Python Django Online Voting System – Smarter Elections Start Here
Get Job-ready with hands-on learning & real-time projects - Enroll Now!
Online Voting System is a simple app created using Django framework with front end created using Bootstrap 5, HTML, and CSS. Users can register and login to the portal and vote for candidates for different positions. Users can only vote once. Only Admin can add candidates and positions for the elections using the Django inbuilt Admin module.
About Python Django Online Voting System
The purpose of this project is to guide you in building an Online Voting System application using the Django framework.
Prerequisite for Online Voting System Using Python Django
Prior to commencing this project, it is assumed that you possess fundamental knowledge of Python programming language, Django framework, HTML, CSS, and Bootstrap. You should have Python and Django installed on your computer. To install the Django framework, enter the following command in your terminal.
pip install django
Download Python Django Online Voting System Project
Please download the source code of Python Django Online Voting System Project: Python Django Online Voting System Project Code.
Steps to Create Online Voting System Using Python Django
Following are the steps for developing the Python Django Online Voting System Project:
Step 1: Create a new Django project by running the command below in your terminal:
Step 2: Create a new Django app by running the following command in your terminal:
Step 3: Create models for your app: Models are used to define the structure of your database tables. You can create models for your app by defining classes in your models.py file.
Step 4: Create views for your app: Views are used to handle requests and return responses. You can create views for your app by defining functions in your views.py file.
Step 5: Create templates for your app: Templates are used to define the structure of your HTML pages. You can create templates for your app by creating HTML files in your templates directory.
Step 6: Create URLs for your app: URLs are used to map requests to views. You can create URLs for your app by defining URL patterns in your urls.py file.
Step 7: Create forms for your app: Forms are used to handle user input. You can create forms for your app by defining classes in your forms.py file.
Step 8: Add admin module to your project: The admin module is used to manage data in your database tables. You can add the admin module to your project by registering your models with the admin site.
Step 9: Testing the Library Management System:
Step 1: Create a new Django project by running the command below in your terminal:
django-admin startproject project_name
Make sure to replace project_name with the actual name of your project.
Step 2: Create a new Django app by running the following command in your terminal:
python manage.py startapp app_name
Replace app_name with the name of your app.
Step 3: Create models for your app:
Models are used to define the structure of your database tables. You can create models for your app by defining classes in your models.py file.
# Importing the required modules
# The models module is used to create the database tables and the fields
from django.db import models
# The User model is used to create the user table using the default django user model
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# ------------------ Online Voting System - Models ------------------ #
# The Position model is used to create the position table
class Position(models.Model):
# The title field is used to store the position title
title = models.CharField(max_length=200, unique=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.title
# The Candidate model is used to create the candidate table
class Candidate(models.Model):
# The name field is used to store the candidate name
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
# The total_vote field is used to store the total number of votes received by the candidate
total_vote = models.IntegerField(default=0, editable=False)
# The position field is used to store the position of the candidate
position = models.ForeignKey(Position, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# The image field is used to store the image of the candidate
image = models.ImageField(verbose_name="Candidate Pic", upload_to='images/')
def __str__(self):
return "{} - {}".format(self.name, self.position.title)
# The ControlVote model is used to create the control_vote table
class ControlVote(models.Model):
# The user field is used to store the user who has voted
user = models.ForeignKey(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# The position field is used to store the position for which the user has voted
position = models.ForeignKey(Position, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
# The status field is used to store the status of the vote
status = models.BooleanField(default=False)
def __str__(self):
return "{} - {} - {}".format(self.user, self.position, self.status)
In this code, we define three models: Position, Candidate, and ControlVote for our online voting system.
- The Position model is used to create the position table with a title field to store the position title. We also define a __str__ method to return the title of the position.
- The Candidate model creates the candidate table and includes a name field for storing the candidate’s name, a total_vote field (which is set to 0 by default and cannot be edited) for keeping track of the total number of votes received by the candidate, a position field for storing the candidate’s position, and an image field for storing their picture. To provide a string representation of the model, we define a str method that returns the candidate’s name and position title.
- The ControlVote model is used to create the control_vote table. It has a user field to store the user who has voted, a position field to store the position for which the user has voted, and a status field to store the status of the vote (which is set to False by default). We define a __str__ method to return the user, position, and status of the vote.
Step 4: Create views for your app:
Views are used to handle requests and return responses. You can create views for your app by defining functions in your views.py file.
# Importing the required modules
# The render module is used to render the html pages,
# the get_object_or_404 module is used to get the object or return 404 error if the object is not found
from django.shortcuts import render, get_object_or_404,redirect
# The HttpResponseRedirect module is used to redirect to a particular page
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
# The RegistrationForm module is used to create the registration form
from .forms import RegistrationForm
# The messages module is used to display the messages in the html pages
from django.contrib import messages
# The login,logout,authenticate, update_session_auth_hash modules are used to login, logout, authenticate and update the session auth hash
from django.contrib.auth import login,logout,authenticate, update_session_auth_hash
# The PasswordChangeForm module is used to create the change password form
from django.contrib.auth.forms import PasswordChangeForm
# The login_required module is used to restrict the access to the page
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
# The Candidate,ControlVote,Position models are used to create the candidate, control_vote and position tables
from .models import Candidate,ControlVote,Position
# The ChangeForm module is used to create the change password form
from .forms import ChangeForm
# ------------------ Online Voting System - Views ------------------ #
# The homeView function is used to render the home page when the user visits the home page
def homeView(request):
return render(request, "poll/home.html")
# The registrationView function is used to render the registration page when the user visits the registration page
def registrationView(request):
# The if statement is used to check if the request method is POST
if request.method == "POST":
# The form variable is used to store the RegistrationForm
form = RegistrationForm(request.POST)
# The if statement is used to check if the form is valid
if form.is_valid():
# The cd variable is used to store the cleaned data of the form
cd = form.cleaned_data
# The if statement is used to check if the password and confirm password are same
if cd['password'] == cd['confirm_password']:
# The obj variable is used to store the form data
obj = form.save(commit=False)
obj.set_password(obj.password)
obj.save()
# The messages.success function is used to display the success message
messages.success(request, 'You have been registered.')
