDK API in our documentation.
- Introduction to the RoboDK API
- Introduction to RoboDK for robot simulation and offline programming
- The
robodkpackage for Python
Requirements
- RoboDK Simulation Software
- Python (Python 2 and Python 3 supported)
Mac and Linux usually have Python 2 installed by default. Although it is not required, Python 3 can be installed on Linux by typing:
sudo apt-get install pip3
sudo apt-get install idle3
The RoboDK API can be used with a free RoboDK license.
How to install
By default, RoboDK automatically uses the PYTHONPATH environment variable pointing to the /RoboDK/Python/ folder to search for the robodk package. Alternatively, you can also install the robodk package for Python:
# cd path-to-python/Scripts
pip install robodk
RoboDK will automatically install external Python dependencies based on your usage. However, if you do not have an active ethernet connection or wish to install them all at once, you can specify external dependencies (see extras_require in setup.py):
# cd path-to-python/Scripts
pip install robodk[cv,apps,lint]
The Python interpreter and editor used by RoboDK can be set in:
RoboDK - Tools - Options - Python
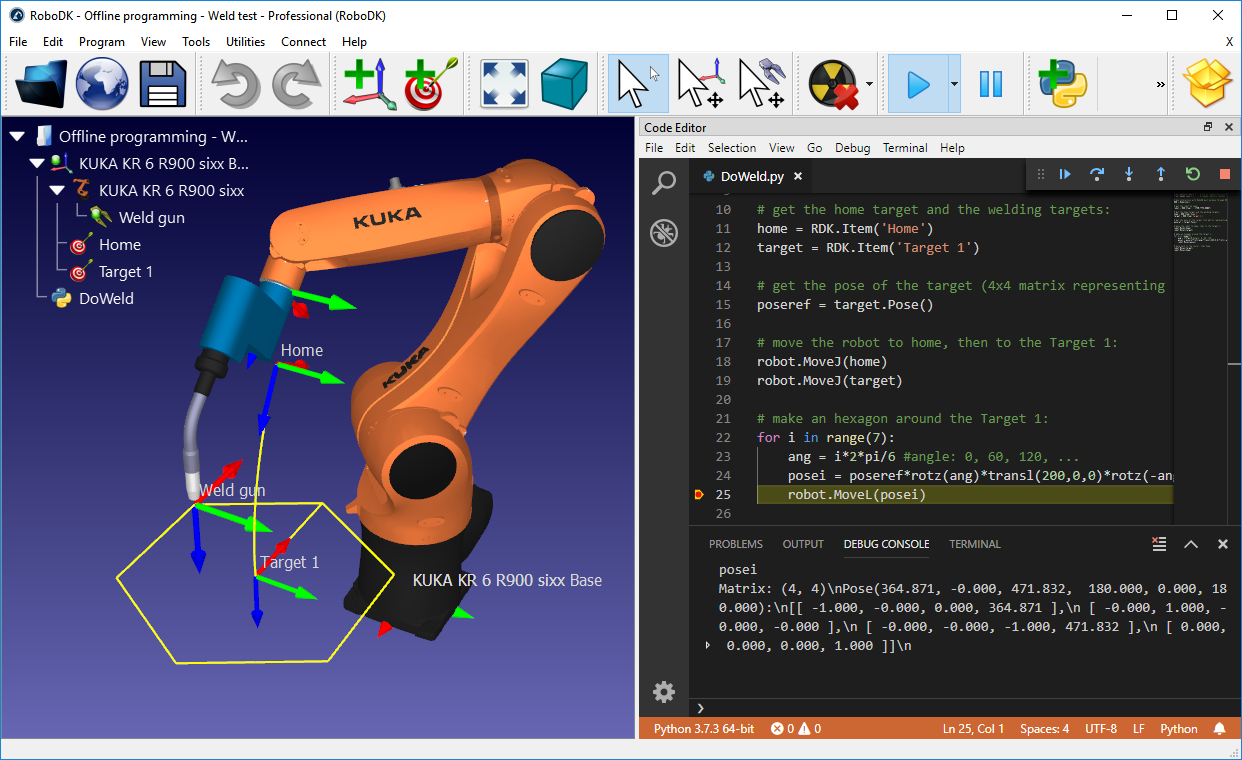
Example
The following script shows an example that uses the robodk package for robot simulation and offline programming. For more examples using the API, see our documented examples.
