Machine Learning Project – House Price Prediction
From learning to earning – Courses that prepare you for job - Enroll now
In the dynamic real estate industry, accurate prediction of house prices is paramount for stakeholders such as buyers, sellers, agents, and investors.
This ML project aims to leverage machine learning techniques to develop a predictive model capable of estimating house prices based on historical housing data. By analyzing relevant features, including location, property size, amenities, and market trends, we seek to provide valuable insights for informed decision-making in residential property transactions. The objectives include comprehensive data exploration, preprocessing, model selection, training, evaluation, and deployment.
Through this Machine Learning House Price Prediction project, we aim to empower stakeholders with actionable insights and contribute to the advancement of machine learning in real estate analytics, addressing complex challenges in the housing market with practical data-driven solutions.
About Machine Learning House Price Prediction Project
In this Machine Learning House Price Prediction project, we employ Pandas for data preprocessing, ensuring the handling of missing values and irrelevant features. Following this, we conduct Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to grasp the distribution of house prices and unearth trends or patterns in the data. Subsequently, we enhance model accuracy through Feature Engineering, involving the selection of pertinent features, encoding categorical variables, and creating new ones.
Further, we experiment with machine learning algorithms such as Linear Regression and Lasso Regression for Model Selection and Training, aiming to build predictive models. To ensure model accuracy, we assess performance via evaluation metrics like R-squared score in Model Evaluation.
Lastly, we deploy models for stakeholder access and perform usability testing to validate their effectiveness in real-world applications.
About Dataset
The dataset used in this ML project comprises housing data scraped from publicly available results posted weekly on Domain.com.au. This dataset provides valuable insights into the Melbourne housing market and includes various attributes related to properties such as Address, Type of Real Estate, Suburb, Method of Selling, Number of Rooms, Price, Real Estate Agent, Date of Sale, and Distance from the Central Business District (CBD).
Key Details:
- Suburb: Indicates the suburb where the property is located.
- Address: Specifies the address of the property.
- Rooms: Represents the number of rooms in the property.
- Price: Indicates the price of the property in Australian dollars.
- Method: Describes the method of selling the property (e.g., property sold, property sold prior, passed in, etc.).
- Type: Specifies the type of property (e.g., house, unit, townhouse, etc.).
- SellerG: Represents the Real Estate Agent handling the sale.
- Date: Specify the date when the property was sold.
- Distance: Indicates the distance of the property from the CBD in kilometres.
- Regionname: Represents the general region where the property is located (e.g., West, North West, North, North East, etc.).
- Propertycount: Indicates the number of properties existing in the suburb.
- Bedroom2: Represents the scraped number of bedrooms from a different source.
- Bathroom: Specifies the number of bathrooms in the property.
- Car: Indicates the number of carspots available.
- Landsize: Specifies the land size in square meters.
- BuildingArea: Indicates the building size in square meters.
- YearBuilt: Specifies the year when the property was built.
- CouncilArea: Represents the governing council for the area.
- Latitude and Longitude: Provide geographical coordinates of the property location.
The link to Dataset can be found: HousingData
Prerequisites For Machine Learning House Price Prediction Project
1. Programming in Python: Proficiency in Python programming language is essential as the entire project is implemented using Python, including data preprocessing, model building, and evaluation.
2. Data Manipulation with Pandas: Understanding of Pandas library for data manipulation is necessary to perform tasks such as reading CSV files (pd.read_csv()), dropping columns (df.drop()), handling missing values (df.dropna()), and creating dummy variables (pd.get_dummies()).
3. Data Visualization: Knowledge of data visualization techniques using libraries such as Matplotlib or Seaborn is beneficial for conducting exploratory data analysis (print(df1.nunique().to_string())) to understand data distributions and identify trends.
4. Machine Learning: Familiarity with machine learning concepts and algorithms is crucial, particularly linear regression (LinearRegression from sklearn.linear_model) and Lasso regression (Lasso from sklearn.linear_model) used for model training and evaluation.
5. Model Evaluation: Understanding model evaluation metrics such as R-squared score (model.score()) is necessary to assess the performance of trained models on both training and testing datasets.
6. Data Splitting and Cross-Validation: Proficiency in techniques like train-test splitting (train_test_split() from sklearn.model_selection) is required to divide the dataset into training and testing subsets for model evaluation.
7. Feature Engineering: Knowledge of feature engineering techniques, including feature selection and encoding categorical variables, is crucial for enhancing model accuracy and performance.
