Python Pandas – An Introduction
Master Programming with Our Comprehensive Courses Enroll Now!
What is Pandas?
Pandas is an open-supply library for Python that helps you to work with and examine facts. It offers you rapid, simple data systems and equipment for reading records. Because it can handle based facts in a number of distinct ways and quickly, Pandas is used in lots of fields, together with information technology, finance, economics, and studies.
Pandas Origin:
Our buddy Wes McKinney made Pandas in 2008 when he was operating at AQR Capital Management. McKinney made Pandas to assist him in dealing with the issues he was having with managing monetary information properly. His goal is to make a sturdy and adaptable tool that might make it easier to deal with statistics and exchange it in distinct ways. Because of this, Pandas have become a massive deal inside the Python network, changing the way records are processed and analyzed in a huge manner.
Since it was first launched, Pandas has turned out to be a popular device that record specialists and statistics enthusiasts can’t do without. Pandas is an essential part of the Python statistics ecosystem because it has a whole lot of useful features and a network of active members that hold it developing.
Getting Started
How to install:
This is the first detail you need to do before you begin the usage of Pandas. Using pip, Python’s package deal manager makes the system smooth. Type the following into your terminal or command spark off:
pip install pandas
With this command, you may get the trendy version of Pandas and all of its dependencies and set up them. You can start the use of Pandas in your Python environment as quickly as the installation is carried out.
Importing Pandas:
As soon as Pandas is set up, it desires to be added for your Python script or Jupyter pocket ebook. The ‘import’ announcement is used for this. Add the subsequent line for your Python script or the primary cell of your Jupyter Notebook:
import pandas as pd
This line of code imports Pandas and offers it the alias “pd,” it truly is how the Pandas community usually does matters. You now have the gear you need to apply Pandas’ features to observe and trade information.
Remember to test for errors messages in some unspecified time in the future of the installation way to make sure Pandas changed into installed efficiently earlier than strolling your script or pocket book.
You are certainly equipped to apply Pandas’ whole energy to your facts evaluation and manipulation obligations!
Data Structures for Pandas
The most vital thing about Pandas is that it has precise facts systems. These frameworks are made to address and manage information easily, supplying a base for beginner Python customers to without problems have a look at records.
Key Structures
DataFrame: DataFrame is a shape of statistics, this ‘2-dimensions like’ selector looks working either like a spreadsheet or a SQL table. It is a set of tables only. Imagine a webpage like this! It consists of columns and rows, every column can be a presentation of the single type of entertaining information. It is like a bewildering, yet, only prolific source of information suitable for performing intense details in the real world.
Series: The courtyard offers a wide range of classes, which are described as the Series and the common feature of this Series is having the cup with one variable, like the column in a DataFrame. It could help to maintain any sort of file and would be preinstalled with a separate index that tracks it. Series are constructed to capture specific and meaningful arguments in the DataFrame.
A panel: A former aspect observer, Pandas used to rely on the Panels feature frame adopting three-dimensional records, however these days DataFrames and Series are able to handle nearly all of these tasks.
Certainly! Let’s delve into Pandas Series with a concise yet comprehensive explanation along with an example: Let’s delve into Pandas Series with a concise yet comprehensive explanation along with an example.`
Pandas Series
Series object is the most common among data structures in Pandas – it means a one-dimensional array with label objects. A Series in a sense is not similar to a simple NumPy array because here each index or a label is linked to an element by itself. Consequently, the Series is an essential and extremely convenient infrastructure in Python which is primarily used to work with data in Python.
Values: The column values are what represent the data. These are the flexible data type containers and can store any type of data with different types like integer, float, string and those can be objects and so on. It is a tool to accomplish this by means of mixed data type handling and to provide a selected data type that will be confined within a single container.
Various Operations on Pandas
Pandas Series supports various operations that can simplify data manipulation tasks: Pandas Series supports various operations that can simplify data manipulation tasks:
1. Indexing:
Indexing is used for Looking up values by their label (index) or position in a Series.
