Fuzzy Logic System in AI
Boost Your Career with In-demand Skills - Start Now!
In our daily lives, we may come across situations when we are unable to determine if a state is true or false. The phrase “fuzzy” describes something that is unclear or perplexing. In AI, fuzzy logic gives you a lot of versatility when it comes to thinking. In this post, we’ll look at this reasoning and how it’s used in Artificial Intelligence.
What Is Fuzzy Logic?
The definition of fuzzy logic is a many-valued logic form in which the truth values of variables might be any real number between 0 and 1. It’s the term used to describe the concept of incomplete truth. In real life, we may encounter a circumstance in which we are unable to determine if a statement is true or false. Fuzzy logic provided a lot of freedom for reasoning at the time.
After examining all relevant facts, the fuzzy logic algorithm aids in the solution of a problem. Then it makes the best decision feasible based on the input. The FL technique mimics how humans make decisions by considering all of the possibilities between digital values T and F.
Implementation Of Fuzzy Logic
To obtain a definitive result, fuzzy logic operates on the layers of input possibilities. Now, let’s talk about how this logic is implemented:
- It can be used in systems of various sizes and capacities, including microcontrollers, big networked systems, and workstation-based systems.
- It can also be implemented in hardware, software, or a hybrid of the two.
The Evolution of Fuzzy Logic Systems
The concept of fuzzy logic, on the other hand, has been investigated since the 1920s. Lotfi Zadeh, a professor at UC Berkeley in California, coined the phrase fuzzy logic in 1965. He realized that traditional computer logic was incapable of dealing with data that represented subjective or ambiguous human concepts.
Control theory and artificial intelligence, for example, have both used fuzzy algorithms.
It was created to allow the computer to distinguish between data that is neither true nor untrue. Something like the human reasoning process. Like a little darkness, a little brightness, and so on.
Fuzzy Logic’s Characteristics
The properties of fuzzy logic are as follows:
- This approach is adaptable, and it is simple to comprehend and implement.
- It is used to assist in the reduction of human-created logic.
- It is the most effective strategy for determining the solution to situations that require approximate or uncertain reasoning.
- It always returns two numbers, indicating the two alternative solutions to a given problem or statement.
- It enables users to develop or create non-linear functions of arbitrary complexity.
- Everything in fuzzy logic is a matter of degree.
- Any system that is logical can be simply fuzzified using fuzzy logic.
- Natural language processing is at the heart of it.
- Quantitative analysts utilize it to improve the execution of their algorithms.
- It also enables users to interact with the software.
Why Fuzzy Logic?
We employ the fuzzy logic system for a variety of commercial and practical applications, including:
- It regulates consumer goods and machines.
- It provides an acceptable explanation even if it isn’t accurate.
- This aids in the management of engineering uncertainty.
Let’s move on to understanding the architecture of fuzzy logic in AI now that you know what it is and why we utilize it.
When It’s Not A Good Idea To Apply Fuzzy Logic?
Fuzzy reasoning, on the other hand, is never a panacea. As a result, it’s also crucial to grasp when we shouldn’t employ fuzzy reasoning.
There are some occasions where you should avoid using Fuzzy Logic:
If mapping an input space to an output space is not convenient, fuzzy logic should not be employed when common sense can suffice.
Without the use of fuzzy logic, many controllers can do a good job.
What is Fuzzy Control?
It’s a method of incorporating human-like reasoning into a control system.
It isn’t designed to provide exact explanation, but it is supposed to provide acceptable reasoning.
It can mimic human deductive reasoning, which is the method through which people draw inferences from what they know.
With the use of fuzzy logic, any uncertainties may be readily dealt with.