8. Handling Warnings: Basic understanding of handling warning messages using Python’s built-in warnings module (warnings.filterwarnings(‘ignore’)) to ensure a clean output during code execution.
Download Machine Learning House Price Prediction Project
Please download the source code of Machine Learning House Price Prediction Project: Machine Learning House Price Prediction Project Code.
Tools and Libraries Used in Machine Learning House Prediction Project
Pandas (pd):
- Pandas is a powerful Python library for data manipulation and analysis, offering data structures like DataFrame and Series.
- It’s extensively used in this code for reading CSV files, manipulating data frames, performing data preprocessing, and creating dummy variables.
Warnings:
- Warnings is a Python built-in module used for handling warning messages during code execution.
- The filterwarnings function from the warnings module is utilized here to suppress any warning messages, ensuring a clean output.
Scikit-learn (sklearn):
- Scikit-learn is a Python library for machine learning, offering a wide range of tools for data mining and analysis.
- It provides algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, and dimensionality reduction.
- Within this code, Scikit-learn is employed for linear regression, train-test splitting, Lasso regression, and model evaluation.
NumPy:
- While not explicitly imported in the code, NumPy is commonly used alongside Pandas and Scikit-learn for numerical computations.
- It supports large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with mathematical functions for array operations.
Steps to Predict House Prices in Machine Learning Project
Here’s the code divided and explained into sections:
Section 1: Importing Libraries and Reading Data
- This section imports necessary libraries: pandas and warnings.
- It sets up a warning filter to ignore any warnings that might occur during code execution.
- It reads data from a CSV file named “Melbourne_housing_FULL.csv” into a DataFrame named df.
import pandas as pd
import warnings
# Ignore warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Read data from CSV file into a DataFrame
df = pd.read_csv("Melbourne_housing_FULL.csv")