# The redirect function is used to redirect to the home page
return redirect('home')
else:
# The messages.success function is used to display the error message if the password and confirm password are not same
return render(request, "poll/registration.html", {'form':form,'note':'password must match'})
else:
# The form variable is used to store the RegistrationForm if the request method is not POST
form = RegistrationForm()
# The render function is used to render the registration page
return render(request, "poll/registration.html", {'form':form})
# The loginView function is used to render the login page when the user visits the login page
def loginView(request):
# The if statement is used to check if the request method is POST
if request.method == "POST":
# The usern variable is used to store the username entered by the user
# The passw variable is used to store the password entered by the user
usern = request.POST.get('username')
passw = request.POST.get('password')
# The user variable is used to store the user object if the user is authenticated
user = authenticate(request, username=usern, password=passw)
if user is not None:
# The login function is used to login the user if the user is authenticated
# and the user is redirected to the dashboard page
login(request,user)
return redirect('dashboard')
else:
# The messages.success function is used to display the error message if the user is not authenticated
# and the user is redirected to the login page
messages.success(request, 'Invalid username or password!')
return render(request, "poll/login.html")
else:
# The render function is used to render the login page if the request method is not POST
# and the user is redirected to the login page
return render(request, "poll/login.html")
# The logoutView function is used to logout the user when the user visits the logout page
@login_required
def logoutView(request):
logout(request)
return redirect('home')
# The dashboardView function is used to render the dashboard page when the user visits the dashboard page
@login_required
def dashboardView(request):
return render(request, "poll/dashboard.html")
# The passwordView function is used to render the position page when the user visits the position page
@login_required
def positionView(request):
# The obj variable is used to store the list of positions
obj = Position.objects.all()
# The render function is used to render the position page
# obj is passed to the position page to display the list of positions
return render(request, "poll/position.html", {'obj':obj})
# The candidateView function is used to render the candidate page when the user visits the candidate page
@login_required
def candidateView(request, pos):
# The obj variable is used to store the position object
obj = get_object_or_404(Position, pk = pos)
# if statement is used to check if the request method is POST
if request.method == "POST":
# The temp variable is used to store the ControlVote object
# it is used to check if the user has already voted for the position
temp = ControlVote.objects.get_or_create(user=request.user, position=obj)[0]
# if statement is used to check if the user has already voted for the position
if temp.status == False:
# The temp2 variable is used to store the Candidate object
# The total_vote of the candidate is incremented by 1
# The status of the ControlVote object is changed to True
# The user is redirected to the position page
temp2 = Candidate.objects.get(pk=request.POST.get(obj.title))
temp2.total_vote += 1
temp2.save()
temp.status = True
temp.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect('/position/')
else:
# if the user has already voted for the position then the user is redirected to the position page
# and the error message is displayed
messages.success(request, 'you have already been voted this position.')
return render(request, 'poll/candidate.html', {'obj':obj})
else:
# if the request method is not POST then the render function is used to render the candidate page
return render(request, 'poll/candidate.html', {'obj':obj})
# The resultView function is used to render the result page when the user visits the result page
@login_required
def resultView(request):
# The obj variable is used to store the list of Candidate objects
obj = Candidate.objects.all().order_by('position','-total_vote')
# The render function is used to render the result page
return render(request, "poll/result.html", {'obj':obj})
# The candidateDetailView function is used to render the candidate detail page when the user visits the candidate detail page
@login_required
def candidateDetailView(request, id):
# The obj variable is used to store the Candidate object
obj = get_object_or_404(Candidate, pk=id)
# The render function is used to render the candidate detail page
# obj is passed to the candidate detail page to display the details of the candidate
return render(request, "poll/candidate_detail.html", {'obj':obj})
# The changePasswordView function is used to render the password page when the user visits the password page
@login_required
def changePasswordView(request):
# if statement is used to check if the request method is POST
if request.method == "POST":
# The form variable is used to store the PasswordChangeForm
form = PasswordChangeForm(user=request.user, data=request.POST)
# check if the form is valid
if form.is_valid():
# User is saved and the session is updated
form.save()
update_session_auth_hash(request,form.user)
# The user is redirected to the dashboard page
return redirect('dashboard')
else:
# if the request method is not POST then the render function is used to render the password page
form = PasswordChangeForm(user=request.user)
# The render function is used to render the password page
return render(request, "poll/password.html", {'form':form})
# The editProfileView function is used to render the edit profile page when the user visits the edit profile page
@login_required
def editProfileView(request):
# Check if the request method is POST
if request.method == "POST":
# The form variable is used to store the ChangeForm
form = ChangeForm(request.POST, instance=request.user)
# Check if the form is valid
if form.is_valid():
# The user is saved and the user is redirected to the dashboard page
form.save()
return redirect('dashboard')
else:
# if the request method is not POST then the render function is used to render the edit profile page
form = ChangeForm(instance=request.user)
# The render function is used to render the edit profile page
return render(request, "poll/edit_profile.html", {'form':form})
In this code we have defined several views for our online voting system. These functions are used to render different pages when the user visits the corresponding URL.
The code begins with importing several modules, including render, get_object_or_404, redirect, and others, which are used throughout the code to perform different tasks. The RegistrationForm and ChangeForm classes are also imported from a module named forms.
- The homeView function is defined first, which renders the home page when the user visits it.
- The registrationView function is used to render the registration page and allows users to register for the voting system. If the request method is POST, the function validates the form data and saves the registration information to the database. If the form is not valid, an error message is displayed.
- The loginView function is used to render the login page and allows users to log in to the system. If the user’s credentials are correct, the user is redirected to the dashboard page. Otherwise, an error message is displayed.
- The logoutView function is used to log out the user when the user visits the logout page.
- The dashboardView function is used to render the dashboard page when the user visits it.
- The positionView function is used to render the position page and display the list of positions available in the voting system.
- The candidateView function is used to render the candidate page and display the list of candidates for a particular position. If the request method is POST, the function saves the user’s vote to the database.
- The voteView function is used to render the vote page and allows the user to vote for a particular candidate. If the request method is POST, the function saves the user’s vote to the database.
- The changePasswordView function is used to render the change password page and allows the user to change their password. If the request method is POST, the function validates the form data and saves the new password to the database.
All the views except the homeView, logoutView, and positionView require the user to be logged in to access the page. In case the user is not currently logged in, they will be directed to the login page.The get_object_or_404 function is used in some views to get an object from the database and return a 404 error if the object is not found. The messages module is used to display success and error messages to the user.