For Example:
import pandas as pd data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] my_series = pd.Series(data, index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']) print(my_series['b'])
Output :
20
2. Slicing:
Slicing is used for Selecting a subset of elements based on their position in the Series.
For Example:
import pandas as pd
data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
my_series = pd.Series(data, index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
print(my_series[1:4])
Output:
3. Arithmetic Operations:
One can Apply arithmetic operations to Series, by broadcasting the operation to each element.
import pandas as pd series_1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3]) series_2 = pd.Series([10, 20, 30]) result = series_1 + series_2 print(result)
Output:
The Pandas Series provides enriched and labeled structures for handling one-dimensional data, with a vast set of operations for effective data manipulation and handling.
Pandas DataFrame
Pandas DataFrame is one of the most basic data formats. It is also presented in a simple table where all the values are stored in a 2-dimensional structure. Data formats can be referred to as Excel or SQL. It serves as an easy-to-use and versatile tool where data from Python can be easily adapted to satisfy the analysts’ needs in the shortest time possible.
Rows and Columns: We have a Dataframe which is similar to a chessboard, its rows and columns being arranged in a regular manner. Every column of a Data Frame possesses the even number of elements that are in other words – Pandas Series. This is the area where one defines the parameters or rules used to evaluate the videos or notes. These columns represent the fields, vertical ones of the table are known as records.
Collection of Series: DataFrame is a collection of Pandas Series by column (Series being each column correspondingly). We can input different types of data like blood type, gender, marital status, etc. in each column of this plan and create a plenty of datasets.
Pandas DataFrame supports many functions, giving users the power to do a wide range of data manipulation tasks:To learn that, Pandas DataFrame supports many functions doing all types of the data manipulation tasks as well, is really interesting.
1. Selection:
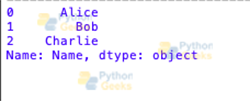
The Selection tool can be used for accessing specific columns or rows within the DataFrame.
For Example:
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df['Name'])
Output :
2. Filtering :
Filtering can be used for Selecting rows based on specific or target oriented conditions.
For Example:
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
filtered_df = df[df['Age'] > 30]
print(filtered_df)
Output :
3. Aggregation:
The Aggregation can be used for Performing operations on the entire DataFrame or specific columns.
For Example:
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
average_age = df['Age'].mean()
print(average_age)
Output :
30.0
The Pandas DataFrame stands as a powerful and efficient tool for handling structured data, by providing a comprehensive set of operations to manipulate and work on with table structured datasets.
How to Run a Pandas Program in Python?
It is very easy to execute a Panda program in Python. Following, “pip install pandas”, and establish Pandas, either create (.py) a Python script or use a Jupyter notebook. The following line executes Pandas into your script: “import pandas as pd”. Then you will be able to write your code in the mode of Data Frames, data Series, for presentation of results. Make sure that Your script is saved. To run the script, type “python your_script.py” in a command line or run the cells in a “Jupyter notebook”.
Pandas’ code is user-friendly, so you can easily adjust data no matter if you are running scripting or Jupyter. This guide shows you how to take advantage of the Pandas features that can help you to analyze data in Python fast.
Summary
Lastly, Pandas, being an efficient and user-friendly Python data manipulation and analysis toolkit, is very flexible. Pandas simplifies complicated data manipulations with several data structures such as Series and DataFrames. This is what makes it necessary for both beginners and experienced data scientists.
Whether you’re dealing with the intricacies of uncovering insights from datasets, cleaning, and transforming data, or working at the more significant end of the spectrum of data analysis, the Pandas framework provides an efficient and effective assembly line for roaming through the universe of data available with Python.
When you embark on your learning journey with Pandas, the amalgamation of simplicity and vastness in the capabilities of this tool will provide you with a good platform to advance in your data research and analysis. Happy coding!