Python Django Project – Online Cake Ordering System
Master programming with our job-ready courses: Enroll Now
An online cake ordering system is a web-based platform that allows customers to browse, select, and order cakes and related products online. This system simplifies the process of ordering cakes, making it convenient for customers and streamlining the operations of cake shops or bakeries.
About Python Django Online Cake Ordering System
The different options available in the app, along with their functions, are as follows –
1. Online Cake Ordering System: A web-based platform for cake ordering.
2. Models: Cake and CartItem models for storing cake and cart item data.
3. User Registration & Login: Allows users to register and log in for personalized services.
4. Cake Ordering View: Displays available cakes and enables search functionality.
5. Add to Cart View: Users can add cakes to their shopping cart.
6. Cart View: This shows cart items associated with the logged-in user.
7. Remove from Cart View: Allows users to remove items from their cart.
8. Django Authentication: Utilizes Django’s authentication and user models.
9. User-Friendly & Secure: Efficient and secure ordering experience with streamlined views and models.
Download Python Django Online Cake Ordering System Project
Please download the source code of Python Django Online Cake Ordering System Project: Python Django Online Cake Ordering System Project Code.
Installation steps:
Download the visual studio from the following provided link:
On the download page, you can choose the appropriate installer for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux). Once the installer is downloaded, run it and follow the installation instructions to install VS Code on your computer.
Here’s a brief explanation of each step, along with the commands to execute:
1. Install Python: Follow the installation instructions for your operating system after downloading and installing the latest version of Python from the official website.
2. Install pip: Download the get-pip.py script and run python get-pip.py to install pip.
3. Create a virtual environment: Run python -m venv myenv to create a new virtual environment named ‘myenv’.
4. Activate the virtual environment: Run source myenv/bin/activate on Linux/Mac or myenv\Scripts\activate on Windows to activate the virtual environment.
5. Install Django: Run pip install django to install the latest stable version of Django.
6. Verify installation: Run python -m django –version to verify that Django is installed correctly.
7. Create a new Django project: Run Django-admin start to project my project to create a new Django project named ‘myproject’.
8. Start the development server: Run python manage.py runserver to start the development server.
That’s it! You should now have a working installation of Django and be ready to start building your web application.
Steps to Create Python Django Online Cake Ordering System Project –
Let’s Move ahead with this amazing project.
1. Open the terminal from the folder where we want to create the project.
Right-click on mouse -> open in terminal -> write “code .” (space is mandatory between code and “.”)
2. Then go to the project folder -> urls.py and inside urls.py of project, do this -> add “include” in import as shown in the code below and add “path(“”, include(“app.urls”))”
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path("", include("app.urls"))
]
3. Create urls.py in the app of the Online Cake Ordering System project (urls.py is mandatory in both project and app).
4. In setting.py, add the ‘app name”. In my case, it is an app only, as below.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app'
]
5. Now run server to check if everything is working or not. If you see the below image, then we are done with the installation part. To runserver, run the command in the terminal as follows “py manage.py runserver”.(if you see the rocket image, then it’s working fine).
6. Now, create the models.py using the ORM technique as follows.
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# Create your models here.