Step 5: Create templates for your app:
Templates are used to define the structure of your HTML pages. You can create templates for your app by creating HTML files in your templates directory.
a. Add Bootstrap 5 to your project: Creating and adding bootstrap to the base html file for the django project.
base.html: It is the base template of the web app. It will show the navigation bar on all the pages and will provide the bootstrap library for all the pages.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"
/>
<link
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet"
integrity="sha384-EVSTQN3/azprG1Anm3QDgpJLIm9Nao0Yz1ztcQTwFspd3yD65VohhpuuCOmLASjC"
crossorigin="anonymous"
/>
<script
src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/[email protected]/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"
integrity="sha384-MrcW6ZMFYlzcLA8Nl+NtUVF0sA7MsXsP1UyJoMp4YLEuNSfAP+JcXn/tWtIaxVXM"
crossorigin="anonymous"
></script>
<script
src="https://kit.fontawesome.com/114f8f7e3d.js"
crossorigin="anonymous"
></script>
<title>{% block title %}{% endblock %}</title>
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-primary">
<div class="container-fluid">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="{% url 'home' %}">Online Voting System</a>
<button
class="navbar-toggler"
type="button"
data-bs-toggle="collapse"
data-bs-target="#navbarNavAltMarkup"
aria-controls="navbarNavAltMarkup"
aria-expanded="false"
aria-label="Toggle navigation"
>
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
{% if request.user.is_authenticated %}
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'dashboard' %}">Dashboard</a>
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'editprofile' %}">Edit Profile</a>
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'changepass' %}"
>Change Password</a
>
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'logout' %}">Logout</a>
{% else %}
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'login' %}">Login</a>
<a class="nav-link" href="{% url 'registration' %}">Register</a>
{% endif %}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<div class>{% block content %} {% endblock %}</div>
</body>
</html>
b. login.html: It is the user login page.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Login{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<div class="alert alert-danger d-flex justify-content-center" role="alert">
{{ message }}
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<h5 class="card-title d-flex justify-content-center">User Login</h5>
<form action="." method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_username">Username:</label>
<input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" id="id_username" required><i
class="iconinput fa fa-user"></i>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="id_password">Password:</label>
<input type="password" name="password" class="form-control" id="id_password" required><i
class="iconinput fa fa-keyboard"></i>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary">Login</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
.as-full {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.form-control {
padding-left: 30px;
padding-right: 30px;
}
.iconinput {
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
left: 10px;
top: -31px;
width: 0;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
c. registration.html: It is the user registration page for the web app.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Registration{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% load widget_tweaks %}
<br />
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
{% if note %}
<h3 class="text text-muted">{{note}}</h3>
{% endif %}
<h5 class="card-title">User Registration</h5>
<form action="" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% for field in form %}
<div class="form-group">
{% if field.errors %}
{% for error in field.errors %}
<ul>
<li>{{error}}</li>
</ul>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{{ field.label_tag }}
{% render_field field class="form-control" %}
{% if field.help_text %}
<small class="form-text text-muted">{{field.help_text}}</small>
{% endif %}
</div>
<br>
{% endfor %}
<button type="submit" class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary">Login</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
.as-full {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.form-control {
padding-left: 30px;
padding-right: 30px;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
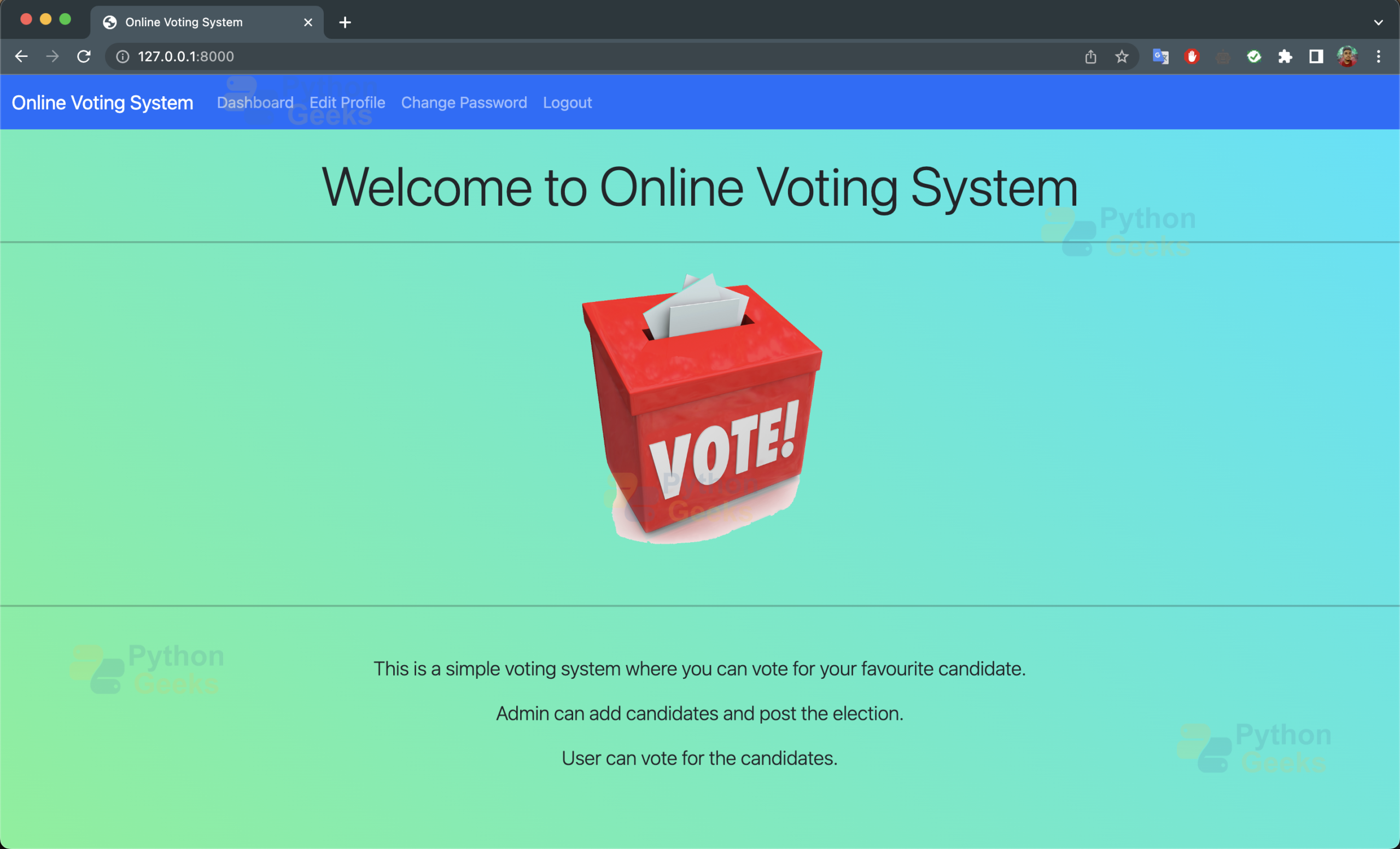
d. home.html: It is the home page when user visits the website.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Online Voting System{%endblock%}
{% block content %}
<br>
<div class="jumbotron">
{% if messages %} {% for message in messages %}
<div class="alert alert-success" role="alert">{{ message }}</div>
{% endfor %} {% endif %}
<h1 class="display-4 d-flex justify-content-center">
Welcome to Online Voting System
</h1>
<hr class="my-4 bg-dark d-flex justify-content-center" style="height: 2px" />
<div class="d-flex justify-content-center">
<img
src="https://www.theheraldtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/kisspng-ballot-box-voting-election-clip-art-voting-box-png-file-5aa1fb83b479c1.8490900715205651237392.png"
alt="Ballot Box"
width="300"
height="300"
/>
</div>
<hr class="my-5 bg-dark d-flex justify-content-center" style="height: 2px" />
<p class="lead d-flex justify-content-center">
This is a simple voting system where you can vote for your favourite
candidate.
