Python Django Project – Online Car Rental System
Get Ready for Your Dream Job: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
The Online Car Rental System is a web application built using Django, designed to streamline the car rental process. It provides features for both customers and administrators to manage car rentals effectively. The system includes functionalities for browsing available cars, making reservations, and managing bookings.
About Python Django Online Car Rental System
The Online Car Rental System project is a Django-based web application. Users can browse available cars, book their preferred vehicles for specific dates, and view booking details. The system manages car availability, ensures bookings are recorded accurately, and calculates total rental costs based on the duration. This project aims to streamline car rental operations for both users and service providers.
Objectives of Python Django Online Car Rental System
- Provide a user-friendly interface for customers to browse and rent cars.
- Enable administrators to manage car inventory and bookings.
- Implement secure user authentication and authorization.
- Ensure data consistency and integrity.
Project Setup
Required Libraries
The project requires the following Python libraries:
- Django: For a web framework and ORM.
- SQLite: For database management.
- Bootstrap: For responsive design and styling.
Technology Stack
- Python
- Django
- SQLite (default database)
- HTML/CSS
- JavaScript
- Bootstrap
Prerequisites for Python Django Online Car Rental System
- Basic understanding of Python programming.
- Familiarity with Django framework.
- Knowledge of HTML/CSS for template design.
Download Python Django Online Car Rental System
Please download the source code for the Python Django Online Car Rental System: Python Django Online Car Rental System Project Code.
Step-by-Step Implementation of Python Django Online Car Rental System
1. Project Initialization
- The first command initializes a new Django project named Car_rental.
- The second command changes the directory to the project folder.
- The third command initializes a new Django app named rental in the same directory. It sets up the basic structure for the project.
django-admin startproject Car_rental cd Car_rental python manage.py startapp rental
2. Setting Up Models
- The Car model defines the attributes of a car available for rental. It includes fields for the car’s name, description, daily price, image, and availability status.
- The Booking model links a user to a car for a specific rental period. It includes references to the User and Car models.
- The Car model’s __str__ method returns the car’s name for easy identification. Used for displaying car names in the Django admin interface.
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
class Car(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
description = models.TextField()
price_per_day = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2)
image = models.ImageField(upload_to='images/')
available = models.BooleanField(default=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class Booking(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
car = models.ForeignKey(Car, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
start_date = models.DateField()
end_date = models.DateField()
total_price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=10, decimal_places=2)
def __str__(self):
return f'{self.user.username} booked {self.car.name}'
3. Making Migrations
- makemigrations: Makes migrations based on the changes detected in the models. Migrations are how Django stores changes to the models.
- migrate: This command applies the migrations to the database, creating the tables and columns.
python3 manage.py makemigrations rental python3 manage.py migrate
4. Defining Views
- The Car List view imports the necessary modules, fetches all cars, and renders the car_list.html template with the vehicles.
- Car Detail View: defines the car_detail view to get a specific car using get_object_or_404.
- Book Car view retrieves the car by ID and prepares the BookingForm for GET requests.
- Success View defines the booking_success view to render a success message.
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, get_object_or_404
from django.contrib.auth import login, authenticate
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
from .models import Car, Booking
from .forms import BookingForm, UserRegistrationForm
from django.utils import timezone
def car_list(request):
cars = Car.objects.all()
return render(request, 'rental/car_list.html', {'cars': cars})
def car_detail(request, car_id):
car = get_object_or_404(Car, pk=car_id)
return render(request, 'rental/car_detail.html', {'car': car})
@login_required
def book_car(request, car_id):
car = get_object_or_404(Car, pk=car_id)
if request.method == 'POST':
form = BookingForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
booking = form.save(commit=False)
booking.user = request.user
booking.car = car
num_days = (booking.end_date - booking.start_date).days + 1
booking.total_price = num_days * car.price_per_day
booking.save()
car.available = False
car.save()
return redirect('booking_success')
else:
form = BookingForm()
return render(request, 'rental/book_car.html', {'form': form, 'car': car})
def booking_success(request):
return render(request, 'rental/booking_success.html')
def register(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
form = UserRegistrationForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
username = form.cleaned_data.get('username')
password = form.cleaned_data.get('password1')
user = authenticate(username=username, password=password)
login(request, user)
return redirect('car_list')
else:
form = UserRegistrationForm()
return render(request, 'rental/register.html', {'form': form})
5. Setting URLs
- Imports necessary modules and the views from the current app.