class Cake(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
image = models.ImageField(upload_to='cakes')
description = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class CartItem(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
cake = models.ForeignKey(Cake, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
quantity = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=1)
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.user.username}'s CartItem - {self.cake.name}"
To create the above field in a database, run the following commands as follows:
- Py manage.py makemigrations
- Py manage.py migrate
7. To insert data in the database
templates/app -> home.html
<form method="POST" action="{% url 'caking-ordering' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="search-bar">
<input type="text" name="search_query" placeholder="Search..." value="{{ request.POST.search_query }}">
<button class="search-button" type="submit">Search a Cake</button>
</div>
</form>
<div class="product-row">
{% for cake in cakes %}
<div class="product-card">
<img src="{{ cake.image.url }}" alt="{{ cake.name }}">
<h3>{{ cake.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ cake.description }}</p>
<form action="{% url 'add_to_cart' pk=cake.pk %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<button class="yellow-button">Add to Cart</button>
</form>
Views.py
@login_required(login_url="login_view")
def cake_ordering_view(request):
search_query = request.POST.get('search_query')
if search_query:
filtered_cakes = Cake.objects.filter(Q(name__icontains=search_query))
context = {'cakes': filtered_cakes, 'search_query': search_query}
else:
cakes = Cake.objects.all()
context = {'cakes': cakes}
return render(request, 'app/home.html', context)
Urls.py
path("caking-ordering", cake_ordering_view, name="caking-ordering"),
8. Show the Cart Data
template/app -> Cart.html
<div class="cart-items">
{% for cart_item in cart_items %}
<div class="cart-item">
{% if request.user == cart_item.user %}
<h3>{{ cart_item.cake.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ cart_item.cake.description }}</p>
<div class="cart-buttons">
<select class="payment-dropdown">
<option value="">------Select Payment------</option>
<option value="">Online Payment</option>
<option value="">Cash on Delivery</option>
</select>
<a class="yellow-button" href="{% url 'remove_from_cart' pk=cart_item.pk %}">Remove from Cart</a>
</div>
{% empty %}
<p>Your cart is empty.</p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
Views.py
@login_required(login_url="login_view")
def add_to_cart(request, pk):
if request.method == 'POST':
try:
cake = Cake.objects.get(pk=pk)
except Cake.DoesNotExist:
return HttpResponse("Invalid cake ID")
# Create a new CartItem
cart_item = CartItem.objects.create(user=request.user, cake=cake)
cart_item.save()
return redirect('cart_view')
return HttpResponse("Invalid request")
@login_required(login_url="login_view")
def cart_view(request):
cart_items = CartItem.objects.filter(user=request.user)
return render(request, 'app/cart.html', {'cart_items': cart_items})
@login_required(login_url="login_view")
def remove_from_cart(request, pk):
try:
cart_item = CartItem.objects.get(pk=pk)
cart_item.delete()
return redirect('cart_view')
except CartItem.DoesNotExist:
return HttpResponse("Invalid cart item ID")
Urls.py
path("add_to_cart/<int:pk>", add_to_cart, name="add_to_cart"),
path("cart_view", cart_view, name="cart_view"),
path("remove_from_cart/<int:pk>", remove_from_cart, name="remove_from_cart"),
path("cart", Index, name="cart"),
9. Login.html
<form action="{% url 'login_view' %}" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<p class="error-message">{{ message }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Login"><br><br>
You can now login here: <a href="{% url 'register' %}">Register here</a>
</form>
Views.py
def login_view(request):
if request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("password")
user = authenticate(request, username=username, password=password)
if user is not None:
login(request, user)
return redirect("caking-ordering")
else:
messages.error(request, "Invalid email or password.")
return render(request, "app/login.html")
Urls.py
path("login_view", login_view, name="login_view"),t
10. Register.html
<form action="{% url 'register' %}" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<p class="error-message">{{ message }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" value="{{request.POST.username}}" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password-confirm">Confirm Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password-confirm" name="password-confirm" required>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Register">
</form>
Views.py
def Register(request):
if request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get("username")
email = request.POST.get("email")
password = request.POST.get("password")
confirm_password = request.POST.get("password-confirm")
if password == confirm_password:
# Check if username or email already exists
if User.objects.filter(username=username).exists():
messages.error(request, "Username already exists.")
elif User.objects.filter(email=email).exists():
messages.error(request, "Email already exists.")
else:
# Create new user
user = User.objects.create_user(
username=username, email=email, password=password
)
messages.success(request, "Registration successful. You can now login.")
return redirect("login_view")
else:
messages.error(request, "Passwords do not match.")