Section 2: Data Preprocessing
- This section involves data cleaning and preparation steps.
- It drops unnecessary columns from the DataFrame df, such as ‘Address’, ‘Date’, etc., and assigns the result to a new DataFrame df1.
- It then drops rows with missing values (NaN) from df1.
# Dropping unnecessary columns df1 = df.drop(columns=['Address','Date','Postcode','YearBuilt','Lattitude','Longtitude']) # Drop rows with missing values df1 = df1.dropna()
Section 3: Data Exploration
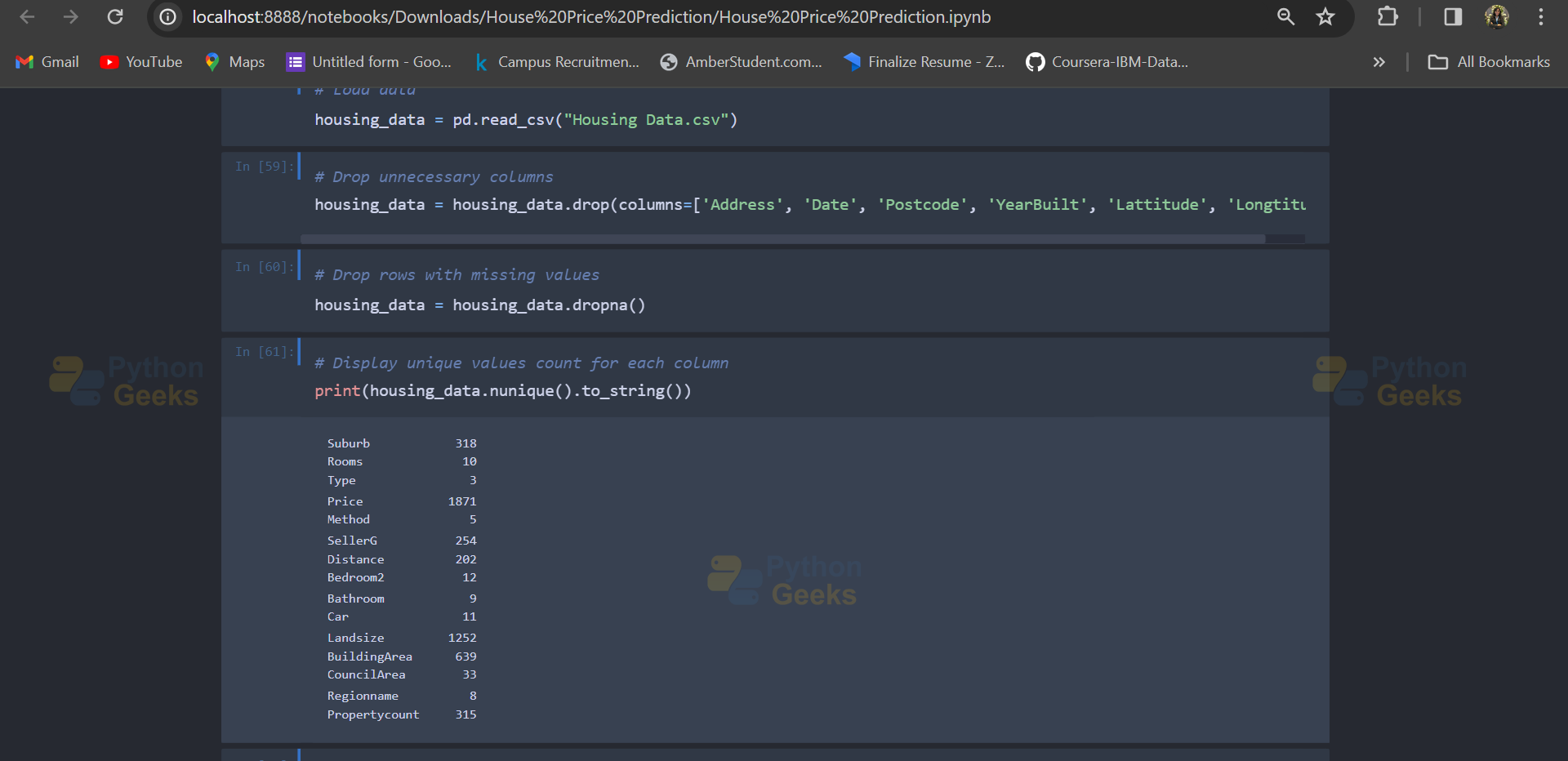
- This section provides a basic exploration of the data.
- It prints the number of unique values for each column in the DataFrame df1.
# Print number of unique values for each column print(df1.nunique().to_string())
Output:
Section 4: Data Transformation (One-Hot Encoding)
- This section transforms categorical variables into dummy variables using one-hot encoding.
- It converts categorical columns in df1 into dummy/indicator variables and assigns the result back to df1.
# Convert categorical variables into dummy/indicator variables df1 = pd.get_dummies(df1, dtype=int)
Section 5: Splitting Data and Model Training (Linear Regression)
- This section involves splitting the data into training and testing sets and training a linear regression model.
- It imports necessary modules for linear regression (LinearRegression) and data splitting (train_test_split).
- It defines features (X) and target variables (Y) from df1.
- It splits the data into training and testing sets using train_test_split.
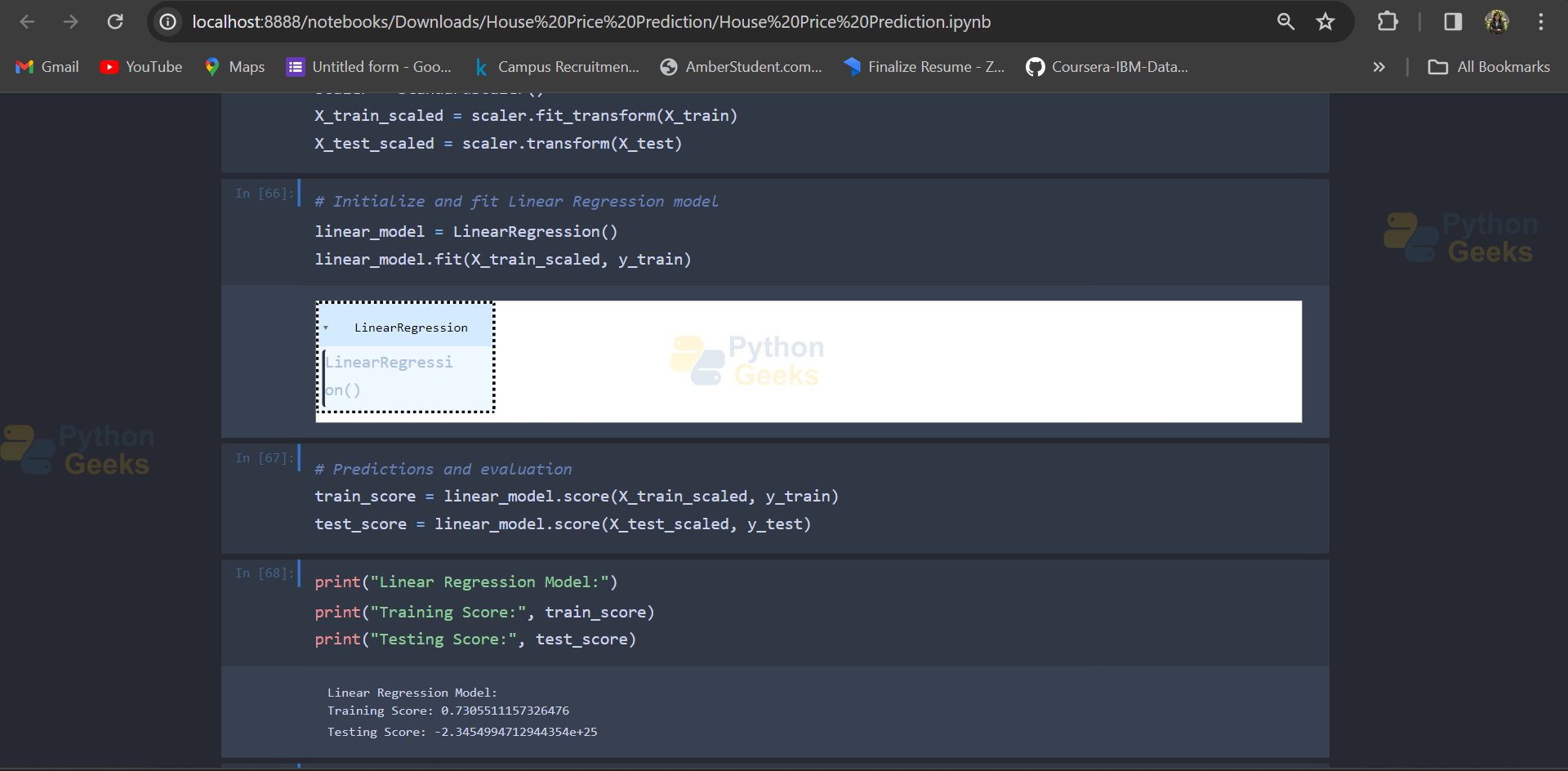
- It initializes a linear regression model (model), fits the model to the training data, and trains it.
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # Define features (X) and target variable (Y) X = df1.drop(columns=['Price']) Y = df1['Price'] # Split data into training and testing sets X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.3) # Initialize and train Linear Regression model model = LinearRegression() model.fit(X, Y)
Section 6: Model Evaluation (Linear Regression)
- This section evaluates the linear regression model’s performance.