- car_list url maps the root URL to the car_list view using the path function. It defines a URL pattern to access car details.
- book_Car url defines a URL pattern to handle car booking, passing car_id to the book_car view.
- booking_success maps the same view that shows a success message after booking.
- register url maps the register view to handle user registration at the register/ URL.
- It includes the Django authentication URLs under the accounts/ path for login and logout.
from django.urls import include, path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.car_list, name='car_list'),
path('car/<int:car_id>/', views.car_detail, name='car_detail'),
path('car/<int:car_id>/book/', views.book_car, name='book_car'),
path('booking_success/', views.booking_success, name='booking_success'),
path('register/', views.register, name='register'),
path('accounts/', include('django.contrib.auth.urls')),
]
6. Creating Templates
base.html:-
- The HTML document has a DOCTYPE declaration and a language attribute.
- It uses Bootstrap to set the document title to “Online Car Rental System”. It links to a Bootstrap CSS file.
- Then it creates a navigation bar using Bootstrap classes with a brand link to the car_list view.
- Finally, defining a container div with a margin-top for spacing. It uses Django template tags {% block content %} to allow content insertion in child templates.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Online Car Rental System</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.5.2/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-light bg-light">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="{% url 'car_list' %}">PythonGeeks@Car Rental System</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNav">
<ul class="navbar-nav ml-auto">
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'logout' %}">Logout</a>
</li>
{% else %}
