Clustering in Machine Learning
Get Job-ready with hands-on learning & real-time projects - Enroll Now!
Have you ever wished to market products of your client in an enhanced way to cater to a specific audience? If your answer is yes, then clustering is meant for you. Then you might ask why is Clustering best for you? What is the best way to learn the concepts of Clustering and understand its applications?
PythonGeeks is here for your rescue. This article from PythonGeeks will guide you through your journey of understanding Clustering. This article will talk about the nitty-gritty involved in the domain of Clustering. We will even talk about the reasons why we should prefer Clustering along with knowing the types of Clustering. Towards the end, we will also look at some of the real-life applications of Clustering. So, without any delay, let us look at the introduction of Clustering.
What is Clustering?
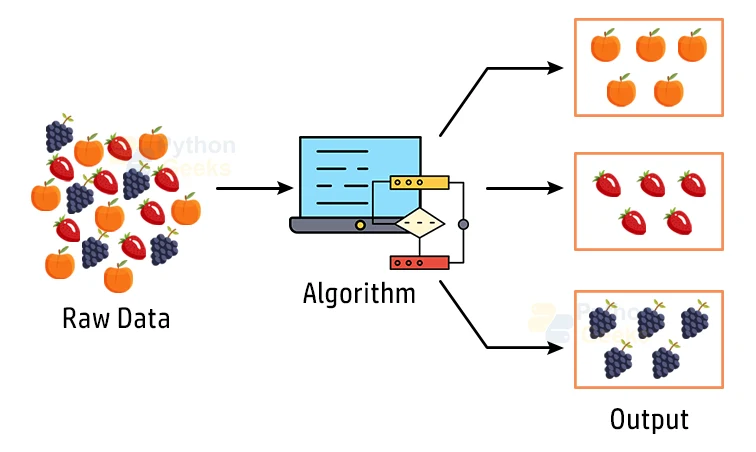
Clustering or also known as cluster analysis is a type of machine learning technique, which aims to group the unlabelled dataset. In a precise way, we can define Clustering as a technique of grouping the data points into different classes of clusters, consisting of data points having similar attributes. The objects with distinguishing similarities remain in a group that has less or almost no similarities with another group.
The algorithm can achieve this by recognizing some similar patterns in the unlabelled dataset like shape, size, color, behavior, and many such attributes, and divides them as per the presence and absence of those similar patterns present in the dataset.
Clustering is a type of unsupervised learning method; hence we do not any supervision for the algorithm, and it deals with the unlabeled dataset in an efficient way.
After deploying this clustering technique, we provide each cluster or group with a cluster ID. Machine Learning systems can make use of this id to simplify the processing of large and complex datasets in an effective way.
We can commonly use the clustering technique for statistical data analysis.
Example of Clustering
Now that we know the basic definition of Clustering, let us try to understand the clustering technique with the real-world example of a mall. When we visit any shopping mall, we are able to observe that the management tends to group together things with similar usage.
As an example, consider the t-shirts grouped in one section, and trousers are in other sections. Similarly, in vegetable sections, apples, bananas, Mangoes, and many such items are grouped in separate sections, in an attempt to make it easier for us to find things. The clustering technique also works on the same principle.
Other examples of clustering are grouping documents according to the topic that they talk about.
The clustering technique can be widely used in various tasks. Some most common uses of this technique are:
- Market Segmentation
- Statistical data analysis
- Social network analysis
- Image segmentation
- Anomaly detection
Apart from these general usages of clustering, Amazon makes use of clustering in its recommendation system to provide recommendations as per the past search of products.
Netflix also makes use of this technique to recommend movies and web series to its users as per their watch history and preferences. Now that we know what exactly clustering is, let us look at the reasons why we should prefer clustering over other algorithms.
Need of Clustering
Clustering, to date, is an important technique as it tends to perform the determination of the intrinsic grouping among the unlabeled dataset that we provide to the model. In clustering, the algorithm does not operate on a standard criterion. All of its work depends on the user and the suitable criteria that satisfy their needs and requirements for the problem they tackle.