return render(request, "app/register.html")
Urls.py
path("", Register, name="register"),
11. For Logout Process
Views.py
@login_required(login_url="login_view")
def logout_view(request):
logout(request)
return redirect('login_view')
Urls.py For Above:
from django.urls import path
from .views import *
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
urlpatterns = [
path("cart", Index, name="cart"),
path("", Register, name="register"),
path("login_view", login_view, name="login_view"),
path("caking-ordering", cake_ordering_view, name="caking-ordering"),
path("add_to_cart/<int:pk>", add_to_cart, name="add_to_cart"),
path("cart_view", cart_view, name="cart_view"),
path("remove_from_cart/<int:pk>", remove_from_cart, name="remove_from_cart"),
path("logout_view", logout_view, name="logout_view")
] + static(settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
Explanation for the above code:
The provided code consists of Django’s views for an online cake ordering system. Let’s understand how the views handle various functionalities of the system and interact with HTML templates.
1. Index View: The Index view renders the “cart.html” template. This serves as the entry point for the cart page.
2. Register View: The Register view handles user registration. When a user submits the registration form, the view checks if the provided username and email are unique. If the registration is successful, the user is created, and appropriate success messages are displayed. If there are errors (e.g., duplicate username or email), the view shows corresponding error messages using Django’s messages framework.
3. Login View: The login_view handles user login. When the user submits the login form, the view authenticates the user’s credentials using Django’s built-in authenticate method. If successful, the user is logged in and redirected to the “cake_ordering_view.” If login fails, an error message is shown.
4. Cake Ordering View: The cake_ordering_view displays available cakes to users. It supports searching for specific cakes based on the “search_query” parameter. If a search query is submitted, the view filters and displays cakes accordingly. If no search query is provided, it shows all cakes.
5. Add to Cart View: The add_to_cart view allows users to add cakes to their shopping carts. When a user selects a cake to add, a new CartItem object is created, linking the logged-in user and the selected cake. The user is then redirected to the “cart_view.”
6. Cart View: The cart_view displays the shopping cart items for the logged-in user. It fetches all CartItem objects associated with the user and renders them in the “cart.html” template.
7. Remove from Cart View: The remove_from_cart view enables users to remove items from their shopping cart. When a user chooses to remove an item, the corresponding CartItem object is deleted, and the user is redirected back to the cart view.
8. Logout View: The logout_view handles user logout. When a user clicks on the logout link, the view logs out the user and redirects them to the login view.
The views interact with Django’s templating engine to render HTML templates. The HTML templates are responsible for presenting data and providing user interfaces for different functionalities.
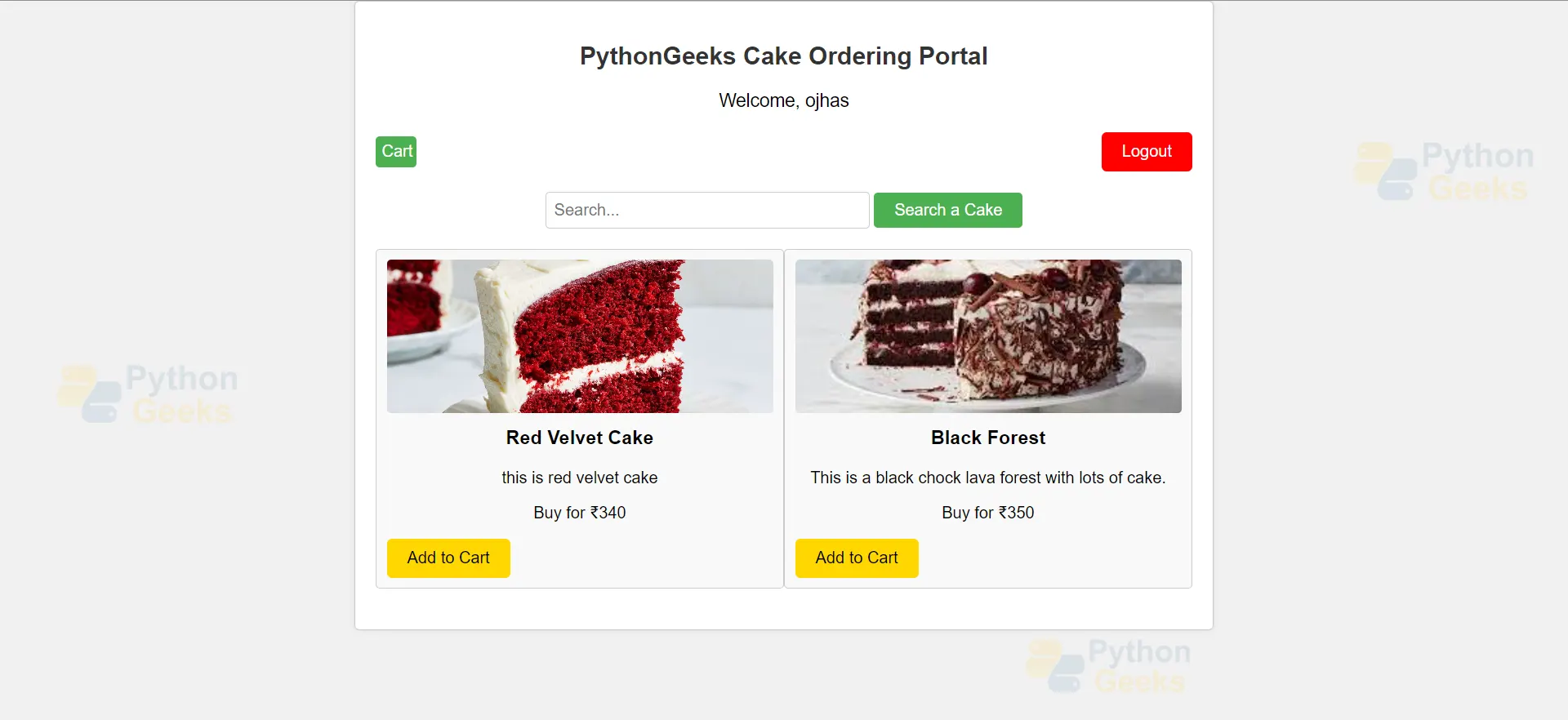
templates/app -> home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PythonGeeks Cake Ordering Portal</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.welcome {
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.welcome p {
font-size: 18px;
}
.options-bar {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.cart-logo {
width: 40px;
height: 30px;
background-color: #4CAF50;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
color: white;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
}
.logout-button {
background-color: red;
border: none;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.search-bar {
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.search-bar input[type="text"] {
width: 300px;