</p>
<p class="lead d-flex justify-content-center">
Admin can add candidates and post the election.
</p>
<p class="lead d-flex justify-content-center">
User can vote for the candidates.
</p>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #6ef195, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
e. dashboard.html: This will be the first page of the user after a successful login. It will show the user options to see the positions for voting and results.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Dashboard{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<br>
<h1 class="text-center">Welcome to Online Voting System</h1>
<h2 class="text-center">Hi, {{request.user.get_full_name }}</h2>
<section class="hero-section">
<div class="card-grid">
<a class="card d-flex" href="{% url 'position' %}">
<div class="card__background" style="background-image: url(https://img.freepik.com/free-vector/realistic-vector-icon-ballot-box-made-glass-hand-putting-voting-paper-inside-election-conce_134830-1493.jpg?w=2000)"></div>
<div class="card__content">
<p class="card__category">Vote</p>
<h3 class="card__heading">Click Here To Vote</h3>
</div>
</a>
<a class="card" href="{% url 'result' %}">
<div class="card__background" style="background-image: url(https://media.istockphoto.com/id/1281075008/vector/success.jpg?s=612x612&w=0&k=20&c=79U0bXwmDlMwkBQ_qyzGItiRtItpXIQJsSKc2UlvQkk=)"></div>
<div class="card__content">
<p class="card__category">Result</p>
<h3 class="card__heading">Click Here To See Result</h3>
</div>
</a>
<div>
</section>
<style>
:root{
--background-dark: #2d3548;
--text-light: rgba(231, 231, 231, 0.9);
--text-lighter: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9);
--spacing-s: 8px;
--spacing-m: 16px;
--spacing-l: 24px;
--spacing-xl: 32px;
--spacing-xxl: 64px;
--width-container: 1200px;
}
*{
border: 0;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
html{
height: 100%;
font-family: 'Montserrat', sans-serif;
font-size: 14px;
}
body{
height: 100%;
background: linear-gradient(45deg,#b57bee, #00e3fd);
}
.hero-section{
align-items: flex-start;
display: flex;
min-height: 100%;
justify-content: center;
padding: var(--spacing-xxl) var(--spacing-l);
}
.card-grid{
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(1, 1fr);
grid-column-gap: var(--spacing-l);
grid-row-gap: var(--spacing-l);
max-width: var(--width-container);
width: 50%;
}
@media(min-width: 540px){
.card-grid{
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
}
}
@media(min-width: 960px){
.card-grid{
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
}
}
.card{
list-style: none;
position: relative;
border-radius: var(--spacing-l);
}
.card:before{
content: '';
display: block;
padding-bottom: 150%;
width: 100%;
}
.card__background{
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
border-radius: var(--spacing-l);
bottom: 0;
filter: brightness(0.60) saturate(1.2) contrast(0.85);
left: 0;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
transform-origin: center;
transform: scale(1) translateZ(0);
transition:
filter 200ms linear,
transform 200ms linear;
}
.card:hover .card__background{
transform: scale(1.05) translateZ(0);
}
.card-grid:hover > .card:not(:hover) .card__background{
filter: brightness(0.5) saturate(0) contrast(1.2) blur(20px);
}
.card__content{
left: 0;
padding: var(--spacing-l);
position: absolute;
top: 0;
}
.card__category{
color: var(--text-light);
font-size: 0.9rem;
margin-bottom: var(--spacing-s);
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.card__heading{
color: var(--text-lighter);
font-size: 1.9rem;
text-shadow: 2px 2px 20px rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
line-height: 1.4;
word-spacing: 100vw;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
f. Password.html: This page will be used to update the password of the user
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Change Password{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% load widget_tweaks %}
<br>
<br>
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">Password Change Form</h5>
<form action="." method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{% for field in form %}
<div class="form-group">
{% if field.errors %}
{% for error in field.errors %}
<ul>
<li>{{error}}</li>
</ul>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{{ field.label_tag }}
{% render_field field class="form-control" %}
<br>
{% if field.help_text %}
<small class="form-text text-muted">{{field.help_text}}</small>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% endfor %}
<button type="submit" class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary">Update</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
g. Position.html: This page will show all the Positions available for the elections, to the user.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %} Position {% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<h1 class="card-title d-flex justify-content-center">
Available Position For Vote
</h1>
</div>
<br />
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Position</th>
<th scope="col">Vote</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for candidateID in obj %}
<tr>
<td>{{candidateID.title}}</td>
<td>
<a