For example, to find out the homogeneous groups, one is able to find the representatives through data reduction and demonstrate their suitable properties. One can even find unusual data objects for outlier detection within the algorithm. The algorithm then tends to make the assumption that constitutes what similarity of points makes valid assumptions spanning over the entire dataset.
Types of Clustering in Machine Learning
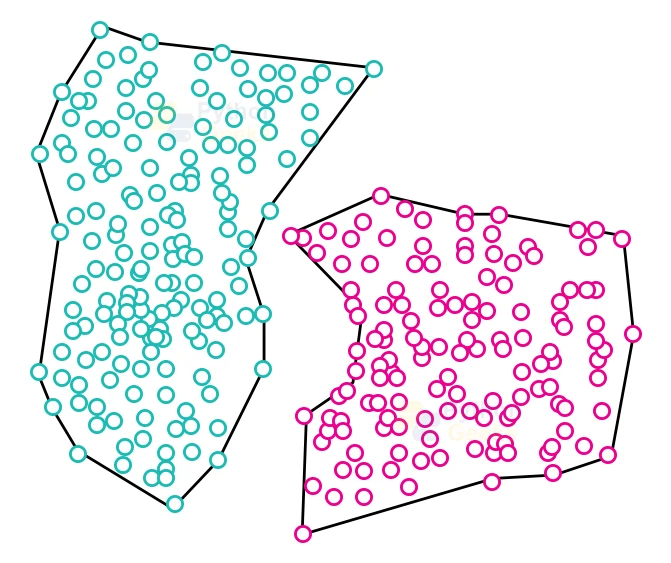
We can broadly classify the clustering methods into two main categories, namely, Hard clustering, in which, data point belongs to a single group, and Soft Clustering, in which, data points may belong to another group as well. However, there even exist other various approaches to Clustering.
Below are the main clustering methods that we can use in Machine learning:
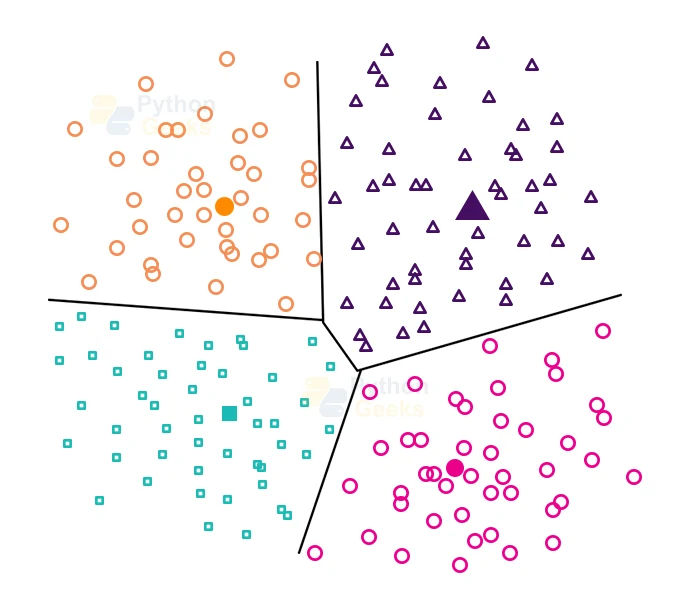
1. Partitioning Clustering
Partition Clustering is a type of clustering that tends to divide the data into non-hierarchical groups. We can also christen it the centroid-based method. The most widely known example of partitioning clustering is the K-Means Clustering algorithm of Machine Learning.
In this type, we tend to divide the dataset into a set of k groups, where K helps us to define the number of pre-defined groups. As the next step, we choose the cluster center in such a way that the distance between the data points of one cluster is minimum as compared to another cluster centroid for the given groups of data points.