from robodk.robolink import * # RoboDK's API
from robodk.robomath import * # Math toolbox for robots
# Start the RoboDK API:
RDK = Robolink()
# Get the robot item by name:
robot = RDK.Item('Fanuc LR Mate 200iD', ITEM_TYPE_ROBOT)
# Get the reference target by name:
target = RDK.Item('Target 1')
target_pose = target.Pose()
xyz_ref = target_pose.Pos()
# Move the robot to the reference point:
robot.MoveJ(target)
# Draw a hexagon around the reference target:
for i in range(7):
ang = i*2*pi/6 #ang = 0, 60, 120, ..., 360
# Calculate the new position around the reference:
x = xyz_ref[0] + R*cos(ang) # new X coordinate
y = xyz_ref[1] + R*sin(ang) # new Y coordinate
z = xyz_ref[2] # new Z coordinate
target_pos.setPos([x,y,z])
# Move to the new target:
robot.MoveL(target_pos)
# Trigger a program call at the end of the movement
robot.RunCode('Program_Done')
# Move back to the reference target:
robot.MoveL(target)
Post Processors
The same script used for simulation can be used for robot programming offline. This means a program will be automatically generated for your robot controller to reproduce the movements on the robot. RoboDK supports a large number of robot controllers and it is easy to include compatibility for new robot controllers using Post Processors.
More information about robot post processors here:
The following list includes the supported robot controllers from different robot manufacturers. You can find the most up to date list of supported robot controllers in our library of post processors and the documentation for Post processors.
- ABB RAPID IRC5: for ABB IRC5 robot controllers
- ABB RAPID S4C: for ABB S4C robot controllers
- Adept Vplus: for Adept V+ programming language
- Allen Bradley Logix5000: for Allen Bradley Logix5000 PLC
- Annin Robotics: for AR3 and AR4 robots.
- Aubo: for AUBO robot controllers
- Aubo ARCS: generates code (.lua and .pro) for AUBO ARCS robotic controllers.
- Automata: for Automata EVA robots.
- Borunte: for Borunte robot arms. Generates zip-package with necessary files for BRTIRUS robot controllers.
- Brooks: for PreciseFlex robots.
- CPR: produces XML-formatted code suitable for CPR robotic systems.
- CSV: generates simple CSV-formatted files for generic robotic and automation controllers. This post processor is versatile and can be used in applications requiring straightforward data import and export.
- CLOOS: for CLOOS robot controllers
- Comau C5G: for Comau C5G robot controllers
- Denso PAC: for Denso RC7 (and older) robot controllers (PAC programming language)
- Denso RC8: for Denso RC8 (and newer) robot controllers (PacScript programming language)
- Dobot: for educational Dobot robots
- Doosan: for Doosan collaborative robots
- Elite: The Elite Robots CS Task post processor allows you to generate code for CS controllers.
- Epson: for Epson robot controllers
- Estun: for Estun robot controllers
- Fairino: produces .lua files and supports the Fairino FR series of robots.
- Fanuc R30iA: for Fanuc R30iA and R30iB robot controllers
- Fanuc R30iA_Arc: for Fanuc Arc welding
- Fanuc RJ3: for Fanuc RJ3 robot controllers
- Flexiv: generates trajectory files (.traj) for Flexiv Hesper controllers
- Foxbot: generates .pac files for Foxbot controllers
- GCode BnR: for B&R robot controllers
- GSK: for GSK robots
- HCR: for Hanwha robot controllers
- HIWIN HRSS: for HIWIN robots
- Huayan: generates programs for Huayan Robotics robots (formerly known as Han's Robot)
- Hyundai: for Hyundai robot controllers
- IGUS: generates XML-formatted code suitable for igus robotic systems
- IIMT: generates .txt files that you can load in IIMT CR robot controllers easily.
- Inexbot: generates .JBI files specifically designed for Inexbot controllers (Inform III)
- JAKA: for JAKA robot controllers
- Kassow: generate code for Kassow Robots KR2 controllers
- KEBA KAIRO: for Keba Kairo robot controllers
- Kinova: for Kinova robots
- Kawasaki: for Kawasaki AS robot controllers
- KUKA IIWA: for KUKA IIWA sunrise programming in Java
- KUKA KRC2: for KUKA KRC2 robot controllers
- KUKA KRC2_CamRob: for KUKA CamRob milling option
- KUKA KRC2_DAT: for KUKA KRC2 robot controllers including DAT data files
- KUKA KRC4: for KUKA KRC4 robot controllers
- KUKA KRC4_Config: for KUKA KRC4 robot controllers with configuration data in each line
- KUKA KRC4_DAT: for KUKA KRC4 robot controllers including DAT data files
- KUKA KRC5: for KUKA KRC5 robot controllers
- MARS: generates .gpl files for MARS systems
- Mecademic: for Mecademic's script code required by the Meca500 robot
- Mecademic Python: it generates a Python script that can control the Mecademic Meca500 robot remotely.