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'login' %}">Login</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'register' %}">Register</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</div>
</nav>
<div class="container mt-4">
{% block content %}
{% endblock %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
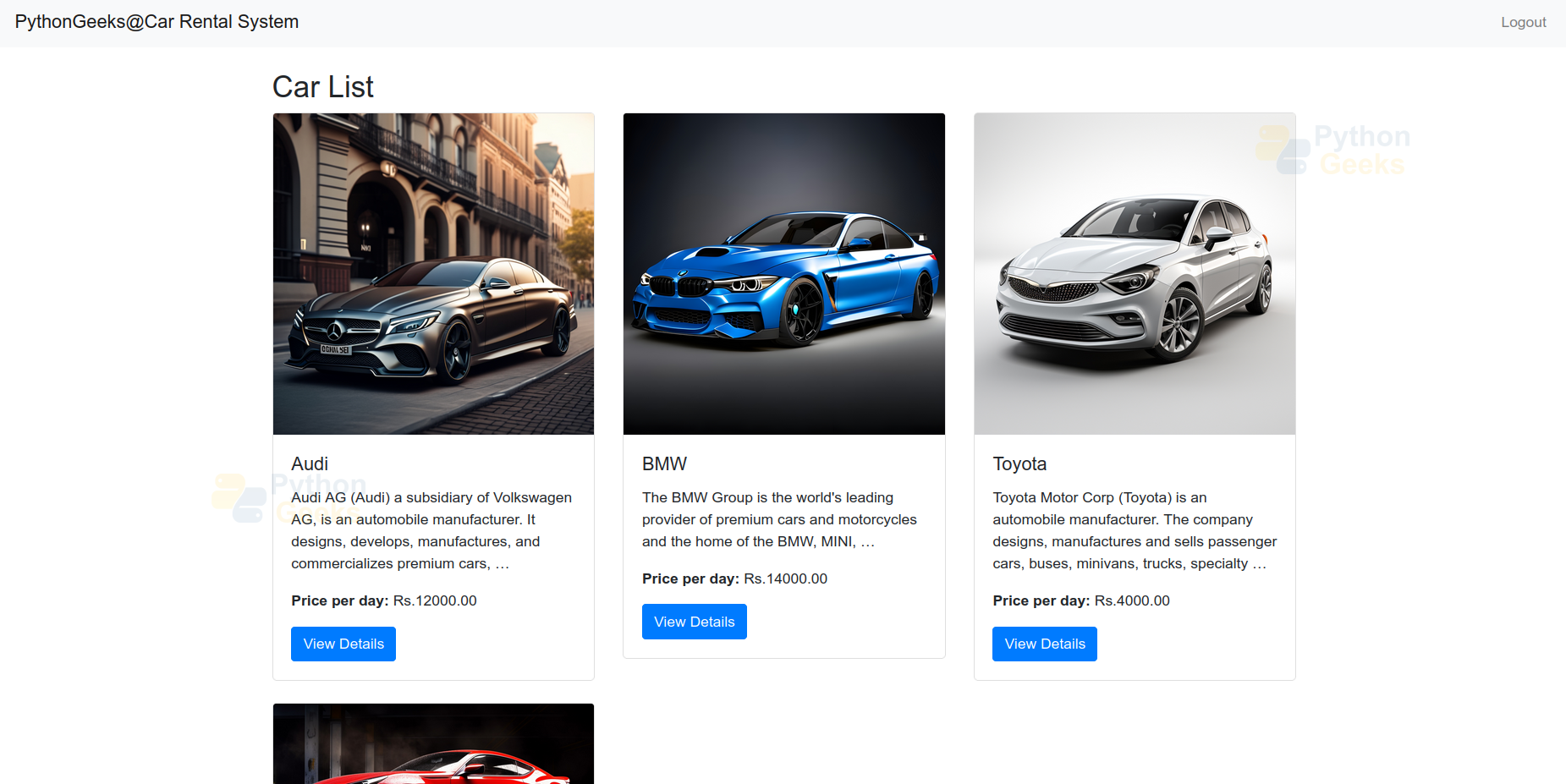
car_list.html:-
- This template extends from rental/base.html to maintain a consistent layout.
- The content block is overridden to provide specific content for the car list page.
- It iterates over Car objects and loops through the cars queryset, generating HTML for each car. For each vehicle, create a column to ensure that three cars are displayed per row.
- Each car is presented in a Bootstrap card component. It displays the car’s image, name, truncated description, and price per day.
- Include a button linking to the car’s detail page for more information.
{% extends 'rental/base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h2>Car List</h2>
<div class="row">
{% for car in cars %}
<div class="col-md-4">
<div class="card mb-4">
<img src="{{ car.image.url }}" class="card-img-top" alt="{{ car.name }}">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{ car.name }}</h5>
<p class="card-text">{{ car.description|truncatewords:20 }}</p>
<p class="card-text"><strong>Price per day:</strong> Rs.{{ car.price_per_day }}</p>
<a href="{% url 'car_detail' car.id %}" class="btn btn-primary">View Details</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% endblock %}
car_detail.html:-
- This template extends from rental/base.html to maintain a consistent layout.
- The content block is overridden to provide specific content for the car detail page.
- The overridden content displays the car’s image at the top of the card. It shows the car’s full description and daily price within the card body.
- Then it checks the car’s availability. If available, provide a ‘Book Now’ button that links to the booking page.
- If unavailable, it displays a message indicating the car’s unavailability.
