Python Project – Predicting Air Quality Index
Get Ready for Your Dream Job: Click, Learn, Succeed, Start Now!
The Air Quality Index (AQI) Predictor is a Python application that forecasts AQI using the provided data. It utilises machine learning techniques to predict air quality based on factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and particulate matter (PM2.5).
About Python Air Quality Index Predictor
The AQI Predictor project harnesses machine learning to estimate air quality indices from historical environmental data. By analysing parameters like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and PM2.5 levels, the model predicts future AQI values. The application is built using Python and Tkinter, offering an intuitive user interface for data input and result visualisation. It emphasises the importance of clean air and helps users take measures to protect their health.
Objectives of Python Air Quality Index Predictor
- Developing a predictive model for estimating AQI based on environmental factors.
- Implementing a user-friendly interface to input data and display predicted AQI.
- Validating the accuracy of the AQI predictions against real-world data.
Project Setup
Required Libraries
The project requires the following standard Python libraries:
- Pandas: For data manipulation and analysis.
- Scikit-learn: For implementing machine learning models.
- Tkinter: For building the graphical user interface.
Technology Stack
- Python
- Pandas
- Scikit-learn
- Tkinter
- Matplotlib
Prerequisites for Python Air Quality Index Predictor
- Basic understanding of Python programming.
- Understanding of machine learning concepts, especially regression models.
- Familiarity with Tkinter for GUI development.
Download Python Air Quality Index Predictor Project
Please download the source code for the Python Air Quality Index Predictor Project: Python Air Quality Index Predictor Project Code.
Step-by-Step Implementation of Python Air Quality Index Predictor
1. Importing Libraries
This helps to import necessary libraries for the GUI of the Alarm Clock:-
- pandas: This library is used for data manipulation and analysis, and it can read data from various file formats.
- scikit-learn: It is used to evaluate the performance of a regression model by calculating the mean squared error.
- joblib: It saves and loads machine learning models and other data objects efficiently.
- tkinter: It creates GUI applications. The messagebox submodule is used for displaying message boxes in the GUI.
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error import joblib import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox
2. Training Model
- data = pd.read_csv(): It reads the dataset from a CSV file named ‘aqi.csv’ into a Pandas DataFrame.
- required_columns: This ensures that the dataset contains all the necessary columns for training the model.
- features & target: This fills any missing values in the specified columns with the mean of those columns.
- X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(): It splits the data into training and testing sets, with 20% of the data used for testing.
- model = RandomForestRegressor(): This creates and trains a Random Forest Regressor model using the training data.
- joblib.dump( ): It saves the trained model to a file named ‘aqi_model.pkl’ using Joblib.
def prepare_and_train_model():
data = pd.read_csv('aqi.csv')
required_columns = ['temperature', 'humidity', 'wind_speed', 'pm2.5', 'value']
missing_columns = [col for col in required_columns if col not in data.columns]
if missing_columns:
raise ValueError(f"Dataset is missing required columns: {missing_columns}")
numeric_columns = ['temperature', 'humidity', 'wind_speed', 'pm2.5', 'value']
data[numeric_columns] = data[numeric_columns].fillna(data[numeric_columns].mean())
features = data[['temperature', 'humidity', 'wind_speed', 'pm2.5']]
target = data['value']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, target, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
model = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, predictions)
print(f"Mean Squared Error: {mse}")
joblib.dump(model, 'aqi_model.pkl')
3. Building Interface
- model = joblib.load(): This loads the trained Random Forest Regressor model from the ‘aqi_model.pkl’ file.
- root = tk.Tk(): It initialises the main Tkinter window.
- labels & entries: This creates label and entry fields for the input parameters (temperature, humidity, wind speed, PM2.5) using a loop, storing them in a dictionary.
- predict_aqi(): This retrieves user input, converts it to a DataFrame, and makes a prediction using the loaded model.
- predict_button: It adds a button that, when clicked, triggers the prediction function and displays the predicted result.
- root.mainloop(): It starts the Tkinter event loop, allowing the GUI to run and interact with the user.
def build_gui():
model = joblib.load('aqi_model.pkl')
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("PythonGeeks@AQI Predictor")
root.geometry("400x300")
labels = ['Temperature', 'Humidity', 'Wind Speed', 'PM2.5']
entries = {}
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
tk.Label(root, text=label).grid(row=i, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
entries[label] = tk.Entry(root)
entries[label].grid(row=i, column=1, padx=10, pady=10)
def predict_aqi():
try:
temp = float(entries['Temperature'].get())
hum = float(entries['Humidity'].get())
wind = float(entries['Wind Speed'].get())
pm = float(entries['PM2.5'].get())
input_data = pd.DataFrame([[temp, hum, wind, pm]], columns=['temperature', 'humidity', 'wind_speed', 'pm2.5'])
aqi_prediction = model.predict(input_data)[0]
result_label.config(text=f"Predicted AQI: {aqi_prediction:.2f}")
except ValueError:
messagebox.showerror("Input Error", "Please enter valid numbers for all fields")
predict_button = tk.Button(root, text="Predict AQI", command=predict_aqi)
predict_button.grid(row=len(labels), column=0, columnspan=2, pady=20)
result_label = tk.Label(root, text="")
result_label.grid(row=len(labels)+1, column=0, columnspan=2)
root.mainloop()
4. Running Main Functions
- prepare_and_train_model(): It loads dataset then checks for required columns and then splits the dataset into training and testing data using RandomForestRegressor model and saves the output into aqi_model.pkl
- build_gui(): It loads the trained model and creates a GUI for user interaction and prediction of AQI.
prepare_and_train_model() build_gui()
Python Air Quality Index Predictor
1. Application Interface
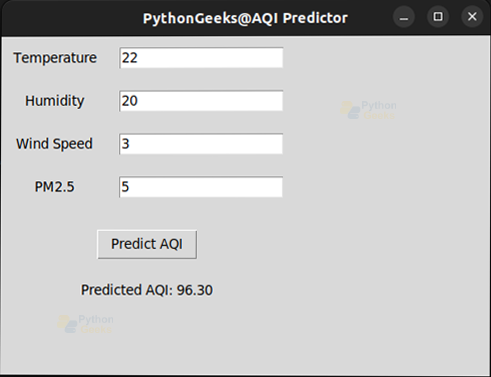
2. Prediction with User Inputs
Conclusion
The AQI Predictor project successfully demonstrates the integration of machine learning techniques with a user-friendly interface built with Tkinter. It provides a practical tool for forecasting AQI based on environmental factors and for decision-making regarding air quality.