padding: 8px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.search-button {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: #fff;
border: none;
padding: 8px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.product-row {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.product-card {
width: calc(50% - 10px);
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.product-card img {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
object-fit: cover;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.product-card h3 {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.product-card p {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.green-button {
background-color: #4CAF50;
border: none;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.yellow-button {
background-color: #FFD700;
border: none;
color: black;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>PythonGeeks Cake Ordering Portal</h2>
<div class="welcome">
<p>Welcome, <span id="username">{{user.username}}</span></p>
</div>
<div class="options-bar">
<div>
<form action="{% url 'cart_view' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
<button class="cart-logo">Cart</button>
</form>
</div>
<div>
<a href="{% url 'logout_view' %}">
<button class="logout-button">Logout</button>
</a>
</div>
</div>
<form method="POST" action="{% url 'caking-ordering' %}">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="search-bar">
<input type="text" name="search_query" placeholder="Search..." value="{{ request.POST.search_query }}">
<button class="search-button" type="submit">Search a Cake</button>
</div>
</form>
<div class="product-row">
{% for cake in cakes %}
<div class="product-card">
<img src="{{ cake.image.url }}" alt="{{ cake.name }}">
<h3>{{ cake.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ cake.description }}</p>
<p>Buy for ₹{{ cake.price }}</p>
<form action="{% url 'add_to_cart' pk=cake.pk %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<button class="yellow-button">Add to Cart</button>
</form>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
templates/app -> login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Login Page</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
.container {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
margin-top: 10%;
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.form-group {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
label {
display: block;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
input[type="text"],
input[type="password"] {
width: 96%;
padding: 8px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
input[type="submit"] {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: #fff;
border: none;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
.error-message {
color: red;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>Login</h2>
<form action="{% url 'login_view' %}" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<p class="error-message">{{ message }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Login"><br><br>
You can now login here: <a href="{% url 'register' %}">Register here</a>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
templates/app -> register.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Registration Page</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
}
.container {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
margin-top: 10%;
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.form-group {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
label {
display: block;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 5px;
}
input[type="text"],
input[type="email"],
input[type="password"] {
width: 96%;
padding: 8px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
input[type="submit"] {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: #fff;
border: none;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
.error-message {
color: red;
margin-top: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2>Register</h2>