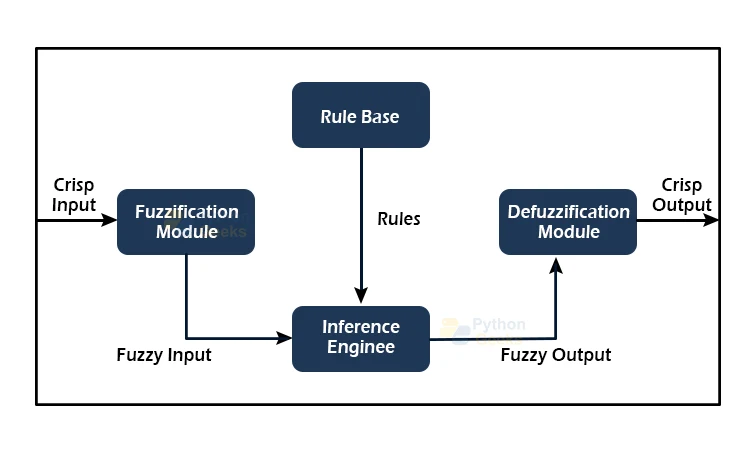
Fuzzy Logic Architecture
Each component in the Fuzzy Logic system’s architecture serves a significant role. The architecture is made up of four components, which are listed below:
- Rule Base
- Fuzzification
- Inference Engine
- Defuzzification
The following diagram shows the architecture or process of a Fuzzy Logic system:
1. Rule Base
The If-Then conditions provided by experts are used to regulate the decision-making systems, and the Rule Base is a component used for storing the set of rules. There have been a lot of recent advancements in fuzzy theory, which give useful approaches for developing and adjusting fuzzy controllers. The number of fuzzy sets of rules is reduced as a result of these changes or innovations.
2. Fuzzification
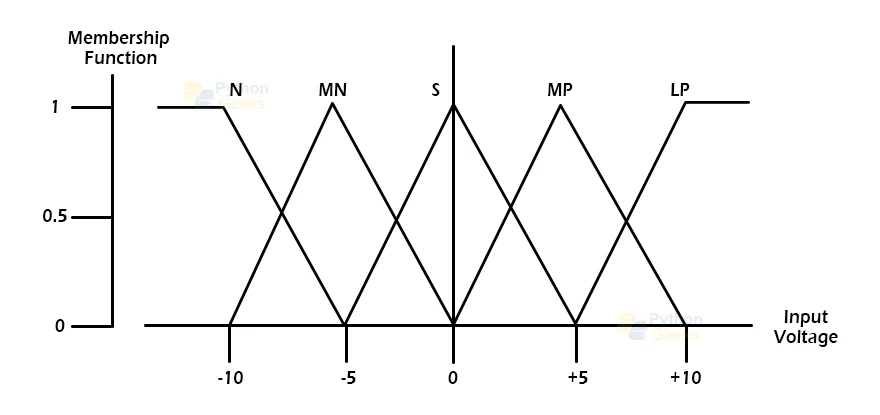
Fuzzification is a system input transformation module or component that turns crisp numbers into fuzzy steps. The crisp numbers are the inputs that the sensors measure and then transfer through fuzzification to the control systems for further processing. In every Fuzzy Logic system, this component separates the input signals into the five states listed below:
- Large Positive (LP)
- Medium Positive (MP)
- Small (S)
- Medium Negative (MN)
- Large negative (LN)
3. Inference Engine
Because the Inference Engine processes all of the input in any Fuzzy Logic system (FLS), it is a critical component. It enables users to determine the degree of correspondence between the current fuzzy input and the rules.
Following the degree of matching, this system determines which rule should be added to the provided input field. After all of the rules have been fired, the control actions are developed by combining them.
4. Defuzzification
Defuzzification is a component or element that turns the fuzzy set inputs supplied by the Inference Engine into a crisp value. It’s the final step in a fuzzy logic system’s development. The crisp value is a type of value that the user accepts. There are several strategies for doing so, but the user must choose the optimal one for reducing errors.
Fuzzy Logic vs Probability
| Fuzzy Logic | Probability |
| Fuzzy: Tom’s degree of membership within the set of old people is 0.90. | Probability: There is a 90% chance that Tom is old. |
| Fuzzy logic takes truth degrees as a mathematical basis on the model of the vagueness phenomenon. | Probability is a mathematical model of ignorance. |
Crisp vs Fuzzy
| Crisp | Fuzzy |
| It has strict boundary T or F | Fuzzy boundary with a degree of membership |
| Some crisp time set can be fuzzy | It can’t be crisp |
| True/False {0,1} | Membership values on [0,1] |
| In Crisp logic law of Excluded Middle and Non- Contradiction may or may not hold | In the fuzzy logic law of Excluded Middle and Non- Contradiction hold |
Classical Set vs Fuzzy set Theory
| Classical Set | Fuzzy Set Theory |
| Classes of objects with sharp boundaries. | Classes of objects do not have sharp boundaries. |
| A classical set is defined by crisp boundaries, i.e., there is clarity about the location of the set boundaries. | A fuzzy set always has ambiguous boundaries, i.e., there may be uncertainty about the location of the set boundaries. |
| Widely used in digital system design | Used only in fuzzy controllers. |
Algorithm
- Define linguistic terminology and variables. (start)
- For them, create membership functions. (start)
- Create a rule-based knowledge base (start)
- Using membership functions, convert crisp data into fuzzy data sets. (fuzzification)
- In the rule basis, evaluate the rules. (Analysis Engine)
- Combine the outcomes of each rule. (Analysis Engine)
- Convert the output data into values that aren’t fuzzy. (defuzzification)
Development
Step 1: Define linguistic terminology and variables.