{% extends 'rental/base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h2>{{ car.name }}</h2>
<div class="card">
<img src="{{ car.image.url }}" class="card-img-top" alt="{{ car.name }}">
<div class="card-body">
<p class="card-text">{{ car.description }}</p>
<p class="card-text"><strong>Price per day:</strong> Rs.{{ car.price_per_day }}</p>
{% if car.available %}
<a href="{% url 'book_car' car.id %}" class="btn btn-success">Book Now</a>
{% else %}
<p class="text-danger">This car is currently not available.</p>
{% endif %}
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
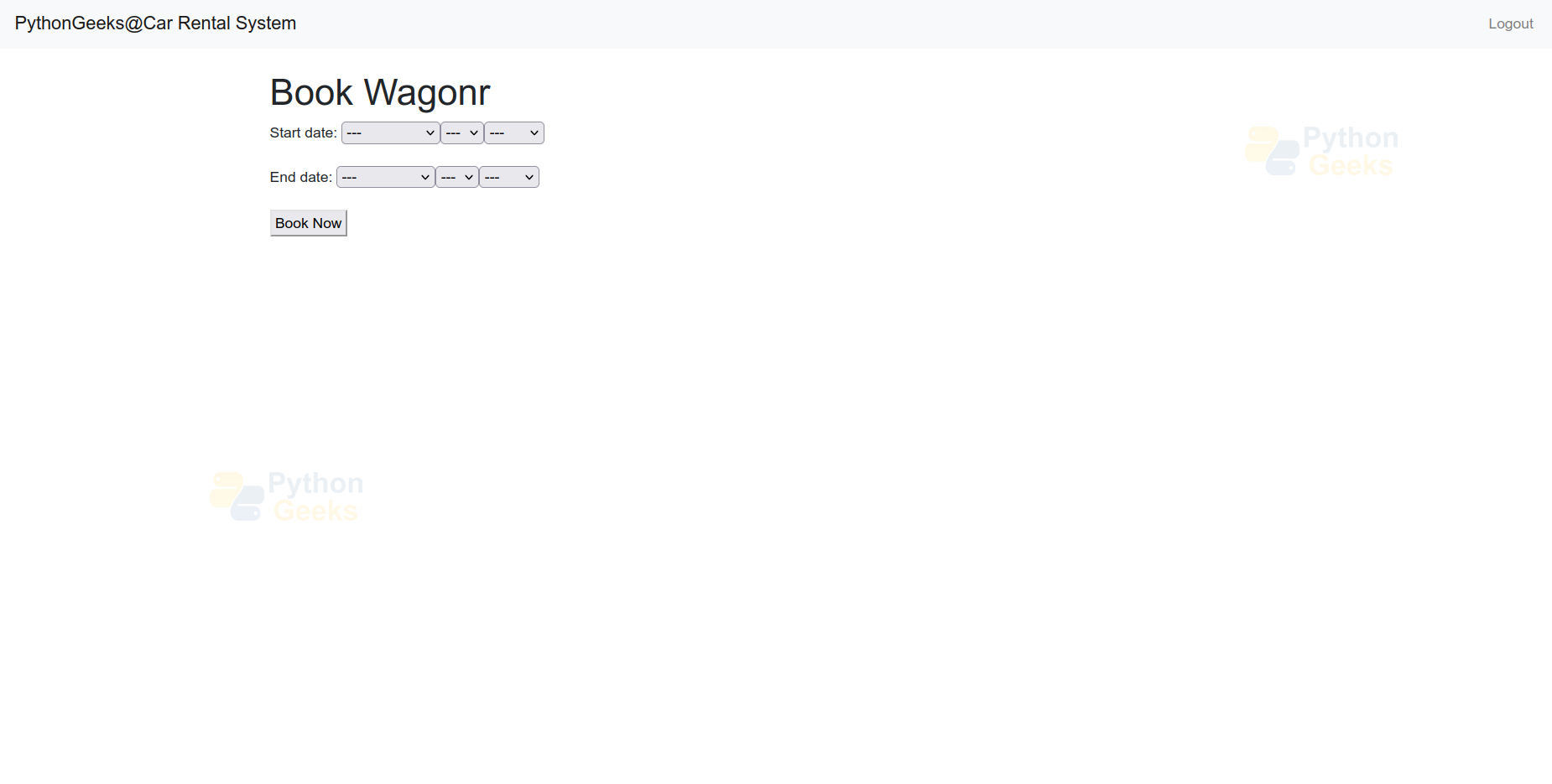
book_car.html:-
- It extends the rental/base.html template for a consistent layout.
- It overrides the content block to customise the booking page.
- Then set the page title to Book Car for clear context. It dynamically includes the car’s name in the title for specificity.
- It shows a form for booking the car, including the necessary fields.
- {% csrf_token %} is used for security against CSRF attacks. It uses form.as_p to render the form fields in paragraph format.
{% extends 'rental/base.html' %}
{% block title %}Book Car{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<h1>Book {{ car.name }}</h1>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Book Now</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}
login.html:-
- It extends the rental/base.html template for a consistent layout.
- It overrides the content block to customise the login page.
- {% csrf_token %} protects against CSRF attacks. It ensures secure form submission and data handling.