href="{% url 'candidate' candidateID.id %}"
class="btn btn-primary btn-sm"
>Vote</a
>
</td>
</tr>
{% empty %}
<p>No Positions Available</p>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
h. edit_profile.html: This page will be used to edit the profile of the user, such as user name, email and profile name.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Update Profile{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% load widget_tweaks %}
<br>
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
{% if note %}
<h3 class="text text-muted">{{note}}</h3>
{% endif %}
<h5 class="card-title d-flex justify-content-center"> Update Profile</h5>
<form action="" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
{% for field in form %}
<div class="form-group">
{% if field.errors %}
{% for error in field.errors %}
<ul>
<li>{{error}}</li>
</ul>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
{{ field.label_tag }}
{% render_field field class="form-control" %}
{% if field.help_text %}
<small class="form-text text-muted">{{field.help_text}}</small>
<br>
{% endif %}
<br>
</div>
{% endfor %}
<button type="submit" class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary">Update</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
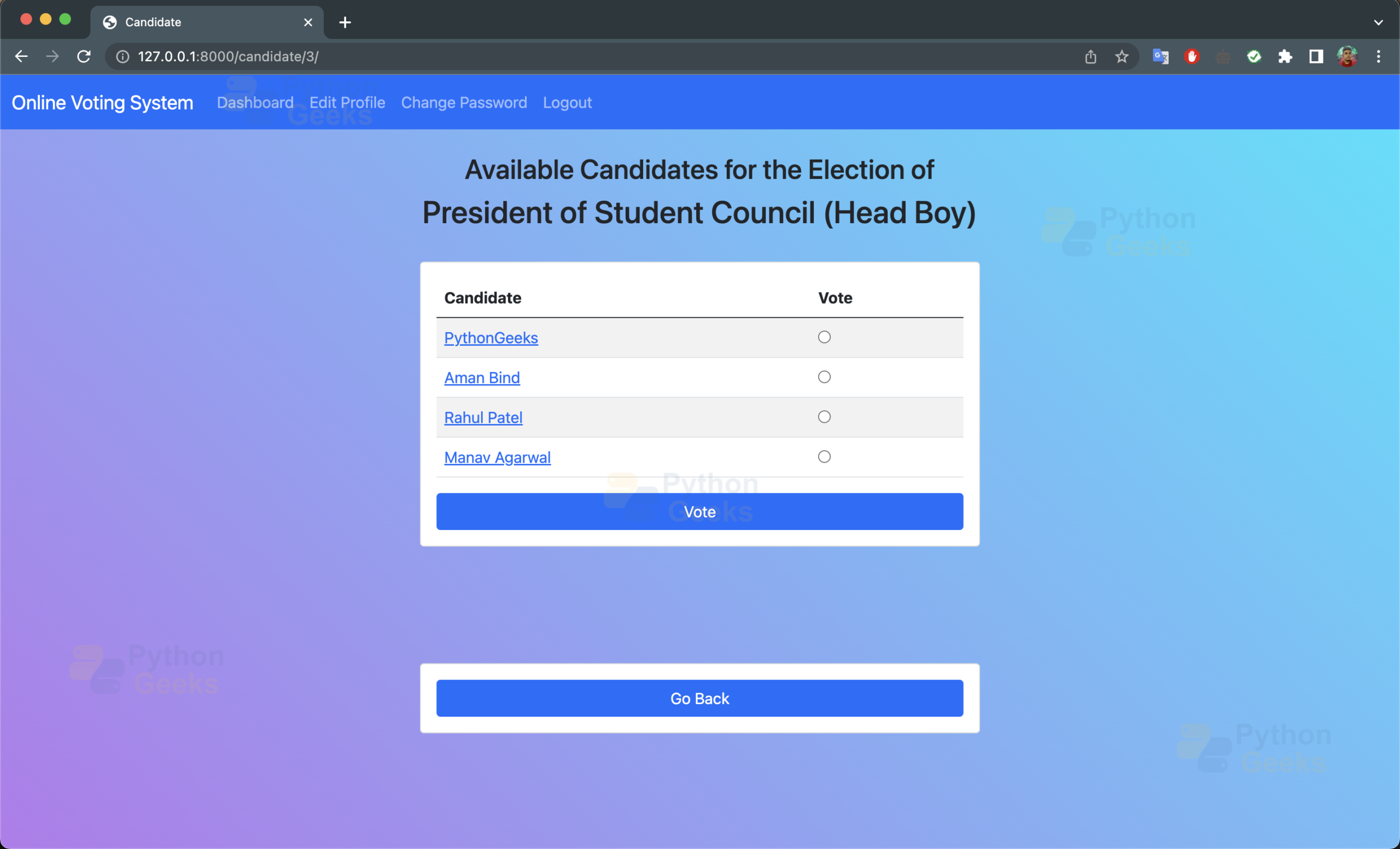
i. candidate.html: This page will show all the candidates competing for the specific position. User can vote using this page.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Candidate{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
{% if messages %}
{% for message in messages %}
<div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert">{{ message }}</div>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<h3 class="card-title d-flex justify-content-center">
Available Candidates for the Election of
</h3>
<h2 class="card-title d-flex justify-content-center">{{ obj.title }}</h2>
</div>
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<form action="" method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Candidate</th>
<th scope="col">Vote</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for candidateID in obj.candidate_set.all %}
<tr>
<td>
<a href="{% url 'detail' candidateID.id %}">{{candidateID.name}}</a>
</td>
<td>
<input
type="radio"
id="id_{{candidateID.id}}"
name="{{candidateID.position}}"
value="{{candidateID.id}}"
class="custom-control-input"
required
/>
</td>
</tr>
{% empty %}
<p>No Candidates Available</p>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
<input
type="submit"
class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary"
value="Vote"
/>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<a href="{% url 'position' %}" class="col-md-12 btn btn-primary">Go Back</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
j. candidate_detail.html: It will show the details about the candidate.
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Candidate Details{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<br>
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-flex d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center" >
<div class="card border-primary mb-3 bg-dark" style="width: 25rem;">
<div class="card-body">
<div class="card border-primary mb-3 bg-light" style="width: 23rem;">
<img src="{{ obj.image.url }}" class="card-img-top" alt="Candidate Image">
<div class="card-body">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<tbody>
<tr>
<td><b>Name</b></td>
<td>{{ obj.name }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><b>Competing For</b></td>
<td>{{ obj.position }}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body{
background: linear-gradient(45deg,#b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
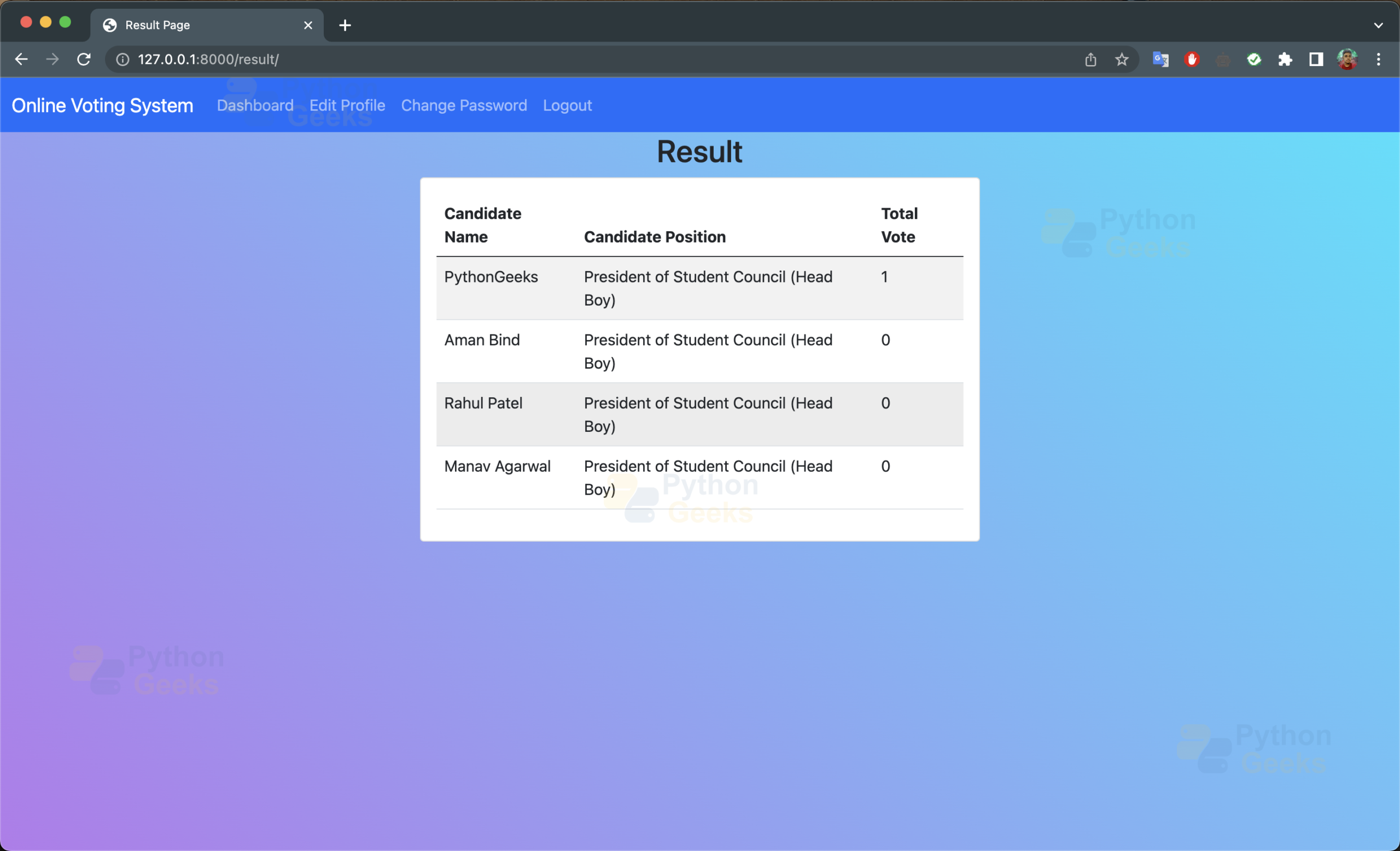
k. result.html: This page will show the results of the elections in real time
{% extends "poll/base.html" %}
{% block title %}Result Page{% endblock %}
{%block content %}
<h2 class="text-center">Result</h2>
<div class="container-fluid as-full">
<div class="row as-full d-flex justify-content-center">
<div class="col-5 align-self-center">
<div class="card">
<div class="card-body">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Candidate Name</th>
<th scope="col">Candidate Position</th>
<th scope="col">Total Vote</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{% for i in obj %}
<tr>
<td>{{ i.name }}</td>
<td>{{ i.position }}</td>
<td>{{ i.total_vote }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<style>
body {
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #b57bee, #00e3fd);
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-attachment: fixed;
background-size: cover;
}
</style>
{% endblock %}
Step 6: Create URLs for your app:
URLs are used to map requests to views. You can create URLs for your app by defining URL patterns in your urls.py file.
# Importing the required modules
# The admin module is used to create the admin site for the application
# using the default django admin site module
from django.contrib import admin
# The path module is used to create the url patterns for the application
# to map the urls to the views
from django.urls import path
# The views module is used to import the views from the views.py file
from poll import views