Linguistic variables are basic words or sentences that serve as input and output variables. Cold, warm, hot, and other linguistic expressions for room temperature.
Temperature (t) = icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy, icy
Every member of this group is a linguistic phrase that can refer to a subset of total temperature data.
Step 2: Create membership functions for them to use.
The temperature variable’s membership functions are as follows:
Step 3: Construct knowledge base rules
Create a matrix of room temperature values versus target temperature values that an air conditioning system is expected to provide.
| RoomTemp. /Target | Very_Cold | Cold | Warm | Hot | Very_Hot |
| Very_Cold | No_Change | Heat | Heat | Heat | Heat |
| Cold | Cool | No_Change | Heat | Heat | Heat |
| Warm | Cool | Cool | No_Change | Heat | Heat |
| Hot | Cool | Cool | Cool | No_Change | Heat |
| Very_Hot | Cool | Cool | Cool | Cool | No_Change |
Build a set of rules into the knowledge base in the form of IF-THEN-ELSE structures.
| Sr. No. | Condition | Action |
| 1 | IF temperature=(Cold OR Very_Cold) AND target=Warm THEN | Heat |
| 2 | IF temperature=(Hot OR Very_Hot) AND target=Warm THEN | Cool |
| 3 | IF (temperature=Warm) AND (target=Warm) THEN | No_Change |
Step 4 − Obtain fuzzy value
Fuzzy set operations perform evaluation of rules. The operations used for OR and AND are Max and Min respectively. Combine all results of evaluation to form a final result. This result is a fuzzy value.
Step 5 − Perform defuzzification
Defuzzification is then performed according to membership function for output variable.
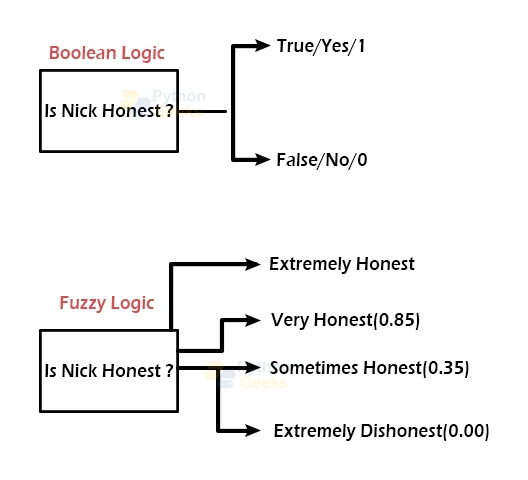
Example of Fuzzy Logic
Take a look at the diagram below. It demonstrates that the values in a Fuzzy system are denoted by a 0 to 1 integer. In this case, 1.0 denotes absolute truth, while 0.0 denotes total falsity.
Membership Function
The membership function is a function that quantifies the linguistic word by representing the graph of fuzzy sets. It’s a graph that converts each element of x into a number between 0 and 1.
μA:X [0,1] is a membership function for a fuzzy set A on the universe of discourse X.
It expresses the degree to which an element in X belongs to the fuzzy set A.
- The universe of conversation is represented by the x-axis.
- The degrees of membership in the [0, 1] interval is represented by the y-axis.
To fuzzify a numerical value, various membership functions can be used. Because complex membership functions do not add precision to the output, simple membership functions are employed. The following are the membership functions for LP, MP, S, MN, and LN:
Among the many membership function forms, triangle membership function shapes are the most prevalent. The input to the 5-level fuzzifier here ranges from -10 to +10 volts. As a result, the output changes as well.