{% extends 'rental/base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<h2>Login</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Login</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}
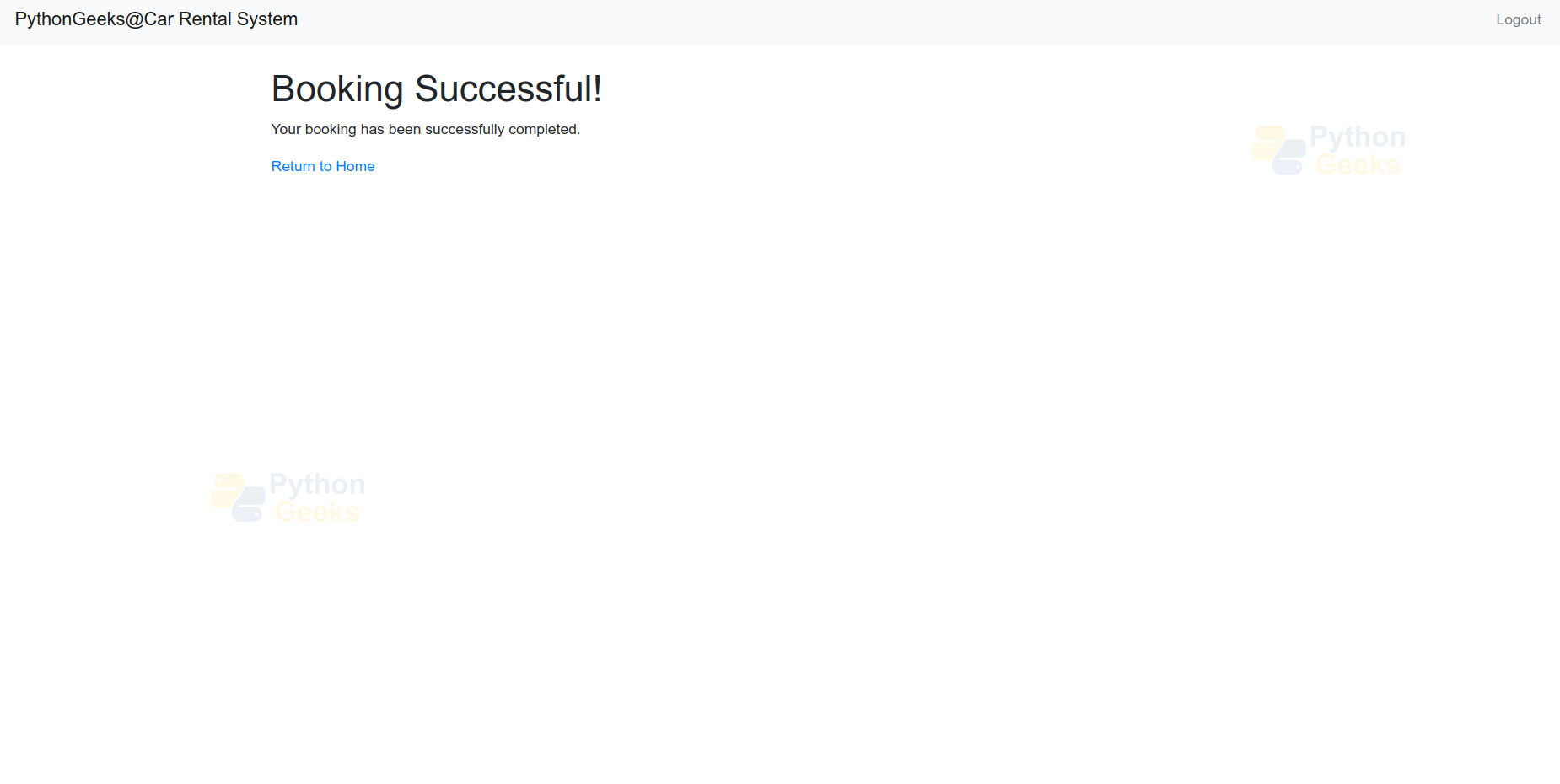
booking_success.html:-
- It extends the rental/base.html template for a consistent layout.
- The content block displays a header that reads “Booking Successful!” Also includes a paragraph confirming the successful booking.
- It provides a link to return to the home page using {% url ‘car_list’ %} to generate the home URL.