# The settings module is used to import the settings from the settings.py file
# to get the media, static files and other settings
from django.conf import settings
# The static module is used to import the static files from the settings.py file
from django.conf.urls.static import static
# The urlpatterns list is used to store the url patterns for the application
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls, name='admin'),
path('', views.homeView, name='home'),
path('register/', views.registrationView, name='registration'),
path('login/', views.loginView, name='login'),
path('dashboard/', views.dashboardView, name='dashboard'),
path('logout/', views.logoutView, name='logout'),
path('position/', views.positionView, name='position'),
path('candidate/<int:pos>/', views.candidateView, name='candidate'),
path('candidate/detail/<int:id>/', views.candidateDetailView, name='detail'),
path('result/', views.resultView, name='result'),
path('changepass/', views.changePasswordView, name='changepass'),
path('editprofile/', views.editProfileView, name='editprofile'),
] + static(settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
In this code we have defined the URL patterns for our online voting system. The code starts by importing the required modules including the Django admin module for creating the admin site, the path module for creating URL patterns, the views module for importing views from views.py, the settings module for getting media, static files and other settings, and the static module for importing static files from settings.py.
The urlpatterns list is used to store the URL patterns for the application. Each pattern is defined using the path function which takes a URL pattern string and a view function. The view function is imported from the views.py file
Step 7: Create forms for your app:
Forms are used to handle user input. You can create forms for your app by defining classes in your forms.py file.
# Importing the required modules
# The forms module is used to create the forms for the application
from django import forms
# The User model is used here to create a form for the default django user model
# It is used to create the registration form and the edit profile form
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# The RegistrationForm class is used to create the registration form for the user
class RegistrationForm(forms.ModelForm):
confirm_password = forms.CharField(max_length=100, widget=forms.PasswordInput)
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['username', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'email', 'password']
widgets = {
'password': forms.PasswordInput,
}
# The ChangePasswordForm class is used to create the change password form for the user
class ChangeForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['username', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'email']
In this code, we created two forms, RegistrationForm and ChangeForm, using Django’s forms module.
The RegistrationForm class inherits from forms.ModelForm, which means it is a ModelForm that is automatically generated based on the User model. The form includes fields for username, first_name, last_name, email, and password, along with a field for confirming the password. The password field is given a PasswordInput widget to obscure the input.
The ChangeForm class is also a ModelForm based on the User model, but only includes fields for username, first_name, last_name, and email.
The ChangeForm class is a ModelForm that relies on the User model, but it exclusively consists of fields for username, first_name, last_name, and email. This form is used for changing the user’s profile information, but not their password.
Overall, these forms are used to create a user registration form and a form for changing a user’s information in the online voting system.
Step 8: Add admin module to your project:
The admin module is used to manage data in your database tables. You can add the admin module to your project by registering your models with the admin site.
# Importing the required modules
# The admin module is used to create the admin site for the application
from django.contrib import admin
# The models module is used to import the models from the models.py file
from .models import Candidate, Position
# The admin.site.register() method is used to register the models to the admin site
@admin.register(Position)
# The PositionAdmin class is used to create the admin site for the Position model
class PositionAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = ('title',)
search_fields = ('title',)
@admin.register(Candidate)
# The CandidateAdmin class is used to create the admin site for the Candidate model
class CandidateAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
list_display = ('name','position')
list_filter = ('position',)
search_fields = ('name','position')
readonly_fields = ('total_vote',)
In this code we created the admin site for the Candidate and Position models in our online voting system. It first imports the required modules, including the admin module to create the admin site and the models module to import the Candidate and Position models from the models.py file.