Application Areas of Fuzzy Logic
The Below given table shows applications of Fuzzy logic by famous companies in their products.
| Product | Company | Fuzzy Logic |
| Anti-lock brakes | Nissan | Uses fuzzy logic to control brakes in hazardous cases depending on car speed, acceleration, wheel speed, and acceleration |
| Auto transmission | NOK/Nissan | Fuzzy logic is used to control the fuel injection and ignition based on throttle setting, cooling water temperature, RPM, etc. |
| Auto engine | Honda, Nissan | Use to select geat based on engine load, driving style, and road conditions. |
| Copy machine | Canon | Using for adjusting drum voltage based on picture density, humidity, and temperature. |
| Cruise control | Nissan, Isuzu, Mitsubishi | Use it to adjust throttle setting to set car speed and acceleration |
| Dishwasher | Matsushita | Use for adjusting the cleaning cycle, rinse and wash strategies based depend upon the number of dishes and the amount of food served on the dishes. |
| Elevator control | Fujitec, Mitsubishi Electric, Toshiba | Use it to reduce waiting for time-based on passenger traffic |
| Golf diagnostic system | Maruman Golf | Selects golf club based on golfer’s swing and physique. |
| Fitness management | Omron | Fuzzy rules implied by them to check the fitness of their employees. |
| Kiln control | Nippon Steel | Mixes cement |
| Microwave oven | Mitsubishi Chemical | Sets lunes power and cooking strategy |
| Palmtop computer | Hitachi, Sharp, Sanyo, Toshiba | Recognizes handwritten Kanji characters |
| Plasma etching | Mitsubishi Electric | Sets etch time and strategy |
The key application areas include:
Automotive Systems
- Automatic Gearboxes
- Four-Wheel Steering
- Vehicle environment control
Consumer Electronic Goods
- Hi-Fi Systems
- Photocopiers
- Still and Video Cameras
- Television
Domestic Goods
- Microwave Ovens
- Refrigerators
- Toasters
- Vacuum Cleaners
- Washing Machines
Environment Control
- Air Conditioners/Dryers/Heaters
- Humidifiers
Fuzzy Logic in Practice
The different application areas where the Fuzzy Logic concept is extensively applied are as follows:
- It’s a decision-making aid that’s employed in businesses.
- It’s utilized in automated systems to control traffic and speed, as well as to improve automatic transmission efficiency. Automatic transmissions in automated systems also use the shift scheduling mechanism.
- This concept is also applied in the Defense Department in a variety of ways. Fuzzy logic methods are mostly used by the military for underwater target recognition and automatic target recognition of thermal infrared pictures.
- In the form of Fuzzy logic-based recognition and handwriting recognition, it is also commonly employed in Pattern Recognition and Classification. It’s also used to find photos that are hazy.
- Securities also employ fuzzy logic systems.
- It’s also used to set the lunes power and cooking strategy in microwave ovens.
- This technique is also utilized in expert systems, which are modern control systems.
- Another application of this notion is in finance, where it is used to forecast the stock market and manage capital.
- It’s also utilized to operate the brakes.
- It’s also utilized in the chemical industry to manage ph and the chemical distillation process.
- It is also utilized in the manufacturing industry to optimize the production of milk and cheese.
- It can also be found in vacuum cleaners and washing machine timers.
- It’s also utilized in humidifiers, warmers, and air conditioners.
Advantages of Fuzzy Logic in AI
- The advantages and benefits of fuzzy logic are numerous. The following are a few of them:
- This concept’s methodology works in a similar way to human reasoning.
- The framework of Fuzzy Logic is simple to grasp for any user.
- Because the techniques may be simply represented with little data, it does not require a huge memory.
- It is frequently utilized in all walks of life and gives simple and effective answers to challenges of tremendous complexity.
- This concept is straightforward because it is based on set theory in mathematics.
- It allows people to operate consumer products and control equipment.
- When compared to traditional methods, fuzzy logic takes less time to design.
- The FLS system’s flexibility allows any user to simply add and delete rules.
Fuzzy Logic’s Drawbacks
- Fuzzy logic has a number of drawbacks and limits. The following are a few of them:
- Fuzzy logic systems have a slow run time and take a long time to create outputs.
- If the instructions are simple, users will be able to understand them quickly.
- The alternatives that the fuzzy logic system generates are not always accurate.
- Using this strategy, many scholars present alternative solutions to a given proposition, resulting in ambiguity.
- Fuzzy logic isn’t good for tasks that require a lot of precision.
- Fuzzy logic systems necessitate extensive testing for verification and validation.
Conclusion
As a result, we’ve looked into AI Fuzzy Logic systems. Also, as implementation, necessity, and so on. As a result, with the aid of graphics, you will be able to comprehend more easily. Furthermore, if you have any questions, please leave them in the comments section.