- Mitsubishi: for Mitsubishi robot controllers
- Motoman/Yaskawa: for different Motoman robot controllers using Inform II and Inform III (JBI)
- Motoman Cartesian: for Yaskawa/Motoman robot controllers using Cartesian values. You may require the Relative Job option on the robot controller if you want to manually modify this program on the robot controller.
- MyCobot: generates Python code compatible with MyCobot robotic arms
- Nachi AX FD: for Nachi AX and FD robot controllers
- Neura: generates a NeuraPy Python script compatible with the Neura Robotics Real-Time NR-Motion Master controller
- NEWKer i6: generates code designed for NEWKer i6 CNC controllers
- Niryo: generates Python code designed for Niryo educational robots
- Omron: for Omron-TM robot controllers
- OTC: for Daihen OTC robot controllers
- Panasonic: for Panasonic PRG programs (requires Panasonic G2PC tools to compile ASCII files to binary files)
- Precise: for Precise Scara robots
- QJAR: generates .rbg files for QJAR robot controllers
- Rainbow Robotics: generates .wsl files for Rainbow Robotics controllers
- Robostar: for Robostar robot controllers
- Rokae: generates .mod files for ROKAE robot controllers
- Rozum RC API: generates .py files to integrate with Rozum RC Series controllers
- Rozum RC Pulse: generates .rcp files designed for Rozum RC Series controllers
- Schneider: for Schneider Electric Lexium controllers
- Siasun: for Siasun robot controllers
- Siemens Sinumerik: for Siemens Sinumerik ROBX robot controller
- Staubli VAL3: to generate Staubli VAL3 robot programs (CS8 controllers and later). It inlines the robot movements.
- Staubli VAL3_Machining: for Staubli VAL3 controllers that have the Machining HSM option.
- Staubli S6: for Staubli S6 robot controllers
- Toshiba: for Toshiba robots
- Techman: for Techman robot controllers
- Turin: outputs .txt files for Turin robot controllers
- Universal Robots: for UR robots, it generates linear movements as pose targets
- Universal Robots URP: for UR robots, it generates a URP that can be loaded and modified in Polyscope (the UR robot controller)
- Universal Robots RobotiQ: for UR robots including support for RobotiQ gripper
- Universal Robots MoveP: for UR robots, it generates linear movements as MoveP commands
- Wlkata: for WLKATA Mirobot robotic arms
- xArm: for uFactory xArm robotic systems
- Yamaha: for Yamaha robots
App loader Plug-In
Once you have a script working in Python, you can easily set it up as an App using the App loader plugin. RoboDK Apps allow you to customize the RoboDK environment for simulation and offline programming. RoboDK Apps can be easily distributed for production. More information here:
Linting (source-code checker)
Pylint is a source-code, bug and quality checker for Python programming. Pylint is integrated by default when using RoboDK's default settings (VScode/VScodium text editor).
If you prefer using other text editors you can use the pylint_robodk module with Pylint for linting. The following argument must be passed to pylint to activate this feature:
--load-plugins=pylint_robodk
More about RoboDK
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distributions
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file robodk-5.9.4-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: robodk-5.9.4-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 122.2 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.10.11
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
96e130b23ccd9f3503da42dea0f286ff6f00439ca2051edf0bbeb90d48389a24
|
|
| MD5 |
262155c8431769cc5a3221de90f73365
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
62dc4d022bbb71407fe084f05e2e315fb2de3ddb3d8781ea2e5118d689573d9f
|
File details
Details for the file robodk-5.9.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: robodk-5.9.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 120.0 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.10.11
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
268e52339665eb6d6e14c7aa8341e8bee7372852bd25f94de5bbd29af0acb57d
|
|
| MD5 |
69acb50e9ae064d9de53bb8577bfe4cd
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3e4a66c03ab0dcb50b8ebaee550dc7acb722f6fce8771bac0537442f421a3340
|