<form action="{% url 'register' %}" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<p class="error-message">{{ message }}</p>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" value="{{request.POST.username}}" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="password-confirm">Confirm Password:</label>
<input type="password" id="password-confirm" name="password-confirm" required>
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Register">
</form><br><br>
You can now login here: <a href="{% url 'login_view' %}">login here</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
templates/app -> cart.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>PythonGeeks Cake Ordering Portal</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f1f1f1;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
h2 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.cart-page {
text-align: center;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.cart-page h3 {
font-size: 18px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.cart-page p {
font-size: 16px;
color: #777;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.cart-items {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
}
.cart-item {
width: 70%;
margin-bottom: 20px;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.cart-item img {
width: 100%;
height: 150px;
object-fit: cover;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.cart-item h3 {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.cart-item p {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 5px;
}
.cart-buttons {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
margin-top: 20px;
}
.green-button {
background-color: #4CAF50;
border: none;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.yellow-button {
background-color: #FFD700;
border: none;
color: black;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.cart-buttons {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.dropdown {
position: relative;
}
.dropdown-button {
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
cursor: pointer;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
transition: background-color 0.3s, color 0.3s;
}
.dropdown-button:hover {
background-color: #e0e0e0;
}
.dropdown-content {
display: none;
position: absolute;
background-color: white;
min-width: 160px;
box-shadow: 0px 8px 16px 0px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
z-index: 1;
}
.dropdown-content a {
color: black;
padding: 12px 16px;
text-decoration: none;
display: block;
}
.dropdown:hover .dropdown-content {
display: block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><a href="{% url 'caking-ordering' %}">Close</a></p>
<center>
<h1>Cart Items</h1>
<p style="color: grey;">You have {{ cart_items | length }} items in Your list</p>
</center>
<div class="cart-items">
{% for cart_item in cart_items %}
<div class="cart-item">
{% if request.user == cart_item.user %}
<h3>{{ cart_item.cake.name }}</h3>
<p>{{ cart_item.cake.description }}</p>
<div class="cart-buttons">
<select class="payment-dropdown">
<option value="">------Select Payment------</option>
<option value="">Online Payment</option>
<option value="">Cash on Delivery</option>
</select>
<a class="yellow-button" href="{% url 'remove_from_cart' pk=cart_item.pk %}">Remove from Cart</a>
</div>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% empty %}
<p>Your cart is empty.</p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</body>
</html>
The above image clearly shows the relevance of the payment method dropdown, like COD or online payment.
Summary
The Online Cake Ordering System is a user-friendly web platform built using Django. It allows customers to browse, customize, and order cakes from a bakery. The system includes features like user registration, login, cake catalogue, search, cart management, and logout. Security measures ensure data protection, and Django models store cake and cart item details in a database for efficient data management.
Overall, the system provides a seamless and secure experience for customers, facilitating the cake-ordering process with ease and convenience.




Very nice nicee
Very nice
good
Ashdhaj