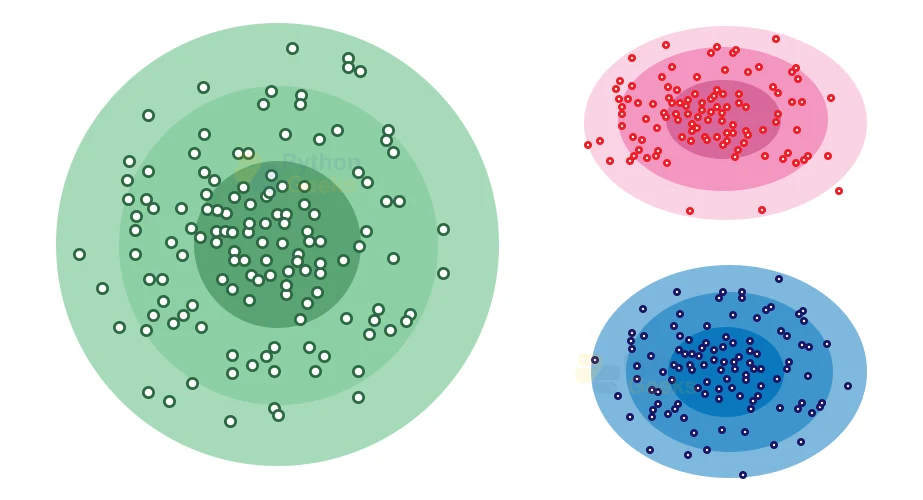
2. Density-Based Clustering
The density-based clustering method tends to connect the highly-dense areas into clusters, and then the algorithm forms the arbitrarily shaped distributions as long as it can connect the dense region. This algorithm achieves this by identifying different clusters in the dataset and connecting the areas of high densities into clusters with each other. The algorithm then divides the dense areas in data space from each other into sparser areas.
These algorithms may face hindrance in clustering the data points if the dataset has varying densities and high dimensions for a dispersed dataset.
3. Distribution Model-Based Clustering
Within the distribution model-based clustering method, the algorithm divides the data on the basis of the probability of how a dataset belongs to a particular distribution. The algorithm then performs grouping by assuming some distributions commonly Gaussian Distribution.
An example of this type of clustering is the Expectation-Maximization Clustering algorithm that makes use of the Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM).
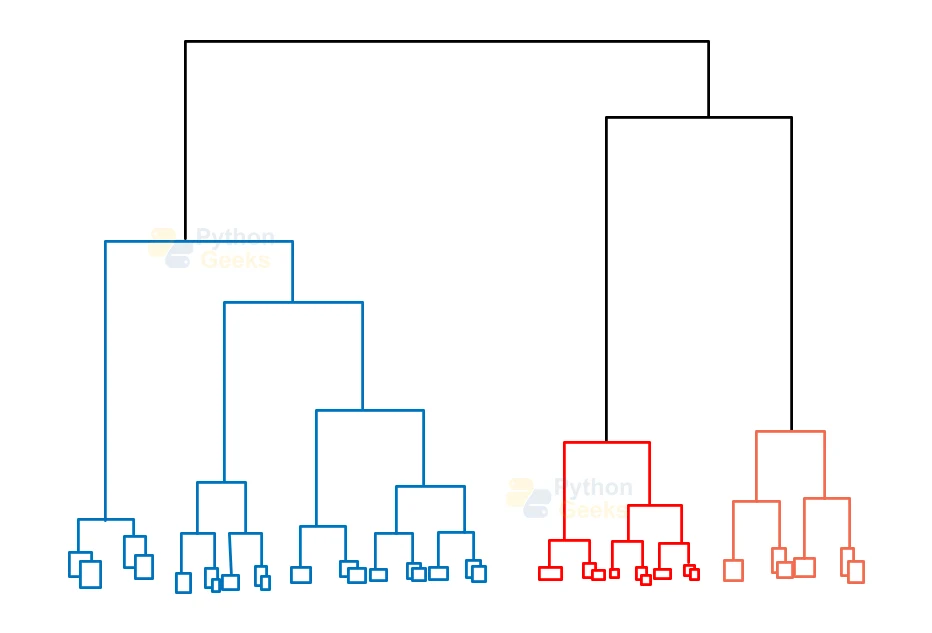
4. Hierarchical Clustering
We can make use of Hierarchical clustering as an alternative for the partitioned clustering as there is no requirement of pre-specifying the number of clusters that we need to specify beforehand.