- It predicts the target variable on the training data (X_train) and assigns the result to ans.
- It calculates the R-squared score (coefficient of determination) of the model on both training and testing data using the score method.
# Predict on training data ans = model.predict(X_train) # Calculate R-squared score on training data model.score(X_train, Y_train) # Calculate R-squared score on testing data model.score(X_test, Y_test)
Output:
Section 7: Model Training and Evaluation (Lasso Regression)
- This section involves training and evaluating a Lasso regression model.
- It imports the Lasso regression model.
- It initializes a Lasso regression model (lasso) with specific hyperparameters (alpha, max_iter, tol).
- It fits the Lasso model to the training data (X_train, Y_train).
- It calculates the R-squared score of the Lasso model on both training and testing data.
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso # Initialize and train Lasso Regression model lasso = Lasso(alpha=25, max_iter=100, tol=0.1) lasso.fit(X_train, Y_train) # Calculate R-squared score on training data lasso.score(X_train, Y_train) # Calculate R-squared score on testing data lasso.score(X_test, Y_test)
Output:
Summary
This ML project aimed to develop predictive models for house prices using machine learning techniques applied to Melbourne housing data. Leveraging Python libraries such as Pandas for data manipulation and Scikit-learn for model building, we successfully constructed models using Linear Regression and Lasso Regression algorithms.
The project involved key stages, including data preprocessing, exploratory data analysis, feature engineering, and model selection and training. Evaluation using metrics like R-squared score showed satisfactory accuracy in predicting house prices based on the given features.
Overall, the project highlights the potential of machine learning in analyzing and predicting house prices, providing valuable insights for stakeholders. Further refinement and optimization, including exploring advanced algorithms and additional features, could enhance the models’ predictive capabilities in future work.
You can check out more such machine learning projects on PythonGeeks.


justin jatu bhai