Then, the admin.site.register() method is used to register the models to the admin site. Two admin.ModelAdmin classes are defined to create the admin site for the Candidate and Position models respectively.
- The PositionAdmin class defines the list_display attribute to specify the fields that will be displayed on the list view of the Position model in the admin site. It also defines the search_fields attribute to specify the fields that can be searched in the Position model.
- The CandidateAdmin class defines the list_display, list_filter, and search_fields attributes to specify the fields that will be displayed on the list view of the Candidate model in the admin site, the fields that can be filtered, and the fields that can be searched. It also defines the readonly_fields attribute to specify the fields that can only be read but not edited in the Candidate model.
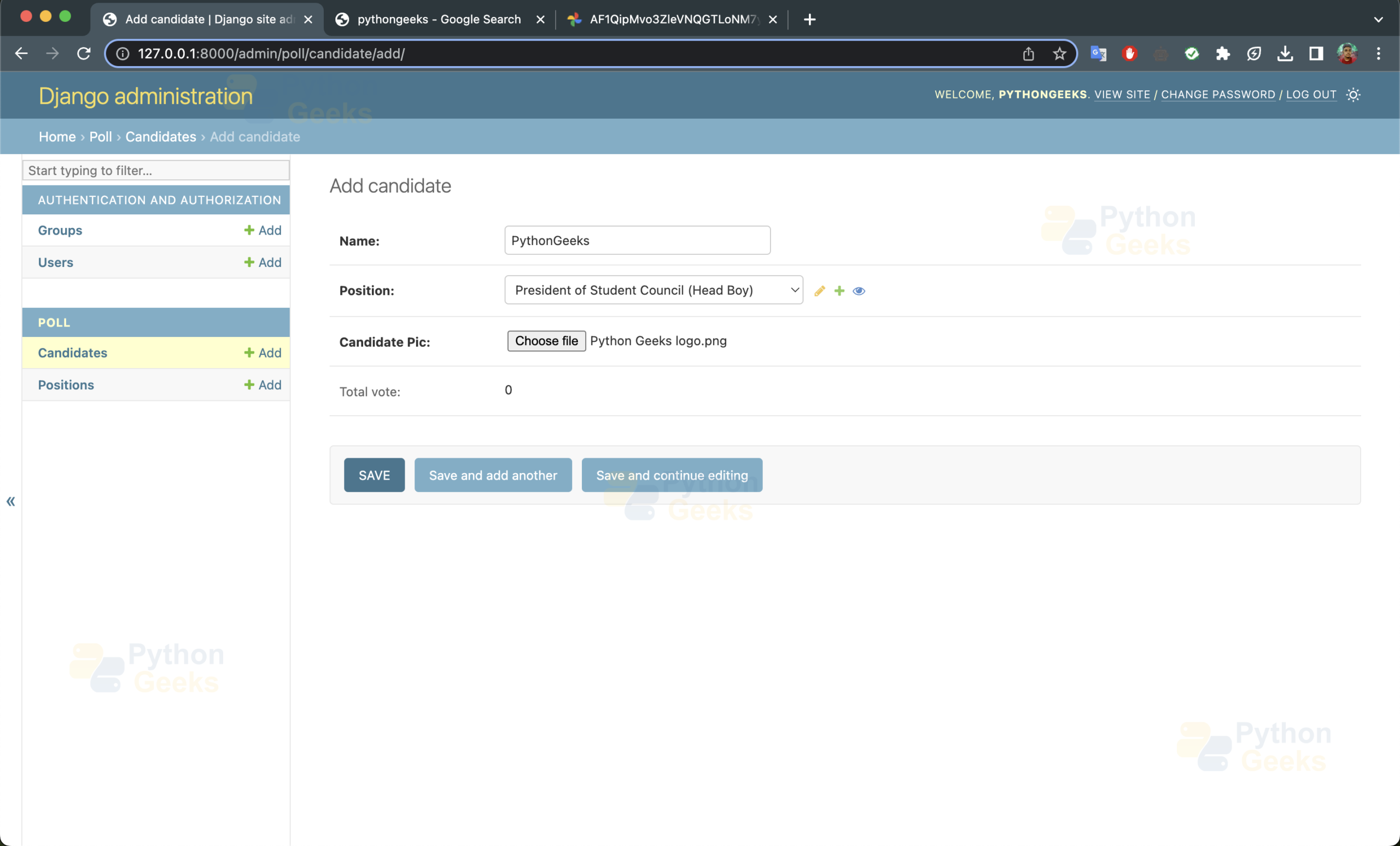
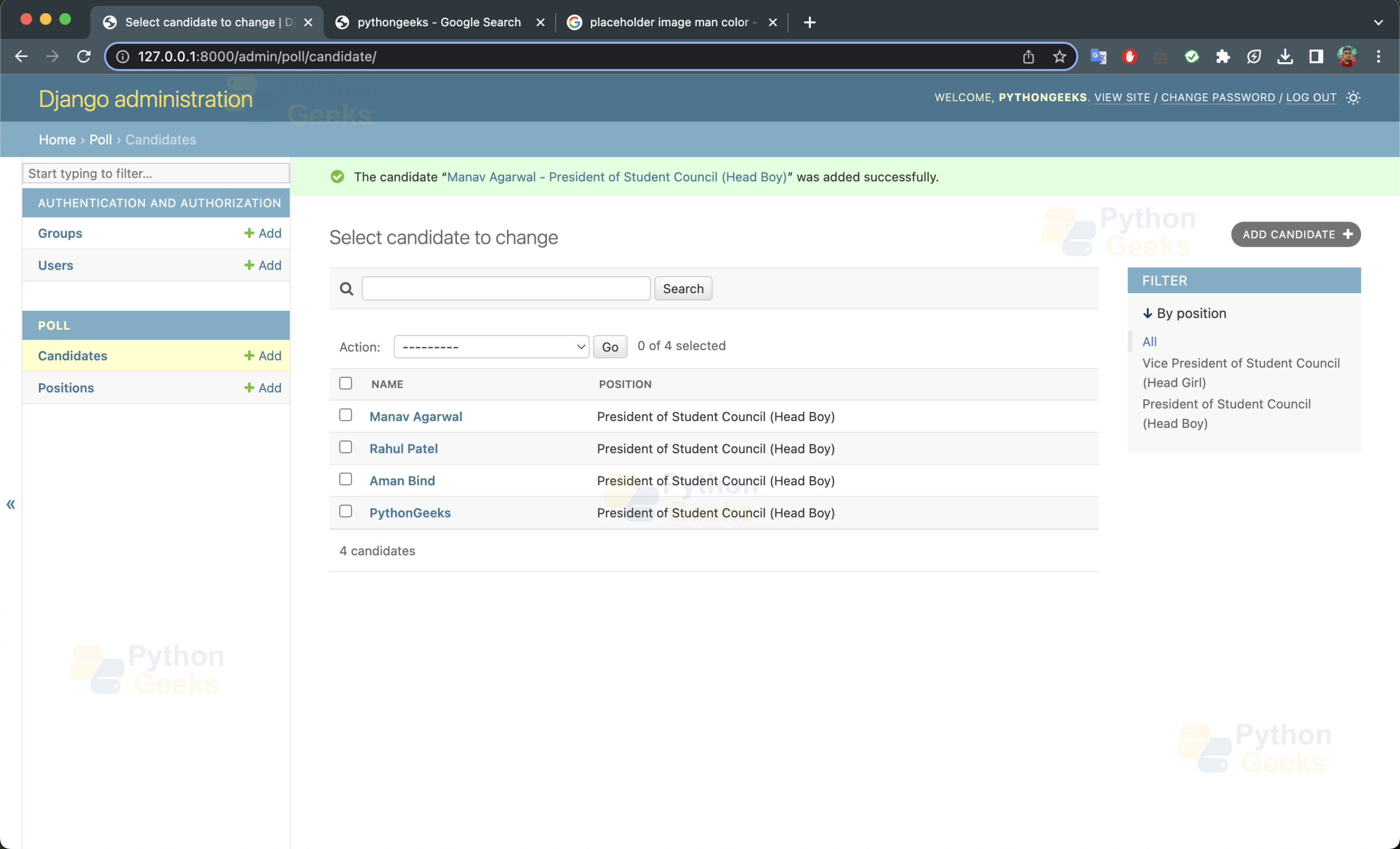