{% extends 'rental/base.html' %}
{% block title %}Booking Successful{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<h1>Booking Successful!</h1>
<p>Your booking has been successfully completed.</p>
<a href="{% url 'car_list' %}">Return to Home</a>
{% endblock %}
Python Django Online Car Rental System Output
1. Application Interface
2. Book Any Car
3. Booking Successful
4. Car Already Booked Page
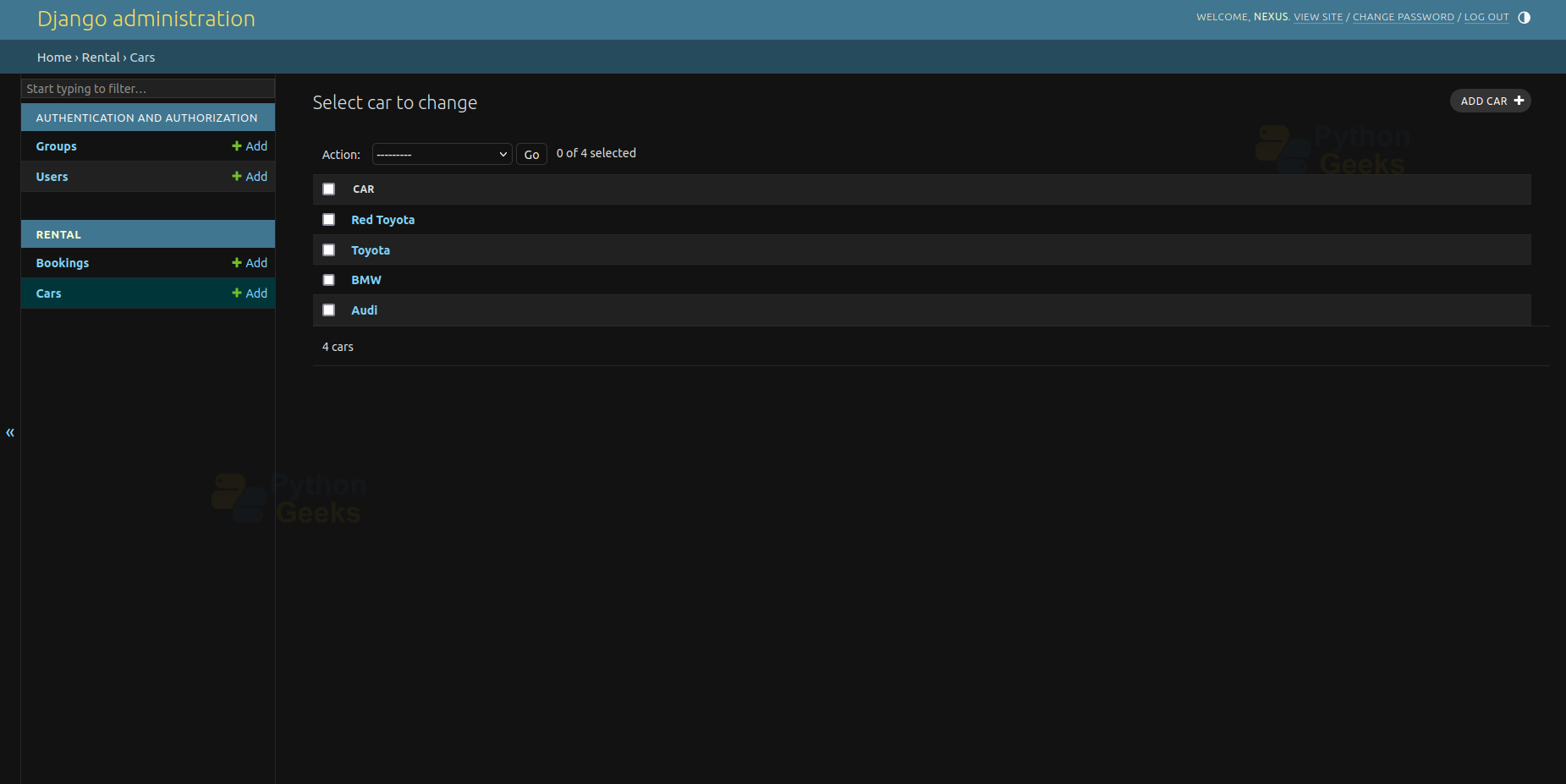
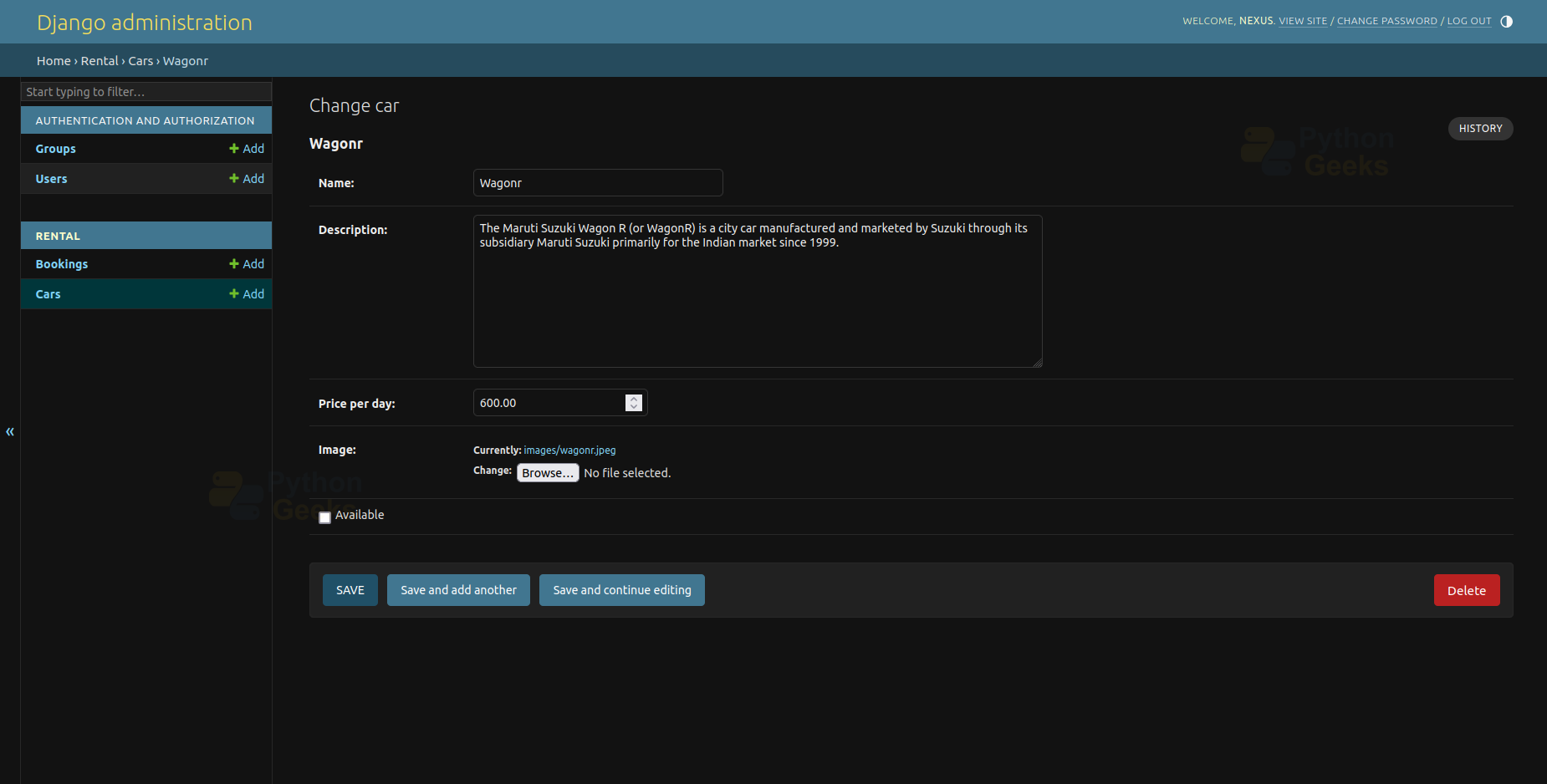
5. Administrative Page
6. Add Cars
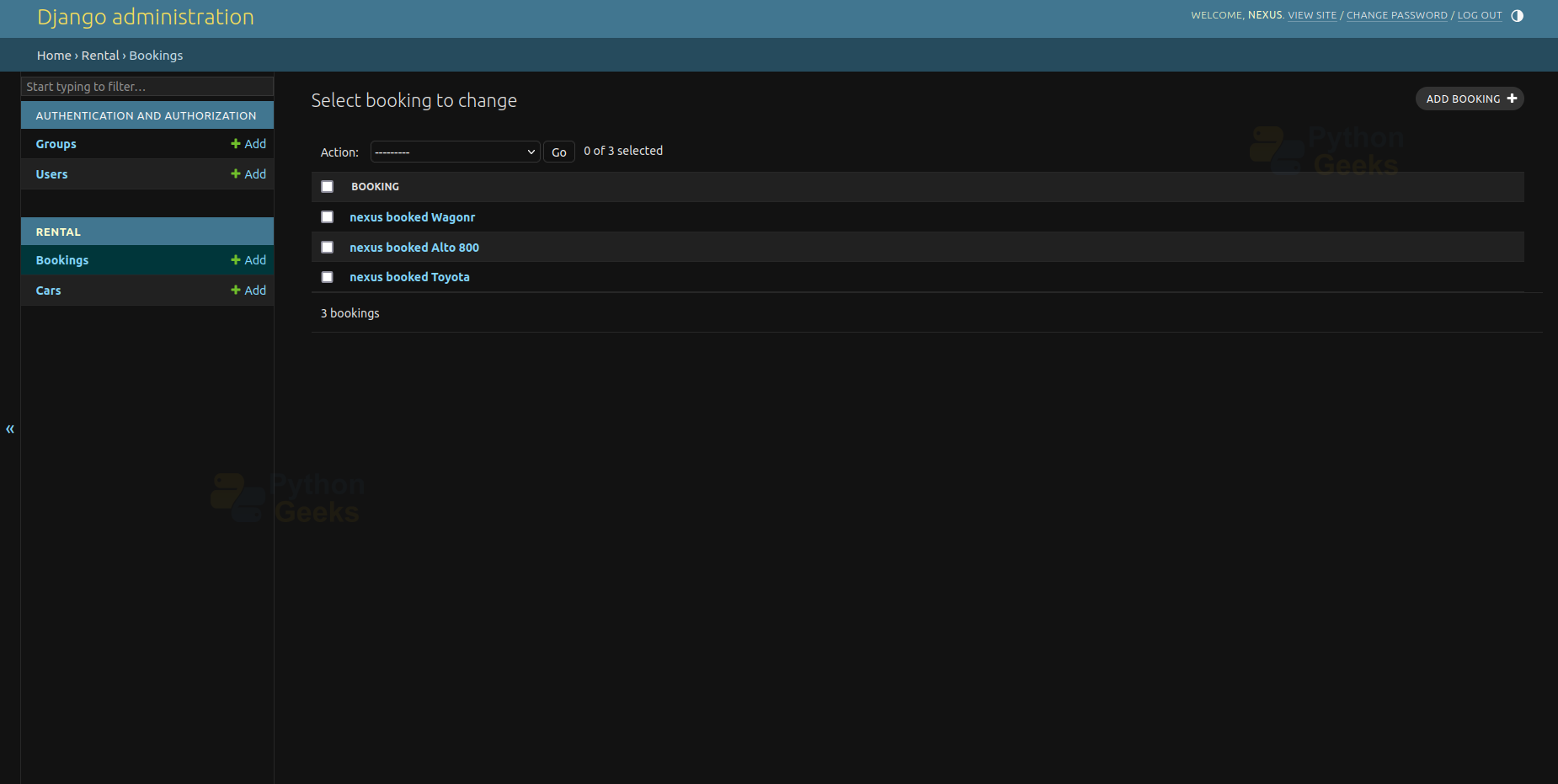
7. Add Bookings
Conclusion
The Online Car Rental System project demonstrates how Django enables the creation of a seamless, efficient car rental platform. By automating the booking process and managing car availability, the system enhances user experience and operational efficiency. The project provides a scalable solution for car rental businesses, offering features that can be further expanded to include advanced functionalities.