In this technique, the algorithm divides the dataset into clusters to create a tree-like structure, which is referred to as a dendrogram. The algorithm can then select the observations or any number of clusters by cutting the tree at the correct level. The most widely-known example of this method is the Agglomerative Hierarchical algorithm.
5. Fuzzy Clustering
Fuzzy clustering is a type of soft clustering method in which a data object may belong to one or more than one group or cluster. Each dataset consists of a set of membership coefficients, which tends to depend on the degree of membership to be in a cluster. The Fuzzy C-means algorithm is a common example of this type of clustering; it is sometimes even referred to as the Fuzzy k-means algorithm.
Clustering Algorithms
We can further divide the Clustering algorithms on the basis of the models that we have explained above. There are different types of clustering algorithms published to date, however, only a few of them are commonly used. The clustering algorithm is based on the kind of data that we are handling.
1. K-Means Algorithm:
The k-means algorithm is one of the most widely-used clustering algorithms. It tends to classify the dataset by dividing the samples into different types of clusters of equal variances. We must specify the number of clusters in this algorithm. It is comparatively faster as it requires fewer computations, having the linear complexity of O(n).
2. Mean-shift algorithm:
Mean-shift algorithm attempts to find the dense areas present in the smooth density of data points. We can consider this as an example of a centroid-based model that tends to work on updating the candidates for the centroid to be the center of the points within a given region of the dataset.
3. DBSCAN Algorithm:
It is the acronym for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise. It is an example of a density-based model analogous to the mean-shift, however, with some remarkable advantages. In this algorithm, the algorithm tends to separate the areas of high density from the areas of low density. As a consequence of this, we can find the clusters in any arbitrary shape.
4. Expectation-Maximization Clustering using GMM:
We can make use of this algorithm as an alternative for the k-means algorithm or in cases where K-means may tend to fail. In GMM, the model tends to assume that the data points are Gaussian distributed.
5. Agglomerative Hierarchical algorithm:
The Agglomerative hierarchical algorithm tends to perform the bottom-up hierarchical clustering on the given dataset. In this, the algorithm treats each data point as a single cluster at the outset and then successively merges them. We can even represent the cluster hierarchy as a tree structure.
6. Affinity Propagation:
It is slightly different from other clustering algorithms as it does not need to specify the number of clusters beforehand. In this, each data point tends to send a message between the pair of data points until the convergence of the dataset. It has the time complexity of O(N2T), which is the major hindrance of this algorithm.
Applications of Clustering
1. Detection of Cancer Cells:
The clustering algorithms are widely deployed for the identification and diagnosis of cancerous cells. It tends to divide the cancerous and non-cancerous data sets into different groups of data.
2. Search Engines:
Search engines also work with the help of the clustering technique. The search result appears on the basis of the closest object to the search query. It achieves this by grouping similar data objects in one group that is dissimilar from the other objects. The precision of the result of a query depends on the quality of the clustering algorithm that we use to tackle the problem.
3. Customer Segmentation:
This algorithm finds its demand in market research to segment the customers on the basis of their interests and preferences.
4. Biology:
Clustering even finds its usage in the biology stream to classify various species of plants and animals using the image recognition technique for accuracy.
5. Land Use:
The clustering technique may be deployed in identifying the area of similar lands that finds its use in the GIS database. This can prove to be very beneficial to find for what purpose we should use the particular land, which indicates for which purpose it is more suitable and yields more benefits.
6. Wireless Networks:
Usage of the clustering algorithm on the wireless nodes helps us to save energy utilized by the wireless sensors. There are numerous clustering-based algorithms in wireless networks to enhance their energy consumption and optimize data transmission.
Conclusion
With that, we have reached the conclusion of the article that talked about the basics of the Clustering technique. Through this article, we came to know about the basic definition of Clustering along with the reasons to prefer it over other algorithms.
Apart from this, we also discussed the various types of Clustering algorithms and their types. Towards the end, we also discussed the real-time applications of the Clustering algorithms. Hope that this article from PythonGeeks was able to give you useful insight into the Clustering algorithm that you needed.