Now the Admin will be able to add candidates and positions for the election using the admin module.
Step 9: Testing the Library Management System:
Navigate to your project directory using the terminal. Next, use the following commands to migrate your app:
python manage.py makemigrations python manage.py migrate
Finally, to run your Django app, use the command:
python manage.py runserver
Python Django Online Voting System Output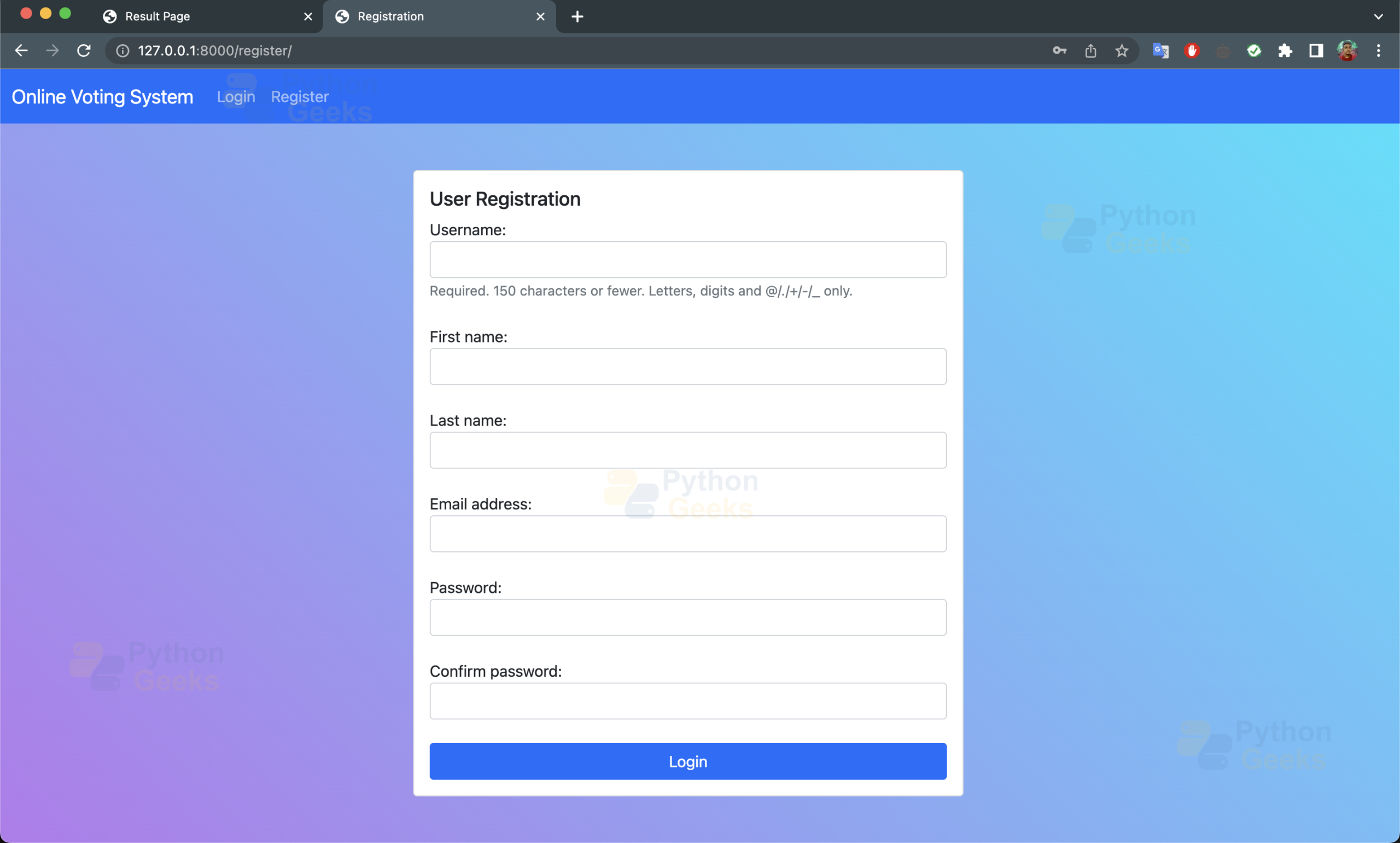
Summary:
Yippee! We have created a fully working Python Django Online Voting System using Django Framework, HTML, CSS, JS and bootstrap. You can now register and login to the portal and vote for candidates for different positions. However, this is not the end! You can add more features according to your needs.

directeries of command to be executed in termial not mentioned.
Goof
Very good but you get the video is better
its helpfull
NICE PLEASE UNDRESTAND IN SAMPAL LAGGEUSE
NICE BUT WRONG
simple but wrong
what is admin login username and password???